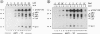Abstract
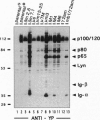
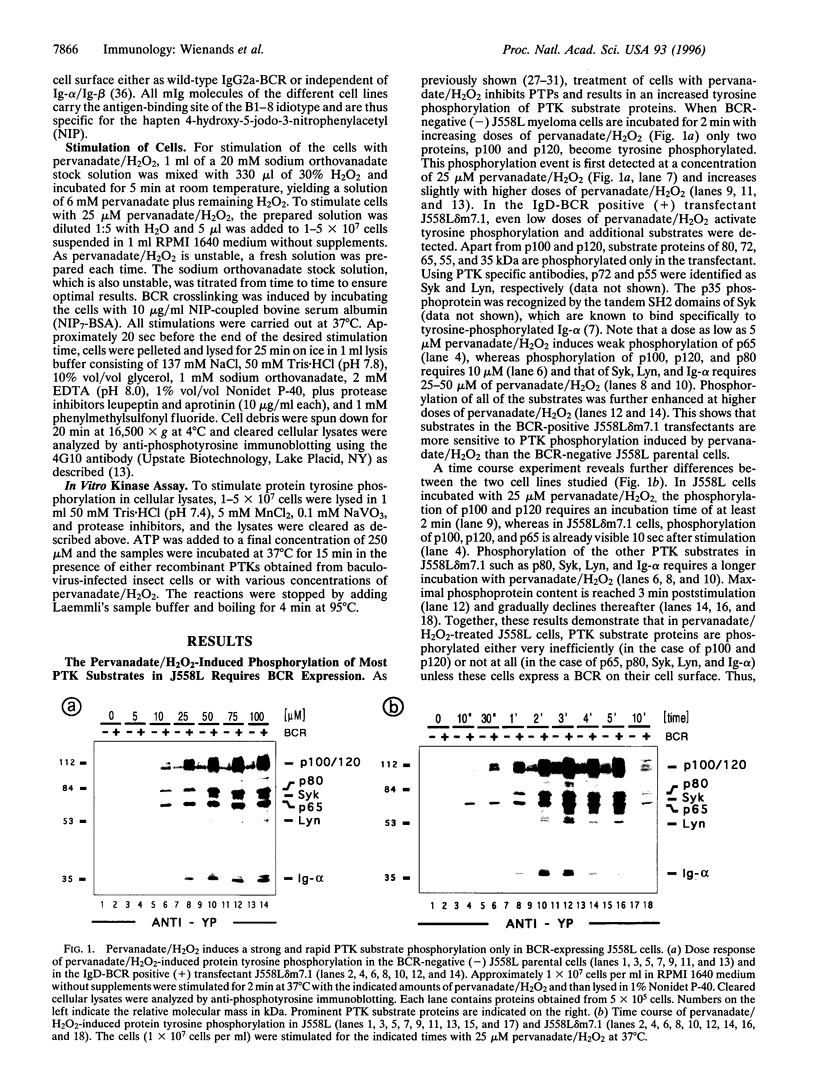
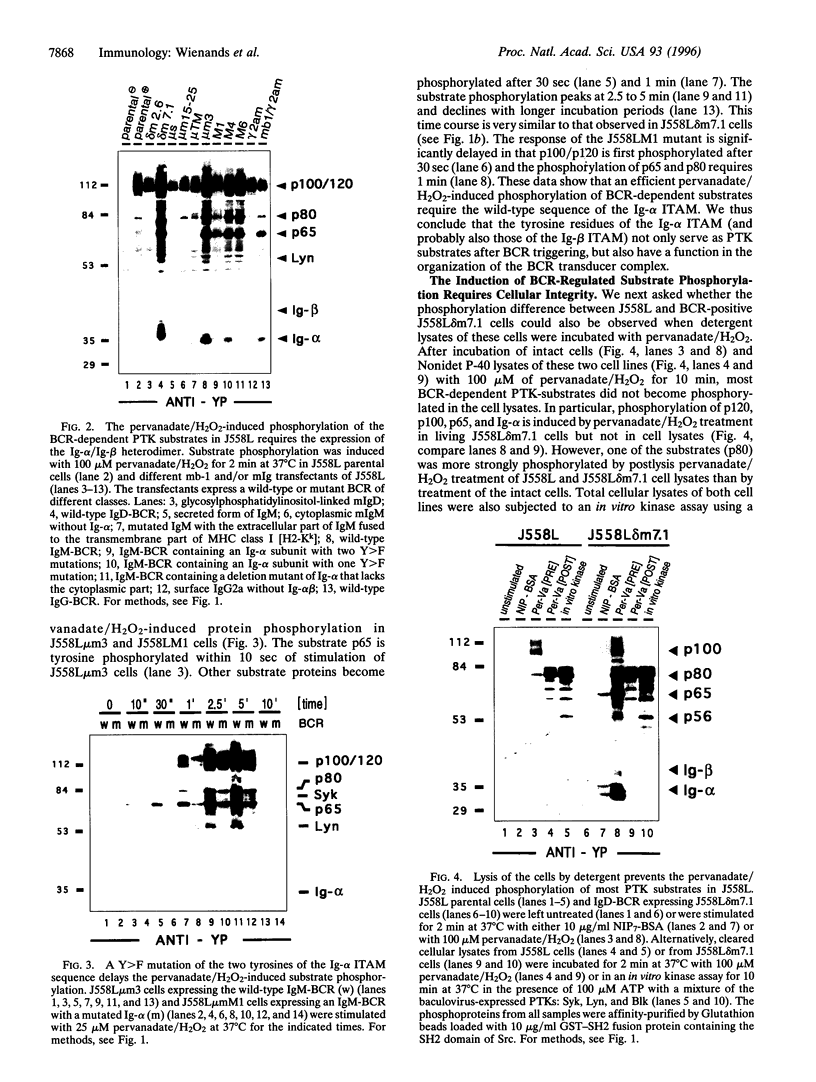
The B cell antigen receptor (BCR) consists of the membrane-bound immunoglobulin (mIg) molecule and the Ig-alpha/Ig-beta heterodimer, which functions as signaling subunit of the receptor. Stimulation of the BCR activates protein tyrosine kinases (PTKs) that phosphorylate a number of substrate proteins, including the Ig-alpha/Ig-beta heterodimer of the BCR itself. How the PTKs become activated after BCR engagement is not known at present. Here, we show that BCR-negative J558L cells treated with the protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor pervanadate/H2O2 display only a weak substrate phosphorylation. However, in BCR-positive transfectants of J558L, treatment with pervanadate/H2O2 induces a strong phosphorylation of several substrate proteins. Treatment with pervanadate/H2O2 does not result in receptor crosslinking, yet the pattern of protein phosphorylation is similar to that observed after BCR stimulation by antigen. The response requires cellular integrity because tyrosine phosphorylation of most substrates is not visible in cell lysates. Cells that express a BCR containing an Ig-alpha subunit with a mutated immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif display a delayed response. The data suggest that, once expressed on the surface, the BCR organizes protein tyrosine phosphatases, PTKs, and their substrates into a transducer complex that can be activated by pervanadate/H202 in the absence of BCR crosslinking. Assembly of this preformed complex seems to be a prerequisite for BCR-mediated signal transduction.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashwell J. D., Klusner R. D. Genetic and mutational analysis of the T-cell antigen receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:139–167. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.001035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann G., Maier D., Freuler F., Tschopp C., Baudisch K., Wienands J. In vitro characterization of major ligands for Src homology 2 domains derived from protein tyrosine kinases, from the adaptor protein SHC and from GTPase-activating protein in Ramos B cells. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Aug;24(8):1799–1807. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhardt A. L., Brunswick M., Bolen J. B., Mond J. J. Anti-immunoglobulin stimulation of B lymphocytes activates src-related protein-tyrosine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7410–7414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambier J. C., Pleiman C. M., Clark M. R. Signal transduction by the B cell antigen receptor and its coreceptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:457–486. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.002325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell K. S., Bedzyk W. D., Cambier J. C. Manipulation of B cell antigen receptor tyrosine phosphorylation using aluminum fluoride and sodium orthovanadate. Mol Immunol. 1995 Nov;32(16):1283–1294. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(95)00088-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. A., Sefton B. M. Association between B-lymphocyte membrane immunoglobulin and multiple members of the Src family of protein tyrosine kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2315–2321. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng A. M., Rowley B., Pao W., Hayday A., Bolen J. B., Pawson T. Syk tyrosine kinase required for mouse viability and B-cell development. Nature. 1995 Nov 16;378(6554):303–306. doi: 10.1038/378303a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. R., Campbell K. S., Kazlauskas A., Johnson S. A., Hertz M., Potter T. A., Pleiman C., Cambier J. C. The B cell antigen receptor complex: association of Ig-alpha and Ig-beta with distinct cytoplasmic effectors. Science. 1992 Oct 2;258(5079):123–126. doi: 10.1126/science.1439759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ambrosio D., Hippen K. L., Minskoff S. A., Mellman I., Pani G., Siminovitch K. A., Cambier J. C. Recruitment and activation of PTP1C in negative regulation of antigen receptor signaling by Fc gamma RIIB1. Science. 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):293–297. doi: 10.1126/science.7716523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaswinkel H., Reth M. Dual role of the tyrosine activation motif of the Ig-alpha protein during signal transduction via the B cell antigen receptor. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 1;13(1):83–89. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06237.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht D., Zick Y. Selective inhibition of protein tyrosine phosphatase activities by H2O2 and vanadate in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Oct 30;188(2):773–779. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91123-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs M. L., Tarlinton D. M., Armes J., Grail D., Hodgson G., Maglitto R., Stacker S. A., Dunn A. R. Multiple defects in the immune system of Lyn-deficient mice, culminating in autoimmune disease. Cell. 1995 Oct 20;83(2):301–311. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90171-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hombach J., Leclercq L., Radbruch A., Rajewsky K., Reth M. A novel 34-kd protein co-isolated with the IgM molecule in surface IgM-expressing cells. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3451–3456. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03219.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hombach J., Tsubata T., Leclercq L., Stappert H., Reth M. Molecular components of the B-cell antigen receptor complex of the IgM class. Nature. 1990 Feb 22;343(6260):760–762. doi: 10.1038/343760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbert V., Peyron J. F., Farahi Far D., Mari B., Auberger P., Rossi B. Induction of tyrosine phosphorylation and T-cell activation by vanadate peroxide, an inhibitor of protein tyrosine phosphatases. Biochem J. 1994 Jan 1;297(Pt 1):163–173. doi: 10.1042/bj2970163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Justement L. B., Campbell K. S., Chien N. C., Cambier J. C. Regulation of B cell antigen receptor signal transduction and phosphorylation by CD45. Science. 1991 Jun 28;252(5014):1839–1842. doi: 10.1126/science.1648262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. M., Alber G., Weiser P., Reth M. Signalling function of the B-cell antigen receptors. Immunol Rev. 1993 Apr;132:125–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1993.tb00840.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. M., Reth M. The B cell antigen receptor of class IgD induces a stronger and more prolonged protein tyrosine phosphorylation than that of class IgM. J Exp Med. 1995 Mar 1;181(3):1005–1014. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.3.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosaki T., Johnson S. A., Pao L., Sada K., Yamamura H., Cambier J. C. Role of the Syk autophosphorylation site and SH2 domains in B cell antigen receptor signaling. J Exp Med. 1995 Dec 1;182(6):1815–1823. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.6.1815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lankester A. C., van Schijndel G. M., Rood P. M., Verhoeven A. J., van Lier R. A. B cell antigen receptor cross-linking induces tyrosine phosphorylation and membrane translocation of a multimeric Shc complex that is augmented by CD19 co-ligation. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Nov;24(11):2818–2825. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830241136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law D. A., Chan V. W., Datta S. K., DeFranco A. L. B-cell antigen receptor motifs have redundant signalling capabilities and bind the tyrosine kinases PTK72, Lyn and Fyn. Curr Biol. 1993 Oct 1;3(10):645–657. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90062-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J., Justement L. B. The MB-1/B29 heterodimer couples the B cell antigen receptor to multiple src family protein tyrosine kinases. J Immunol. 1992 Sep 1;149(5):1548–1555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea J. J., McVicar D. W., Bailey T. L., Burns C., Smyth M. J. Activation of human peripheral blood T lymphocytes by pharmacological induction of protein-tyrosine phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10306–10310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pani G., Kozlowski M., Cambier J. C., Mills G. B., Siminovitch K. A. Identification of the tyrosine phosphatase PTP1C as a B cell antigen receptor-associated protein involved in the regulation of B cell signaling. J Exp Med. 1995 Jun 1;181(6):2077–2084. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.6.2077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reth M. Antigen receptor tail clue. Nature. 1989 Mar 30;338(6214):383–384. doi: 10.1038/338383b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reth M. Antigen receptors on B lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:97–121. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.000525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reth M., Wienands J., Tsubata T., Hombach J. Identification of components of the B cell antigen receptor complex. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1991;292:207–214. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5943-2_23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley R. B., Burkhardt A. L., Chao H. G., Matsueda G. R., Bolen J. B. Syk protein-tyrosine kinase is regulated by tyrosine-phosphorylated Ig alpha/Ig beta immunoreceptor tyrosine activation motif binding and autophosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 12;270(19):11590–11594. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.19.11590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Secrist J. P., Burns L. A., Karnitz L., Koretzky G. A., Abraham R. T. Stimulatory effects of the protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor, pervanadate, on T-cell activation events. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5886–5893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvennoinen O., Nishigaki H., Kitanaka A., Kumagai M., Ito C., Malavasi F., Lin Q., Conley M. E., Campana D. CD38 signal transduction in human B cell precursors. Rapid induction of tyrosine phosphorylation, activation of syk tyrosine kinase, and phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Immunol. 1996 Jan 1;156(1):100–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takata M., Sabe H., Hata A., Inazu T., Homma Y., Nukada T., Yamamura H., Kurosaki T. Tyrosine kinases Lyn and Syk regulate B cell receptor-coupled Ca2+ mobilization through distinct pathways. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 15;13(6):1341–1349. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06387.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniuchi I., Kitamura D., Maekawa Y., Fukuda T., Kishi H., Watanabe T. Antigen-receptor induced clonal expansion and deletion of lymphocytes are impaired in mice lacking HS1 protein, a substrate of the antigen-receptor-coupled tyrosine kinases. EMBO J. 1995 Aug 1;14(15):3664–3678. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00036.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. L. Of ITAMs and ITIMs: turning on and off the B cell antigen receptor. J Exp Med. 1995 Jun 1;181(6):1953–1956. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.6.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner M., Mee P. J., Costello P. S., Williams O., Price A. A., Duddy L. P., Furlong M. T., Geahlen R. L., Tybulewicz V. L. Perinatal lethality and blocked B-cell development in mice lacking the tyrosine kinase Syk. Nature. 1995 Nov 16;378(6554):298–302. doi: 10.1038/378298a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkitaraman A. R., Williams G. T., Dariavach P., Neuberger M. S. The B-cell antigen receptor of the five immunoglobulin classes. Nature. 1991 Aug 29;352(6338):777–781. doi: 10.1038/352777a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser P., Riesterer C., Reth M. The internalization of the IgG2a antigen receptor does not require the association with Ig-alpha and Ig-beta but the activation of protein tyrosine kinases does. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Mar;24(3):665–671. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wienands J., Freuler F., Baumann G. Tyrosine-phosphorylated forms of Ig beta, CD22, TCR zeta and HOSS are major ligands for tandem SH2 domains of Syk. Int Immunol. 1995 Nov;7(11):1701–1708. doi: 10.1093/intimm/7.11.1701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wienands J., Hombach J., Radbruch A., Riesterer C., Reth M. Molecular components of the B cell antigen receptor complex of class IgD differ partly from those of IgM. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):449–455. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08130.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wienands J., Reth M. Glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol linkage as a mechanism for cell-surface expression of immunoglobulin D. Nature. 1992 Mar 19;356(6366):246–248. doi: 10.1038/356246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanashi Y., Kakiuchi T., Mizuguchi J., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. Association of B cell antigen receptor with protein tyrosine kinase Lyn. Science. 1991 Jan 11;251(4990):192–194. doi: 10.1126/science.1702903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanashi Y., Okada M., Semba T., Yamori T., Umemori H., Tsunasawa S., Toyoshima K., Kitamura D., Watanabe T., Yamamoto T. Identification of HS1 protein as a major substrate of protein-tyrosine kinase(s) upon B-cell antigen receptor-mediated signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3631–3635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]