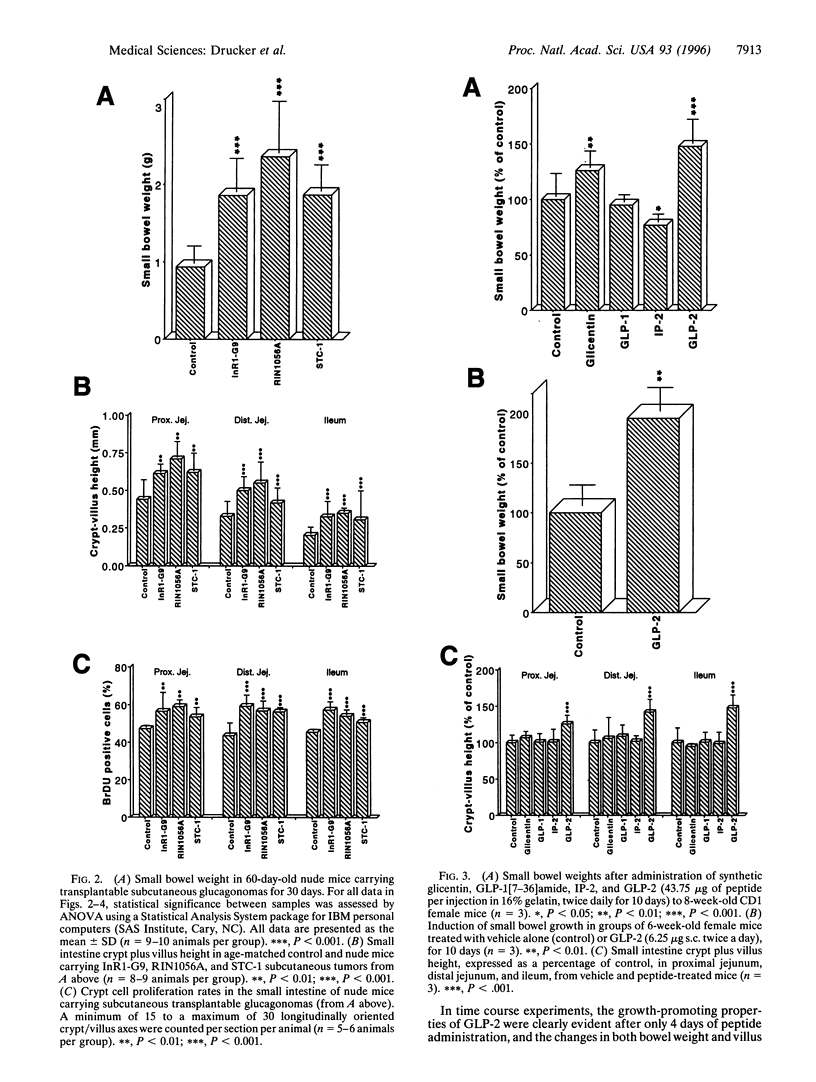
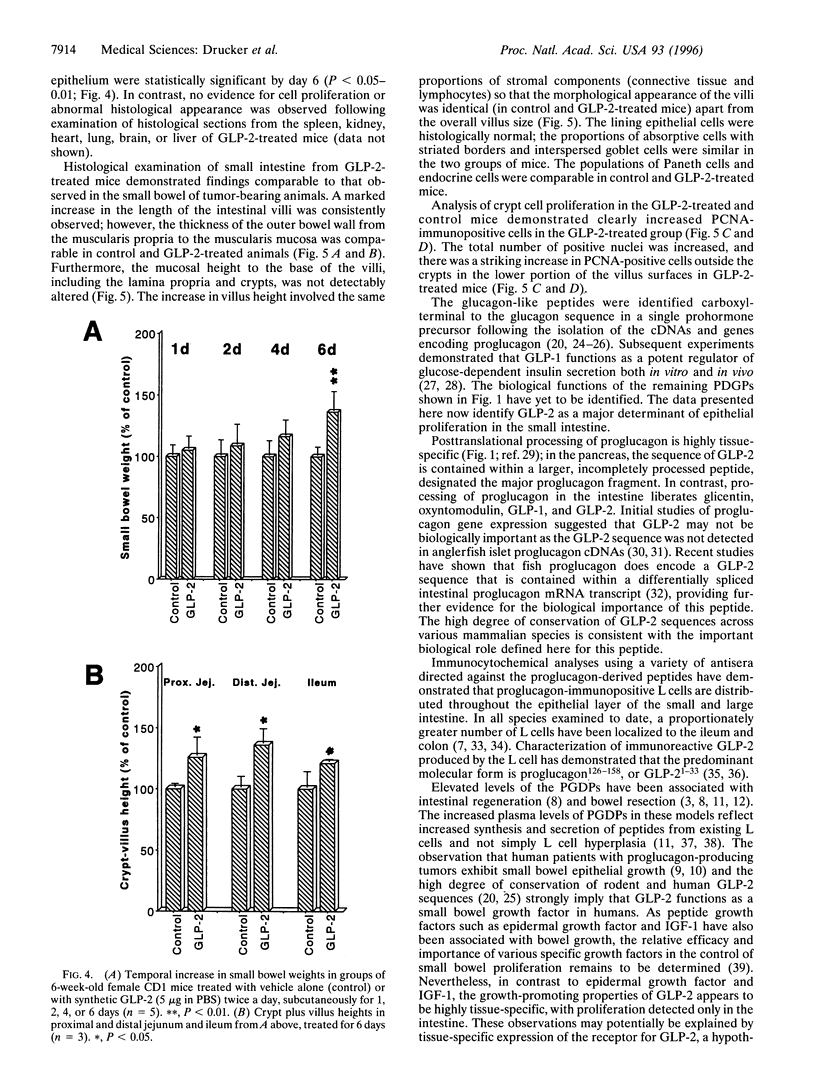
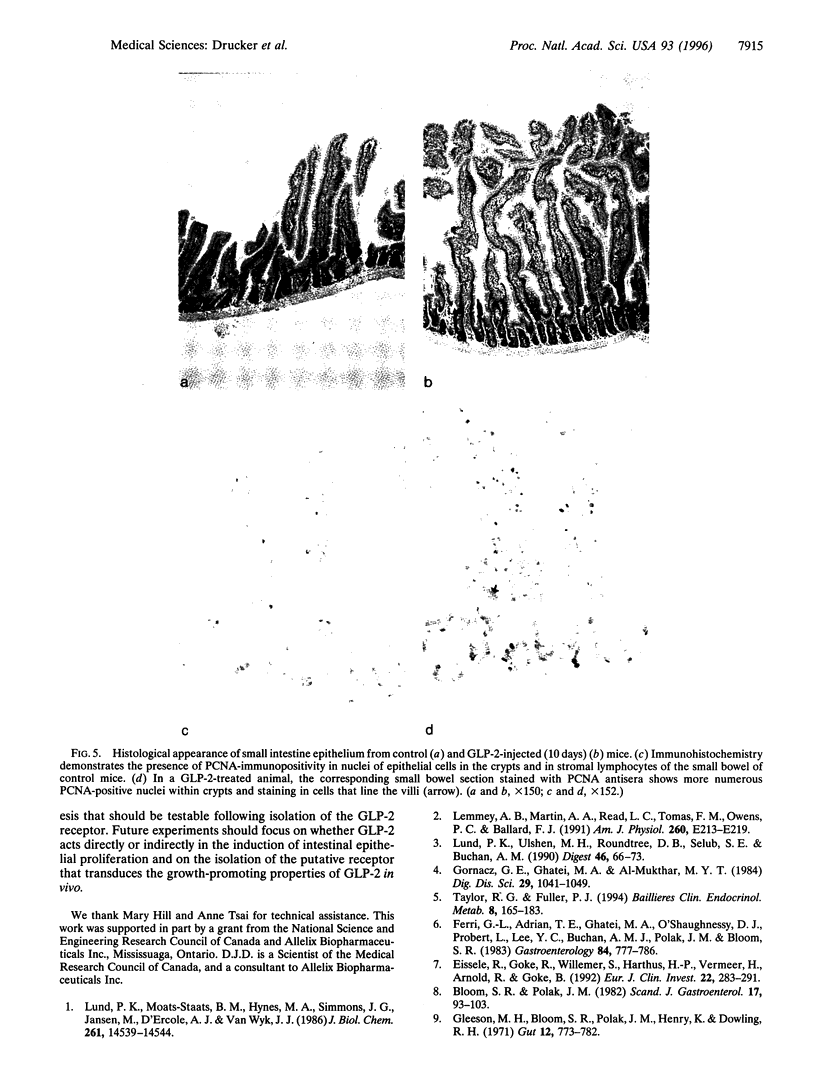
Abstract
Injury, inflammation, or resection of the small intestine results in severe compromise of intestinal function. Nevertheless, therapeutic strategies for enhancing growth and repair of the intestinal mucosal epithelium are currently not available. We demonstrate that nude mice bearing subcutaneous proglucagon-producing tumors exhibit marked proliferation of the small intestinal epithelium. The factor responsible for inducing intestinal proliferation was identified as glucagon-like peptide 2 (GLP-2), a 33-aa peptide with no previously ascribed biological function. GLP-2 stimulated crypt cell proliferation and consistently induced a marked increase in bowel weight and villus growth of the jejunum and ileum that was evident within 4 days after initiation of GLP-2 administration. These observations define a novel biological role for GLP-2 as an intestinal-derived peptide stimulator of small bowel epithelial proliferation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell G. I., Sanchez-Pescador R., Laybourn P. J., Najarian R. C. Exon duplication and divergence in the human preproglucagon gene. 1983 Jul 28-Aug 3Nature. 304(5924):368–371. doi: 10.1038/304368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Santerre R. F., Mullenbach G. T. Hamster preproglucagon contains the sequence of glucagon and two related peptides. Nature. 1983 Apr 21;302(5910):716–718. doi: 10.1038/302716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Polak J. M. The hormonal pattern of intestinal adaptation. A major role for enteroglucagon. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1982;74:93–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blume N., Skouv J., Larsson L. I., Holst J. J., Madsen O. D. Potent inhibitory effects of transplantable rat glucagonomas and insulinomas on the respective endogenous islet cells are associated with pancreatic apoptosis. J Clin Invest. 1995 Nov;96(5):2227–2235. doi: 10.1172/JCI118278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker P. L., Lee Y. C., Drucker D. J. Alterations in proglucagon processing and inhibition of proglucagon gene expression in transgenic mice which contain a chimeric proglucagon-SV40 T antigen gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):20728–20733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchan A. M., Griffiths C. J., Morris J. F., Polak J. M. Enteroglucagon cell hyperfunction in rat small intestine after gut resection. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jan;88(1 Pt 1):8–12. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(85)80125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhl T., Thim L., Kofod H., Orskov C., Harling H., Holst J. J. Naturally occurring products of proglucagon 111-160 in the porcine and human small intestine. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8621–8624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H., Leblond C. P. Origin, differentiation and renewal of the four main epithelial cell types in the mouse small intestine. V. Unitarian Theory of the origin of the four epithelial cell types. Am J Anat. 1974 Dec;141(4):537–561. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001410407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drucker D. J., Lee Y. C., Asa S. L., Brubaker P. L. Inhibition of pancreatic glucagon gene expression in mice bearing a subcutaneous glucagon-producing GLUTag transplantable tumor. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Dec;6(12):2175–2184. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.12.1491697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drucker D. J., Philippe J., Mojsov S., Chick W. L., Habener J. F. Glucagon-like peptide I stimulates insulin gene expression and increases cyclic AMP levels in a rat islet cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3434–3438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drucker D. J., Philippe J., Mojsov S. Proglucagon gene expression and posttranslational processing in a hamster islet cell line. Endocrinology. 1988 Oct;123(4):1861–1867. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-4-1861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich P., Tucker D., Asa S. L., Brubaker P. L., Drucker D. J. Inhibition of pancreatic proglucagon gene expression in mice bearing subcutaneous endocrine tumors. Am J Physiol. 1994 Nov;267(5 Pt 1):E662–E671. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1994.267.5.E662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eissele R., Göke R., Willemer S., Harthus H. P., Vermeer H., Arnold R., Göke B. Glucagon-like peptide-1 cells in the gastrointestinal tract and pancreas of rat, pig and man. Eur J Clin Invest. 1992 Apr;22(4):283–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1992.tb01464.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferri G. L., Adrian T. E., Ghatei M. A., O'Shaughnessy D. J., Probert L., Lee Y. C., Buchan A. M., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R. Tissue localization and relative distribution of regulatory peptides in separated layers from the human bowel. Gastroenterology. 1983 Apr;84(4):777–786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller P. J., Beveridge D. J., Taylor R. G. Ileal proglucagon gene expression in the rat: characterization in intestinal adaptation using in situ hybridization. Gastroenterology. 1993 Feb;104(2):459–466. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90414-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleeson M. H., Bloom S. R., Polak J. M., Henry K., Dowling R. H. Endocrine tumour in kidney affecting small bowel structure, motility, and absorptive function. Gut. 1971 Oct;12(10):773–782. doi: 10.1136/gut.12.10.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gornacz G. E., Ghatei M. A., Al-Mukhtar M. Y., Yeats J. C., Adrian T. E., Wright N. A., Bloom S. R. Plasma enteroglucagon and CCK levels and cell proliferation in defunctioned small bowel in the rat. Dig Dis Sci. 1984 Nov;29(11):1041–1049. doi: 10.1007/BF01311257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich G., Gros P., Lund P. K., Bentley R. C., Habener J. F. Pre-proglucagon messenger ribonucleic acid: nucleotide and encoded amino acid sequences of the rat pancreatic complementary deoxyribonucleic acid. Endocrinology. 1984 Dec;115(6):2176–2181. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-6-2176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irwin D. M., Wong J. Trout and chicken proglucagon: alternative splicing generates mRNA transcripts encoding glucagon-like peptide 2. Mol Endocrinol. 1995 Mar;9(3):267–277. doi: 10.1210/mend.9.3.7776976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson L. I., Holst J., Håkanson R., Sundler F. Distribution and properties of glucagon immunoreactivity in the digestive tract of various mammals: an immunohistochemical and immunochemical study. Histochemistry. 1975 Sep 29;44(4):281–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00490364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. C., Asa S. L., Drucker D. J. Glucagon gene 5'-flanking sequences direct expression of simian virus 40 large T antigen to the intestine, producing carcinoma of the large bowel in transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10705–10708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemmey A. B., Martin A. A., Read L. C., Tomas F. M., Owens P. C., Ballard F. J. IGF-I and the truncated analogue des-(1-3)IGF-I enhance growth in rats after gut resection. Am J Physiol. 1991 Feb;260(2 Pt 1):E213–E219. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1991.260.2.E213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund P. K., Goodman R. H., Dee P. C., Habener J. F. Pancreatic preproglucagon cDNA contains two glucagon-related coding sequences arranged in tandem. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):345–349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund P. K., Goodman R. H., Habener J. F. Pancreatic pre-proglucagons are encoded by two separate mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6515–6518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund P. K., Goodman R. H., Montminy M. R., Dee P. C., Habener J. F. Anglerfish islet pre-proglucagon II. Nucleotide and corresponding amino acid sequence of the cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3280–3284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund P. K., Moats-Staats B. M., Hynes M. A., Simmons J. G., Jansen M., D'Ercole A. J., Van Wyk J. J. Somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor-II mRNAs in rat fetal and adult tissues. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14539–14544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund P. K., Ulshen M. H., Rountree D. B., Selub S. E., Buchan A. M. Molecular biology of gastrointestinal peptides and growth factors: relevance to intestinal adaptation. Digestion. 1990;46 (Suppl 2):66–73. doi: 10.1159/000200369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mojsov S., Heinrich G., Wilson I. B., Ravazzola M., Orci L., Habener J. F. Preproglucagon gene expression in pancreas and intestine diversifies at the level of post-translational processing. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11880–11889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mojsov S., Weir G. C., Habener J. F. Insulinotropin: glucagon-like peptide I (7-37) co-encoded in the glucagon gene is a potent stimulator of insulin release in the perfused rat pancreas. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):616–619. doi: 10.1172/JCI112855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov C., Buhl T., Rabenhøj L., Kofod H., Holst J. J. Carboxypeptidase-B-like processing of the C-terminus of glucagon-like peptide-2 in pig and human small intestine. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 24;247(2):193–196. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81332-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippe J., Mojsov S., Drucker D. J., Habener J. F. Proglucagon processing in a rat islet cell line resembles phenotype of intestine rather than pancreas. Endocrinology. 1986 Dec;119(6):2833–2839. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-6-2833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podolsky D. K. Regulation of intestinal epithelial proliferation: a few answers, many questions. Am J Physiol. 1993 Feb;264(2 Pt 1):G179–G186. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1993.264.2.G179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rindi G., Grant S. G., Yiangou Y., Ghatei M. A., Bloom S. R., Bautch V. L., Solcia E., Polak J. M. Development of neuroendocrine tumors in the gastrointestinal tract of transgenic mice. Heterogeneity of hormone expression. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jun;136(6):1349–1363. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rountree D. B., Ulshen M. H., Selub S., Fuller C. R., Bloom S. R., Ghatei M. A., Lund P. K. Nutrient-independent increases in proglucagon and ornithine decarboxylase messenger RNAs after jejunoileal resection. Gastroenterology. 1992 Aug;103(2):462–468. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90835-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens F. M., Flanagan R. W., O'Gorman D., Buchanan K. D. Glucagonoma syndrome demonstrating giant duodenal villi. Gut. 1984 Jul;25(7):784–791. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.7.784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. G., Fuller P. J. Humoral regulation of intestinal adaptation. Baillieres Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994 Jan;8(1):165–183. doi: 10.1016/s0950-351x(05)80230-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. G., Verity K., Fuller P. J. Ileal glucagon gene expression: ontogeny and response to massive small bowel resection. Gastroenterology. 1990 Sep;99(3):724–729. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90961-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varndell I. M., Bishop A. E., Sikri K. L., Uttenthal L. O., Bloom S. R., Polak J. M. Localization of glucagon-like peptide (GLP) immunoreactants in human gut and pancreas using light and electron microscopic immunocytochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Oct;33(10):1080–1086. doi: 10.1177/33.10.3900195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dierendonck J. H., Wijsman J. H., Keijzer R., van de Velde C. J., Cornelisse C. J. Cell-cycle-related staining patterns of anti-proliferating cell nuclear antigen monoclonal antibodies. Comparison with BrdUrd labeling and Ki-67 staining. Am J Pathol. 1991 May;138(5):1165–1172. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]