Abstract
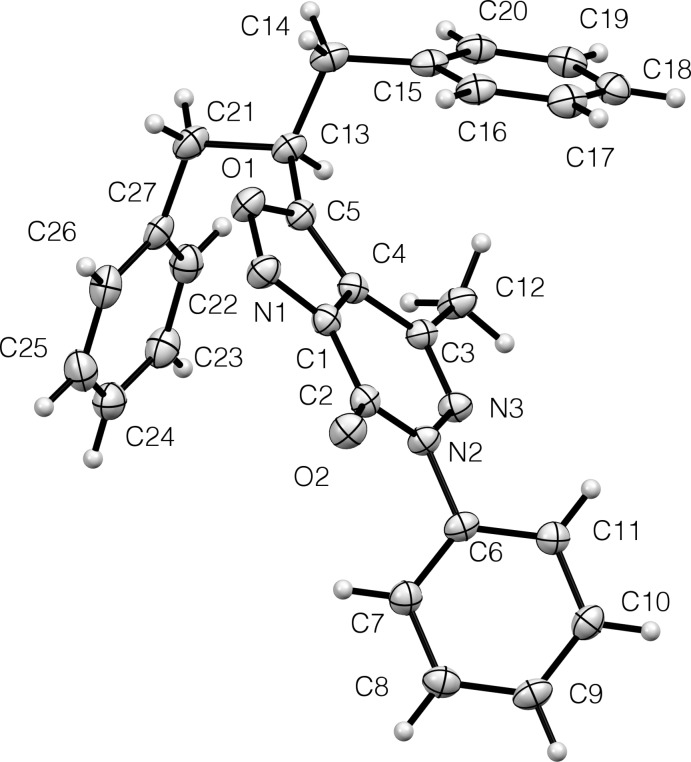
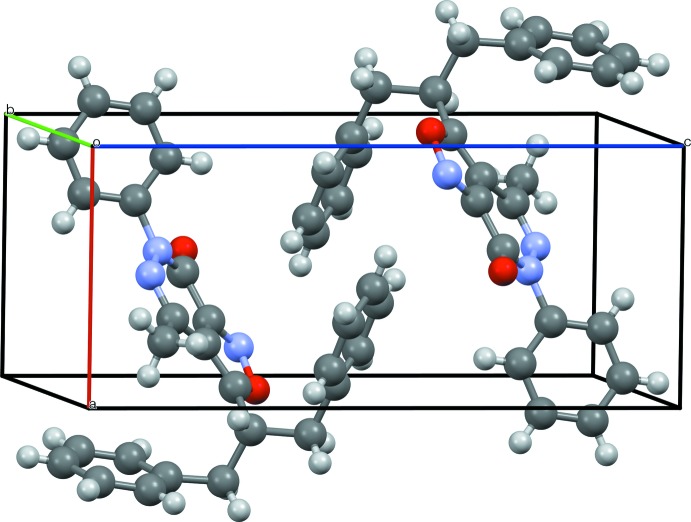
In the title compound, C27H23N3O2, the geminal benzyl groups branching out from the methine adjacent to the isoxazole group are both syn-oriented to the methyl group of the pyridazinone moiety, as reflected by C—C distances of 3.812 (2) and 4.369 (2) Å between the methyl carbon and the nearest ring carbon of each benzyl group. This kind of conformation is retained in CDCl3 solution, as evidenced by distinct phenyl-shielding effects on the 1H NMR signals of the methyl H atoms. The isoxazolo[3,4-d]pyridazin ring system is virtually planar (r.m.s. deviation from planarity = 0.031 Å), but the N-bonded phenyl group is inclined to the former by an ring–ring angle of 55.05 (3)°. In the crystal, the T-shaped molecules are arranged in an interlocked fashion, forming rod-like assemblies along [10-1]. The molecules are held together by unremarkable weak C—H⋯N, C—H⋯O and C—H⋯π interactions (C—O,N,C > 3.4 A), while significant π–π-stacking interactions are absent.
Related literature
For chemistry of isoxazolo[3,4-d]pyridazinone preparation, see: Renzi & Dal Piaz (1965 ▶). For deprotonation with sodium alkoxides, see: Dal Piaz et al. (1975 ▶); Chimichi et al. (1986 ▶). For the rearrangement of the isoxazolo[3,4-d]pyridazinone ring system to pyrazole, see: Dal Piaz et al. (1985 ▶). For isoxazole lateral metalation, see: Natale & Niou (1984 ▶); Natale et al. (1985 ▶); Niou & Natale (1986 ▶); Schlicksupp & Natale (1987 ▶). For recent applications of lateral metalation and electrophilic quenching of isoxazoles to targets of biological interest, see: Nakamura et al. (2010 ▶); Hulubei et al. (2012 ▶). For a review of the lateral metalation and electrophilic quenching of isoxazoles, see: Natale & Mirzaei (1993 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C27H23N3O2
M r = 421.48
Triclinic,
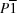
a = 7.5163 (4) Å
b = 9.6774 (5) Å
c = 15.9053 (8) Å
α = 86.798 (1)°
β = 83.512 (1)°
γ = 69.385 (1)°
V = 1075.75 (10) Å3
Z = 2
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 0.66 mm−1
T = 100 K
0.40 × 0.22 × 0.19 mm
Data collection
Bruker D8 Venture PHOTON 100 CMOS diffractometer
Absorption correction: numerical (SADABS; Bruker, 2012 ▶) T min = 0.80, T max = 0.89
12012 measured reflections
3714 independent reflections
3597 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.017
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.032
wR(F 2) = 0.078
S = 1.03
3714 reflections
313 parameters
86 restraints
Only H-atom displacement parameters refined
Δρmax = 0.22 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.14 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2012 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2012 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: Mercury (Macrae et al., 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681302802X/qk2060sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681302802X/qk2060Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681302802X/qk2060Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C26—H26⋯O1i | 0.95 | 2.61 | 3.4159 (13) | 143 |
| C24—H24⋯N1ii | 0.95 | 2.73 | 3.5407 (15) | 143 |
| C11—H11⋯C18iii | 0.95 | 2.78 | 3.6182 (15) | 148 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 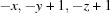 ; (ii)
; (ii) 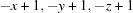 ; (iii)
; (iii) 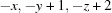 .
.
Acknowledgments
NRN, JM, CG and CK thank the National Institutes of Health for grants NINDS P20RR015583 Center for Structural and Functional Neuroscience (CSFN) and P20 RR017670 Center for Environmental Health Sciences (CEHS), We also thank NINDS P30 (NN and JM), and the University of Montana Grant Program (NN).
supplementary crystallographic information
1. Comment
The title compound (Fig. 1) was prepared by lateral metalation with lithium hexamethyldisilazide and electrophilic quenching with benzyl bromide (Natale & Mirzaei, 1993), under thermodynamic conditions (Niou & Natale, 1986; Schlicksupp & Natale, 1987), during which a facile second deprotonation and quenching leads to double incorporation (Natale et al., 1985, Natale & Niou, 1984). Mono-alkylation and recovered starting material account for sufficient material balance to rule out substantial rearrangement under these conditions. The present study unambiguously establishes the regiochemistry of double alkylation. Previous reports on analogous deprotonation with sodium alkoxides (Dal Piaz, et al., 1975; Chimichi, et al., 1986), reported rearrangement to pyrazoles with longer reaction times (Dal Piaz et al., 1985). The lateral metalation and electrophilic quenching of isoxazoles continues to lead to candidates with promising biological activity (Nakamura, et al., 2010; Hulubei et al., 2012) and is the subject of active investigation, to be reported in due course. The conformation observed in the solid state (Fig. 1) would be expected to result in magnetic anisotropy if maintained in solution, and this is indeed observed, as the 1H NMR resonance of the C(4) methyl is observed at δ 2.55 in the starting material, δ 2.21 in the monoalkylated product, and δ 1.86 in the title compound. Further chemistry and pharmacology studies based upon this reaction are underway and will be reported in due course.
2. Experimental
Starting material, 3-methyl-4-methyl-6-phenylisoxazolo[3,4-d]pyridazin-7(6H)-one (Fig. 2) was prepared according to Renzi and Dal Piaz (1965). To starting material (88 mg, 0.36 mmol) was added freshly distilled tetrahydrofuran (THF, 25 ml), under an argon atmosphere. The temperature was lowered to 195 K, and a solution of lithium hexamethyldisilazide (1 ml, 1.0M in THF, Aldrich, 28% excess) was added dropwise over five minutes. After stirring for 1 h, benzyl bromide was added via syringe (0.1 ml, 0.84 mmol, 14% excess). The reaction was allowed to come to room temperature with stirring overnight, after which time the solvent was removed in vacuo by rotary evaporator, and the residue chromatographed on an 80 x 35 cm silica gel column. Gradient chromatogrpahy was performed beginning with chloroform-hexane (1:1), and the gradient slowly increased in polarity to ethyl acetate (EtOAc)-hexane-chloroform (1:2:1). The product 3-(1,3-diphenylpropan-2-yl)-4-methyl-6-phenylisoxazolo[3,4-d]pyridazin-7(6H)-one was obtained from the column fraction with Rf 0.6 (SiO2, EtOAc-hexane-chloroform 2:1:1) as a solid (57.1 mg, 38% yield), and was recrystallized by slow evaporation from EtOAc/hexanes to which a small amount of heptane had been added. The resulting crystals were used in the single crystal X-ray study. A clear light yellow prism-like specimen was selected for the X-ray data collection with a Bruker D8 Venture PHOTON 100 CMOS system equipped with a Cu Kα INCOATEC micro-focus source (λ = 1.54178 Å).
3. Refinement
A DELU restraint (Sheldrick, 2008) was used for the Uij of all non-H atoms. Hydrogen atoms were positioned geometrically and refined as riding atoms, with C—H = 0.96–0.99 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C) for methyl H atoms, and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) for all other H atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of the title compound, with H atoms represented by small spheres of arbitrary radius and displacement ellipsoids at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
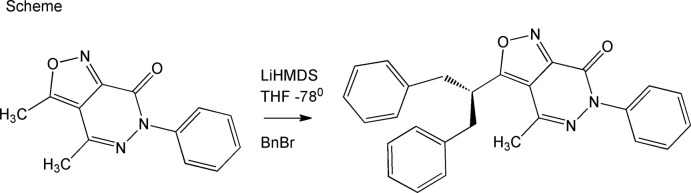
Benzylation of 3-methyl-4-methyl-6-phenylisoxazolo[3,4-d]pyridazin-7(6H)-one as precursor to give the title compound.
Fig. 3.
The unit cell of the title compound.
Crystal data
| C27H23N3O2 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 421.48 | F(000) = 444 |
| Triclinic, P1 | calculated from global refinement |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Dx = 1.301 Mg m−3 |
| a = 7.5163 (4) Å | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| b = 9.6774 (5) Å | Cell parameters from 9923 reflections |
| c = 15.9053 (8) Å | θ = 2.8–68.4° |
| α = 86.798 (1)° | µ = 0.66 mm−1 |
| β = 83.512 (1)° | T = 100 K |
| γ = 69.385 (1)° | Prism, clear light yellow |
| V = 1075.75 (10) Å3 | 0.40 × 0.22 × 0.19 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker D8 Venture PHOTON 100 CMOS diffractometer | 3714 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Cu Kα | 3597 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Mirrors monochromator | Rint = 0.017 |
| Detector resolution: 10.4167 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 66.6°, θmin = 2.8° |
| ω and phi scans | h = −8→3 |
| Absorption correction: numerical (SADABS; Bruker, 2012) | k = −11→11 |
| Tmin = 0.80, Tmax = 0.89 | l = −18→18 |
| 12012 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.032 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.078 | Only H-atom displacement parameters refined |
| S = 1.03 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0352P)2 + 0.337P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3714 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 313 parameters | Δρmax = 0.22 e Å−3 |
| 86 restraints | Δρmin = −0.14 e Å−3 |
| 0 constraints |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.00502 (11) | 0.47448 (8) | 0.64153 (5) | 0.02756 (18) | |
| N1 | 0.15001 (13) | 0.33590 (10) | 0.65000 (6) | 0.0270 (2) | |
| C1 | 0.25346 (14) | 0.36020 (11) | 0.70485 (6) | 0.0222 (2) | |
| C2 | 0.42780 (15) | 0.24940 (11) | 0.73381 (6) | 0.0226 (2) | |
| O2 | 0.49243 (11) | 0.11970 (8) | 0.71482 (5) | 0.02828 (18) | |
| N2 | 0.51293 (12) | 0.31237 (9) | 0.78613 (5) | 0.02217 (19) | |
| N3 | 0.44085 (12) | 0.45480 (9) | 0.81882 (5) | 0.0235 (2) | |
| C3 | 0.28457 (14) | 0.54911 (11) | 0.79389 (6) | 0.0224 (2) | |
| C4 | 0.18507 (14) | 0.50724 (11) | 0.73305 (6) | 0.0217 (2) | |
| C5 | 0.02762 (15) | 0.57547 (12) | 0.69057 (6) | 0.0232 (2) | |
| C6 | 0.69832 (14) | 0.22965 (11) | 0.81342 (7) | 0.0224 (2) | |
| C7 | 0.85159 (15) | 0.16976 (11) | 0.75336 (7) | 0.0260 (2) | |
| H7 | 0.8334 | 0.1771 | 0.6949 | 0.030 (3)* | |
| C8 | 1.03243 (15) | 0.09880 (12) | 0.77969 (7) | 0.0278 (2) | |
| H8 | 1.1385 | 0.0572 | 0.739 | 0.034 (3)* | |
| C9 | 1.05866 (16) | 0.08840 (12) | 0.86484 (7) | 0.0284 (2) | |
| H9 | 1.1823 | 0.0391 | 0.8826 | 0.033 (3)* | |
| C10 | 0.90441 (16) | 0.15001 (12) | 0.92425 (7) | 0.0273 (2) | |
| H10 | 0.9229 | 0.1434 | 0.9827 | 0.032 (3)* | |
| C11 | 0.72289 (15) | 0.22140 (11) | 0.89891 (7) | 0.0248 (2) | |
| H11 | 0.6171 | 0.264 | 0.9396 | 0.025 (3)* | |
| C12 | 0.21729 (16) | 0.69938 (12) | 0.83066 (8) | 0.0295 (2) | |
| H12A | 0.3036 | 0.7028 | 0.8717 | 0.039 (4)* | |
| H12B | 0.0879 | 0.7216 | 0.8591 | 0.039 (4)* | |
| H12C | 0.2161 | 0.7725 | 0.7854 | 0.043 (4)* | |
| C13 | −0.11611 (15) | 0.72853 (12) | 0.68583 (7) | 0.0255 (2) | |
| H13 | −0.0688 | 0.7945 | 0.7162 | 0.019 (3)* | |
| C14 | −0.31156 (15) | 0.73629 (12) | 0.73267 (7) | 0.0279 (2) | |
| H14A | −0.4109 | 0.831 | 0.7186 | 0.032 (3)* | |
| H14B | −0.3481 | 0.6549 | 0.7141 | 0.029 (3)* | |
| C15 | −0.29925 (14) | 0.72404 (12) | 0.82684 (7) | 0.0256 (2) | |
| C16 | −0.24282 (15) | 0.58718 (12) | 0.86891 (7) | 0.0280 (2) | |
| H16 | −0.222 | 0.5 | 0.8387 | 0.028 (3)* | |
| C17 | −0.21682 (16) | 0.57717 (13) | 0.95421 (7) | 0.0306 (3) | |
| H17 | −0.1802 | 0.4835 | 0.9822 | 0.038 (4)* | |
| C18 | −0.24399 (15) | 0.70303 (13) | 0.99886 (7) | 0.0302 (3) | |
| H18 | −0.2237 | 0.6958 | 1.0571 | 0.034 (3)* | |
| C19 | −0.30114 (15) | 0.83994 (13) | 0.95784 (7) | 0.0296 (2) | |
| H19 | −0.3209 | 0.9268 | 0.9882 | 0.032 (3)* | |
| C20 | −0.32932 (15) | 0.85002 (12) | 0.87290 (7) | 0.0278 (2) | |
| H20 | −0.3697 | 0.9442 | 0.8456 | 0.034 (3)* | |
| C21 | −0.12730 (16) | 0.78383 (13) | 0.59301 (7) | 0.0302 (3) | |
| H21A | −0.1683 | 0.7183 | 0.5602 | 0.029 (3)* | |
| H21B | −0.2235 | 0.8846 | 0.5907 | 0.038 (4)* | |
| C22 | 0.13242 (17) | 0.89367 (13) | 0.57720 (7) | 0.0308 (3) | |
| H22 | 0.0532 | 0.9691 | 0.6146 | 0.037 (4)* | |
| C23 | 0.31273 (18) | 0.89326 (13) | 0.54685 (7) | 0.0336 (3) | |
| H23 | 0.357 | 0.9668 | 0.5641 | 0.039 (4)* | |
| C24 | 0.42832 (17) | 0.78538 (14) | 0.49126 (7) | 0.0343 (3) | |
| H24 | 0.5519 | 0.7848 | 0.47 | 0.039 (4)* | |
| C25 | 0.36233 (18) | 0.67858 (14) | 0.46702 (7) | 0.0355 (3) | |
| H25 | 0.4407 | 0.6048 | 0.4285 | 0.046 (4)* | |
| C26 | 0.18236 (18) | 0.67824 (13) | 0.49847 (7) | 0.0322 (3) | |
| H26 | 0.1394 | 0.6036 | 0.4817 | 0.036 (3)* | |
| C27 | 0.06465 (16) | 0.78583 (12) | 0.55409 (7) | 0.0271 (2) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0275 (4) | 0.0247 (4) | 0.0302 (4) | −0.0066 (3) | −0.0104 (3) | 0.0004 (3) |
| N1 | 0.0273 (5) | 0.0231 (5) | 0.0295 (5) | −0.0062 (4) | −0.0071 (4) | 0.0001 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0238 (5) | 0.0218 (5) | 0.0219 (5) | −0.0093 (4) | −0.0024 (4) | 0.0019 (4) |
| C2 | 0.0245 (5) | 0.0203 (5) | 0.0230 (5) | −0.0085 (4) | −0.0019 (4) | 0.0013 (4) |
| O2 | 0.0309 (4) | 0.0197 (4) | 0.0334 (4) | −0.0068 (3) | −0.0064 (3) | −0.0008 (3) |
| N2 | 0.0219 (4) | 0.0175 (4) | 0.0257 (4) | −0.0045 (3) | −0.0044 (3) | 0.0001 (3) |
| N3 | 0.0227 (4) | 0.0194 (4) | 0.0273 (5) | −0.0057 (3) | −0.0033 (3) | −0.0016 (3) |
| C3 | 0.0203 (5) | 0.0218 (5) | 0.0249 (5) | −0.0074 (4) | −0.0030 (4) | 0.0017 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0218 (5) | 0.0200 (5) | 0.0229 (5) | −0.0075 (4) | −0.0013 (4) | 0.0021 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0232 (5) | 0.0241 (5) | 0.0236 (5) | −0.0094 (4) | −0.0042 (4) | 0.0017 (4) |
| C6 | 0.0216 (5) | 0.0163 (5) | 0.0296 (5) | −0.0063 (4) | −0.0059 (4) | 0.0031 (4) |
| C7 | 0.0282 (6) | 0.0219 (5) | 0.0261 (5) | −0.0065 (4) | −0.0039 (4) | 0.0013 (4) |
| C8 | 0.0244 (5) | 0.0222 (5) | 0.0336 (6) | −0.0045 (4) | −0.0011 (4) | −0.0012 (4) |
| C9 | 0.0241 (5) | 0.0215 (5) | 0.0383 (6) | −0.0049 (4) | −0.0097 (4) | 0.0030 (4) |
| C10 | 0.0300 (6) | 0.0238 (5) | 0.0283 (6) | −0.0083 (4) | −0.0089 (4) | 0.0037 (4) |
| C11 | 0.0249 (5) | 0.0219 (5) | 0.0273 (5) | −0.0081 (4) | −0.0027 (4) | 0.0013 (4) |
| C12 | 0.0243 (5) | 0.0244 (6) | 0.0389 (6) | −0.0051 (4) | −0.0086 (5) | −0.0052 (5) |
| C13 | 0.0237 (5) | 0.0230 (5) | 0.0295 (6) | −0.0065 (4) | −0.0082 (4) | 0.0033 (4) |
| C14 | 0.0224 (5) | 0.0244 (6) | 0.0363 (6) | −0.0064 (4) | −0.0080 (4) | 0.0026 (4) |
| C15 | 0.0171 (5) | 0.0251 (5) | 0.0349 (6) | −0.0078 (4) | −0.0035 (4) | 0.0023 (4) |
| C16 | 0.0235 (5) | 0.0232 (5) | 0.0387 (6) | −0.0097 (4) | −0.0046 (4) | 0.0010 (5) |
| C17 | 0.0270 (6) | 0.0267 (6) | 0.0391 (6) | −0.0116 (4) | −0.0044 (5) | 0.0081 (5) |
| C18 | 0.0246 (5) | 0.0354 (6) | 0.0303 (6) | −0.0111 (5) | −0.0002 (4) | 0.0022 (5) |
| C19 | 0.0230 (5) | 0.0274 (6) | 0.0365 (6) | −0.0072 (4) | 0.0013 (4) | −0.0040 (5) |
| C20 | 0.0210 (5) | 0.0214 (5) | 0.0384 (6) | −0.0050 (4) | −0.0018 (4) | 0.0033 (4) |
| C21 | 0.0293 (6) | 0.0295 (6) | 0.0318 (6) | −0.0084 (5) | −0.0124 (5) | 0.0076 (5) |
| C22 | 0.0362 (6) | 0.0266 (6) | 0.0277 (6) | −0.0081 (5) | −0.0059 (5) | 0.0013 (4) |
| C23 | 0.0416 (7) | 0.0345 (6) | 0.0302 (6) | −0.0188 (5) | −0.0100 (5) | 0.0050 (5) |
| C24 | 0.0332 (6) | 0.0421 (7) | 0.0279 (6) | −0.0138 (5) | −0.0056 (5) | 0.0075 (5) |
| C25 | 0.0425 (7) | 0.0348 (7) | 0.0256 (6) | −0.0099 (5) | −0.0003 (5) | −0.0002 (5) |
| C26 | 0.0437 (7) | 0.0307 (6) | 0.0251 (5) | −0.0153 (5) | −0.0088 (5) | 0.0018 (4) |
| C27 | 0.0304 (6) | 0.0271 (6) | 0.0235 (5) | −0.0081 (4) | −0.0116 (4) | 0.0078 (4) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C5 | 1.3506 (13) | C13—H13 | 1.0 |
| O1—N1 | 1.4100 (11) | C14—C15 | 1.5067 (16) |
| N1—C1 | 1.3138 (14) | C14—H14A | 0.99 |
| C1—C4 | 1.4122 (14) | C14—H14B | 0.99 |
| C1—C2 | 1.4734 (14) | C15—C20 | 1.3937 (16) |
| C2—O2 | 1.2176 (13) | C15—C16 | 1.3968 (15) |
| C2—N2 | 1.3873 (13) | C16—C17 | 1.3857 (17) |
| N2—N3 | 1.3979 (12) | C16—H16 | 0.95 |
| N2—C6 | 1.4434 (13) | C17—C18 | 1.3851 (17) |
| N3—C3 | 1.2961 (13) | C17—H17 | 0.95 |
| C3—C4 | 1.4425 (15) | C18—C19 | 1.3898 (16) |
| C3—C12 | 1.4909 (15) | C18—H18 | 0.95 |
| C4—C5 | 1.3688 (15) | C19—C20 | 1.3839 (17) |
| C5—C13 | 1.4986 (14) | C19—H19 | 0.95 |
| C6—C7 | 1.3851 (15) | C20—H20 | 0.95 |
| C6—C11 | 1.3869 (15) | C21—C27 | 1.5105 (16) |
| C7—C8 | 1.3906 (16) | C21—H21A | 0.99 |
| C7—H7 | 0.95 | C21—H21B | 0.99 |
| C8—C9 | 1.3835 (16) | C22—C23 | 1.3850 (17) |
| C8—H8 | 0.95 | C22—C27 | 1.3940 (16) |
| C9—C10 | 1.3861 (16) | C22—H22 | 0.95 |
| C9—H9 | 0.95 | C23—C24 | 1.3847 (18) |
| C10—C11 | 1.3895 (15) | C23—H23 | 0.95 |
| C10—H10 | 0.95 | C24—C25 | 1.3825 (18) |
| C11—H11 | 0.95 | C24—H24 | 0.95 |
| C12—H12A | 0.98 | C25—C26 | 1.3893 (18) |
| C12—H12B | 0.98 | C25—H25 | 0.95 |
| C12—H12C | 0.98 | C26—C27 | 1.3881 (16) |
| C13—C21 | 1.5431 (15) | C26—H26 | 0.95 |
| C13—C14 | 1.5492 (15) | ||
| C5—O1—N1 | 110.86 (8) | C14—C13—H13 | 107.2 |
| C1—N1—O1 | 103.37 (8) | C15—C14—C13 | 109.92 (8) |
| N1—C1—C4 | 113.41 (9) | C15—C14—H14A | 109.7 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 124.88 (9) | C13—C14—H14A | 109.7 |
| C4—C1—C2 | 121.68 (9) | C15—C14—H14B | 109.7 |
| O2—C2—N2 | 123.36 (9) | C13—C14—H14B | 109.7 |
| O2—C2—C1 | 125.71 (10) | H14A—C14—H14B | 108.2 |
| N2—C2—C1 | 110.93 (9) | C20—C15—C16 | 118.33 (10) |
| C2—N2—N3 | 127.80 (8) | C20—C15—C14 | 119.92 (10) |
| C2—N2—C6 | 120.74 (8) | C16—C15—C14 | 121.55 (10) |
| N3—N2—C6 | 111.46 (8) | C17—C16—C15 | 120.73 (10) |
| C3—N3—N2 | 119.61 (9) | C17—C16—H16 | 119.6 |
| N3—C3—C4 | 120.23 (9) | C15—C16—H16 | 119.6 |
| N3—C3—C12 | 116.70 (9) | C18—C17—C16 | 120.33 (10) |
| C4—C3—C12 | 123.07 (9) | C18—C17—H17 | 119.8 |
| C5—C4—C1 | 104.21 (9) | C16—C17—H17 | 119.8 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 136.51 (10) | C17—C18—C19 | 119.48 (11) |
| C1—C4—C3 | 119.28 (9) | C17—C18—H18 | 120.3 |
| O1—C5—C4 | 108.15 (9) | C19—C18—H18 | 120.3 |
| O1—C5—C13 | 115.96 (9) | C20—C19—C18 | 120.14 (11) |
| C4—C5—C13 | 135.89 (10) | C20—C19—H19 | 119.9 |
| C7—C6—C11 | 121.11 (10) | C18—C19—H19 | 119.9 |
| C7—C6—N2 | 119.36 (9) | C19—C20—C15 | 120.97 (10) |
| C11—C6—N2 | 119.33 (9) | C19—C20—H20 | 119.5 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 119.17 (10) | C15—C20—H20 | 119.5 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 120.4 | C27—C21—C13 | 110.58 (9) |
| C8—C7—H7 | 120.4 | C27—C21—H21A | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 120.33 (10) | C13—C21—H21A | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 119.8 | C27—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 119.8 | C13—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 119.94 (10) | H21A—C21—H21B | 108.1 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 120.0 | C23—C22—C27 | 121.42 (11) |
| C10—C9—H9 | 120.0 | C23—C22—H22 | 119.3 |
| C9—C10—C11 | 120.40 (10) | C27—C22—H22 | 119.3 |
| C9—C10—H10 | 119.8 | C24—C23—C22 | 119.85 (11) |
| C11—C10—H10 | 119.8 | C24—C23—H23 | 120.1 |
| C6—C11—C10 | 119.05 (10) | C22—C23—H23 | 120.1 |
| C6—C11—H11 | 120.5 | C25—C24—C23 | 119.42 (11) |
| C10—C11—H11 | 120.5 | C25—C24—H24 | 120.3 |
| C3—C12—H12A | 109.5 | C23—C24—H24 | 120.3 |
| C3—C12—H12B | 109.5 | C24—C25—C26 | 120.56 (11) |
| H12A—C12—H12B | 109.5 | C24—C25—H25 | 119.7 |
| C3—C12—H12C | 109.5 | C26—C25—H25 | 119.7 |
| H12A—C12—H12C | 109.5 | C27—C26—C25 | 120.70 (11) |
| H12B—C12—H12C | 109.5 | C27—C26—H26 | 119.6 |
| C5—C13—C21 | 110.34 (9) | C25—C26—H26 | 119.6 |
| C5—C13—C14 | 110.96 (9) | C26—C27—C22 | 118.05 (11) |
| C21—C13—C14 | 113.70 (9) | C26—C27—C21 | 121.96 (10) |
| C5—C13—H13 | 107.2 | C22—C27—C21 | 119.91 (10) |
| C21—C13—H13 | 107.2 | ||
| C5—O1—N1—C1 | 0.42 (11) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −0.07 (16) |
| O1—N1—C1—C4 | −0.08 (11) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | −0.54 (16) |
| O1—N1—C1—C2 | −178.31 (9) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.47 (16) |
| N1—C1—C2—O2 | −4.53 (17) | C7—C6—C11—C10 | −0.83 (16) |
| C4—C1—C2—O2 | 177.38 (10) | N2—C6—C11—C10 | −175.73 (9) |
| N1—C1—C2—N2 | 174.91 (10) | C9—C10—C11—C6 | 0.20 (16) |
| C4—C1—C2—N2 | −3.18 (13) | O1—C5—C13—C21 | −53.31 (12) |
| O2—C2—N2—N3 | −172.66 (9) | C4—C5—C13—C21 | 125.98 (13) |
| C1—C2—N2—N3 | 7.88 (14) | O1—C5—C13—C14 | 73.63 (11) |
| O2—C2—N2—C6 | 7.42 (15) | C4—C5—C13—C14 | −107.07 (14) |
| C1—C2—N2—C6 | −172.03 (8) | C5—C13—C14—C15 | 71.49 (11) |
| C2—N2—N3—C3 | −6.84 (15) | C21—C13—C14—C15 | −163.44 (9) |
| C6—N2—N3—C3 | 173.09 (9) | C13—C14—C15—C20 | 86.05 (12) |
| N2—N3—C3—C4 | 0.28 (14) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −88.63 (12) |
| N2—N3—C3—C12 | −179.32 (9) | C20—C15—C16—C17 | −0.22 (15) |
| N1—C1—C4—C5 | −0.26 (12) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | 174.54 (10) |
| C2—C1—C4—C5 | 178.03 (9) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | −0.90 (16) |
| N1—C1—C4—C3 | 179.63 (9) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | 1.23 (16) |
| C2—C1—C4—C3 | −2.08 (15) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | −0.44 (16) |
| N3—C3—C4—C5 | −176.42 (11) | C18—C19—C20—C15 | −0.69 (16) |
| C12—C3—C4—C5 | 3.15 (19) | C16—C15—C20—C19 | 1.01 (15) |
| N3—C3—C4—C1 | 3.73 (15) | C14—C15—C20—C19 | −173.84 (10) |
| C12—C3—C4—C1 | −176.70 (10) | C5—C13—C21—C27 | −59.69 (12) |
| N1—O1—C5—C4 | −0.60 (11) | C14—C13—C21—C27 | 174.90 (9) |
| N1—O1—C5—C13 | 178.88 (8) | C27—C22—C23—C24 | 1.06 (17) |
| C1—C4—C5—O1 | 0.51 (11) | C22—C23—C24—C25 | −0.34 (17) |
| C3—C4—C5—O1 | −179.35 (11) | C23—C24—C25—C26 | −0.50 (17) |
| C1—C4—C5—C13 | −178.82 (11) | C24—C25—C26—C27 | 0.65 (17) |
| C3—C4—C5—C13 | 1.3 (2) | C25—C26—C27—C22 | 0.05 (16) |
| C2—N2—C6—C7 | 56.43 (13) | C25—C26—C27—C21 | −176.67 (10) |
| N3—N2—C6—C7 | −123.50 (10) | C23—C22—C27—C26 | −0.90 (16) |
| C2—N2—C6—C11 | −128.58 (10) | C23—C22—C27—C21 | 175.88 (10) |
| N3—N2—C6—C11 | 51.49 (12) | C13—C21—C27—C26 | 103.38 (12) |
| C11—C6—C7—C8 | 0.76 (16) | C13—C21—C27—C22 | −73.27 (12) |
| N2—C6—C7—C8 | 175.67 (9) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C26—H26···O1i | 0.95 | 2.61 | 3.4159 (13) | 143 |
| C24—H24···N1ii | 0.95 | 2.73 | 3.5407 (15) | 143 |
| C11—H11···C18iii | 0.95 | 2.78 | 3.6182 (15) | 148 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+1, −z+1; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (iii) −x, −y+1, −z+2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: QK2060).
References
- Bruker (2012). SMART, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Chimichi, S., Ciciani, G., Dal Piaz, V., De Sio, F., Sarti-Fantoni, P. & Torroba, T. (1986). Heterocycles, 24, 3467–3471.
- Dal Piaz, V., Ciciani, G. & Chimichi, S. (1985). Heterocycles, 23, 365–369.
- Dal Piaz, V., Pinzauti, S. & Lacrimini, P. (1975). J. Heterocycl. Chem. 13, 409–410.
- Hulubei, V., Meikrantz, S. B., Quincy, D. A., Houle, T., McKenna, J. I., Rogers, M. E., Steiger, S. A. & Natale, N. R. (2012). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 20, 6613–6620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Nakamura, M., Kurihara, H., Suzuki, G., Mitsuya, M., Ohkubo, M. & Ohta, H. (2010). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 20, 726–729. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Natale, N. R., McKenna, J. I., Niou, C.-S., Borth, M. & Hope, H. (1985). J. Org. Chem. 50, 5660–5666.
- Natale, N. R. & Mirzaei, Y. R. (1993). Org. Prep. Proc. Int. 25, 515–556.
- Natale, N. R. & Niou, C.-S. (1984). Tetrahedron Lett. 25, 3943–3946.
- Niou, C.-S. & Natale, N. R. (1986). Heterocycles, 24, 401–412.
- Renzi, G. & Dal Piaz, V. (1965). Gazz. Chim. Ital. 95, 1478–1491.
- Schlicksupp, L. & Natale, N. R. (1987). J. Heterocycl. Chem. 24, 1345–1348.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681302802X/qk2060sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681302802X/qk2060Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681302802X/qk2060Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report