Abstract
Muscle membranes were partially purified from rat leg muscles. Externally oriented membrane functions were used to monitor and characterize the resulting membrane fractions. Na+K+-stimulated Mg++-adenosinetriphosphatase, acetylcholinesterase, and cholinergic receptor activities are present and enriched in the density-gradient subfractions of crude sarcolemma when compared with the first pellet. The physical separation of the cholinesterase and receptor activities on the gradient subfractions is demonstrated.
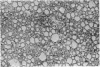
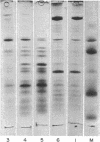
Receptor activity, determined by specific 125I-labeled alpha-bungarotoxin binding, appears in fractions with densities similar to other plasma membranes (D420 1.1015-1.1520). Acetylcholinesterase, on the other hand, is preferentially distributed in lighter density fractions (D420 1.0507-1.0780) and parallels the gradient distribution of the ATPase. In sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, a high-molecular-weight glycoprotein sediments with the higher density fractions only.
The data suggest a molecular dissection of the layers of the sarcolemma. The receptor is tentatively felt to be an integral component of the junctional plasma membrane. Acetylcholinesterase is felt to be superficially located on the ectolamina of the junctional sarcolemma, and may be woven within the matrix of the intersynaptic basement membrane.
Keywords: membrane ATPase, bungarotoxin, acetylcholinesterase, cholinergic, nicotinic
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg D. K., Kelly R. B., Sargent P. B., Williamson P., Hall Z. W. Binding of -bungarotoxin to acetylcholine receptors in mammalian muscle (snake venom-denervated muscle-neonatal muscle-rat diaphragm-SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):147–151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz W., Sakmann B. "Disjunction" of frog neuromuscular synapses by treatment with proteolytic enzymes. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 21;232(29):94–95. doi: 10.1038/newbio232094a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boegman R. J., Manery J. F., Pinteric L. The separation and partial purification of membrane-bound (Na + + K + )-dependent Mg 2+ -ATPase and (Na + +K + (Na + +K + )-independent Mg 2+ -ATPase from frog skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jun 2;203(3):506–530. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90189-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Gautron J., Israël M., Podleski T. Séparation de membranes excitables à partir de l'organe électrique d'Electrophorus electricus. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1969 Nov 3;269(18):1788–1791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. G., Macmurchie D. D., Elliott E., Wolcott R. G., Landel A. M., Raftery M. A. Elapid neurotoxins. Purification, characterization, and immunochemical studies of -bungarotoxin. Biochemistry. 1972 Apr 25;11(9):1663–1668. doi: 10.1021/bi00759a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. B., Weber M., Huchet M., Changeux J. P. Purification from Torpedo marmorata electric tissue of membrane fragments particularly rich in cholinergic receptor protein. FEBS Lett. 1972 Oct 1;26(1):43–47. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80538-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE ROBERTIS E., RODRIGUEZ DE LORES ARNAIZ G., SALGANICOFF L., PELLEGRINO DE IRALDI A., ZIEHER L. M. Isolation of synaptic vesicles and structural organization of the acetycholine system within brain nerve endings. J Neurochem. 1963 Apr;10:225–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1963.tb05038.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUGGAN P. F. SOME PROPERTIES OF THE MONOVALENT-CATION-STIMULATED ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATASE OF FROG SARTORIUS MICROSOMES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Apr 26;99:144–155. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(65)80013-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David G. S. Solid state lactoperoxidase: a highly stable enzyme for simple, gentle iodination of proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jul 25;48(2):464–471. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80074-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D. M., Hartzell H. C. Acetylcholine receptors: number and distribution at neuromuscular junctions in rat diaphragm. Science. 1972 Apr 14;176(4031):189–191. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4031.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Kahn R., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin interactions with liver plasma membranes. Independence of binding of the hormone and its degradation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3953–3961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOKETSU K., KITAMURA R., TANAKA R. BINDING OF CALCIUM IONS TO CELL MEMBRANE ISOLATED FROM BULLFROG SKELETAL MUSCLE. Am J Physiol. 1964 Aug;207:509–512. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.2.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KONO T., COLOWICK S. P. Isolation of skeletal muscle cell membrane and some of its properties. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Jun;93:520–533. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(61)80046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y., Chang S. L., Kau S. T., Luh S. H. Chromatographic separation of the venom of Bungarus multicinctus and characterization of its components. J Chromatogr. 1972 Oct 5;72(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(72)80009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi V. T., Tillack T. W., Jackson R. L., Segrest J. P., Scott R. E. Chemical characterization and surface orientation of the major glycoprotein of the human erythrocyte membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1445–1449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Molinoff P., Potter L. T. Isolation of the cholinergic receptor protein of Torpedo electric tissue. Nature. 1971 Feb 19;229(5286):554–557. doi: 10.1038/229554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Potter L. T. Acetylcholine receptors in muscle fibres. Nature. 1971 Oct 29;233(5322):599–603. doi: 10.1038/233599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter J. B. A (Na+ K+) ATPase of sarcolemma from skeletal muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Sep 30;40(6):1362–1367. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter L. T. A radiometric microassay of acetylcholinesterase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1967 Jun;156(3):500–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery M. A., Schmidt J., Clark D. G. Specificity of -bungarotoxin binding to Torpedo californica electroplax. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Oct;152(2):882–886. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90285-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery M. A., Schmidt J., Clark D. G., Wolcott R. G. Demonstration of a specific -bungarotoxin binding component in electrophorus electricus electroplax membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Dec 17;45(6):1622–1629. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90207-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solyom A., Trams E. G. Enzyme markers in characterization of isolated plasma membranes. Enzyme. 1972;13(5-6):329–372. doi: 10.1159/000459682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperelakis N., Lee E. C. Characterization of (Na + ,K + )-ATPase isolated from embryonic chick hearts and cultured chick heart cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 1;233(3):562–579. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90155-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulakhe P. V., Fedelesova M., McNamara D. B., Dhalla N. S. Isolation of skeletal muscle membrane fragments containing active Na+-K+ stimulated ATPase: comparison of normal and dystrophic muscle sarcolemma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Mar 5;42(5):793–800. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90499-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAHLER B. E., WOLLENBERGER A. Zur Bestimmung des Orthophosphats neben säure-molybdat-labilen Phosphorsäureverbindungen. Biochem Z. 1958;329(6):508–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]