Abstract
The experiments described in this paper implicate chloroplast protein synthesis in the regulation of nuclear DNA replication. The inhibition of nuclear DNA replication in the lower eukaryote, Chlamydomonas reinhardi strain 21gr, was examined after growth of cells with a series of antibiotics (streptomycin, neamine, spectinomycin, cleocin, chloramphenicol, and rifampicin) each of which has a known effect upon chloroplast RNA or protein synthesis in this organism. Each antibiotic inhibited nuclear DNA replication at drug concentrations at which there was little or no inhibition of adenine incorporation into chloroplast DNA. That chloroplast DNA was replicating under these conditions rather than merely being repaired, was shown first by the high incorporation rates and second by a 14N-15N density transfer experiment in which chloroplast DNA doubled in the presence of streptomycin, while no incorporation into nuclear DNA was detected. A small DNA peak, Component III, located between nuclear and chloroplast DNA's in CsCl gradients, possibly mitochondrial, was more pronounced in DNA from antibiotic-inhibited cultures than from controls.
Keywords: replication, organelle, feedback, antibiotics
Full text
PDF

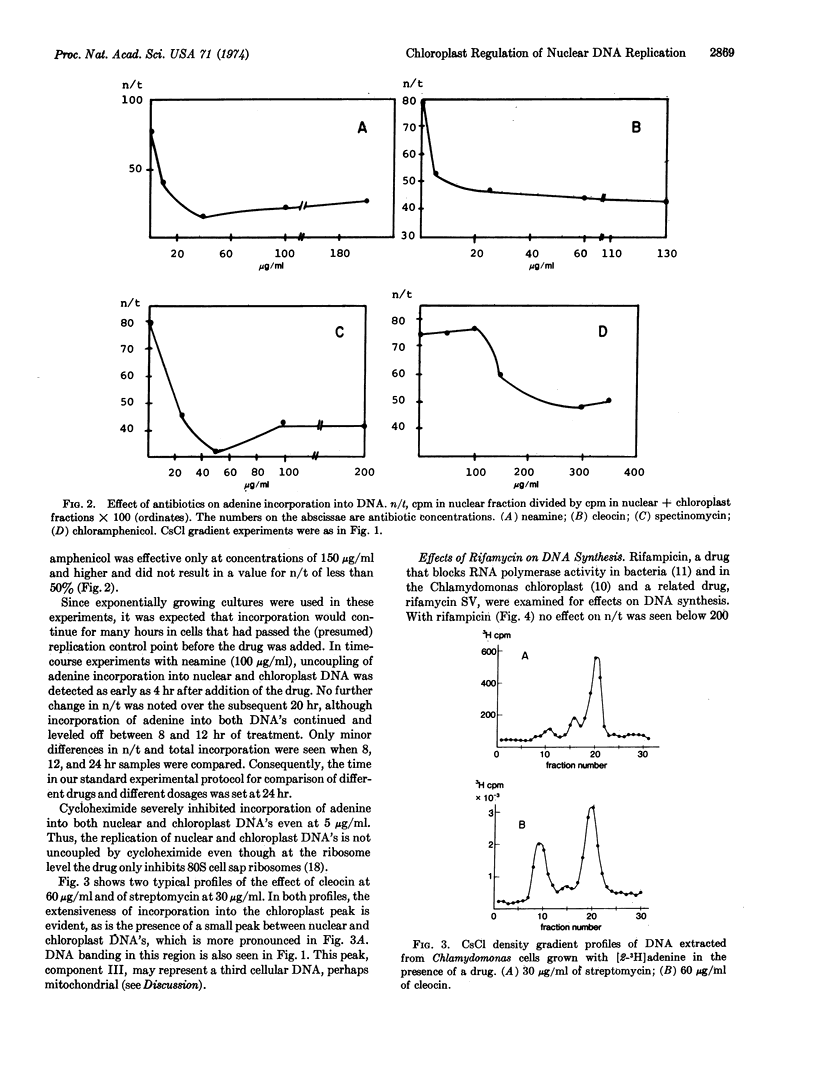
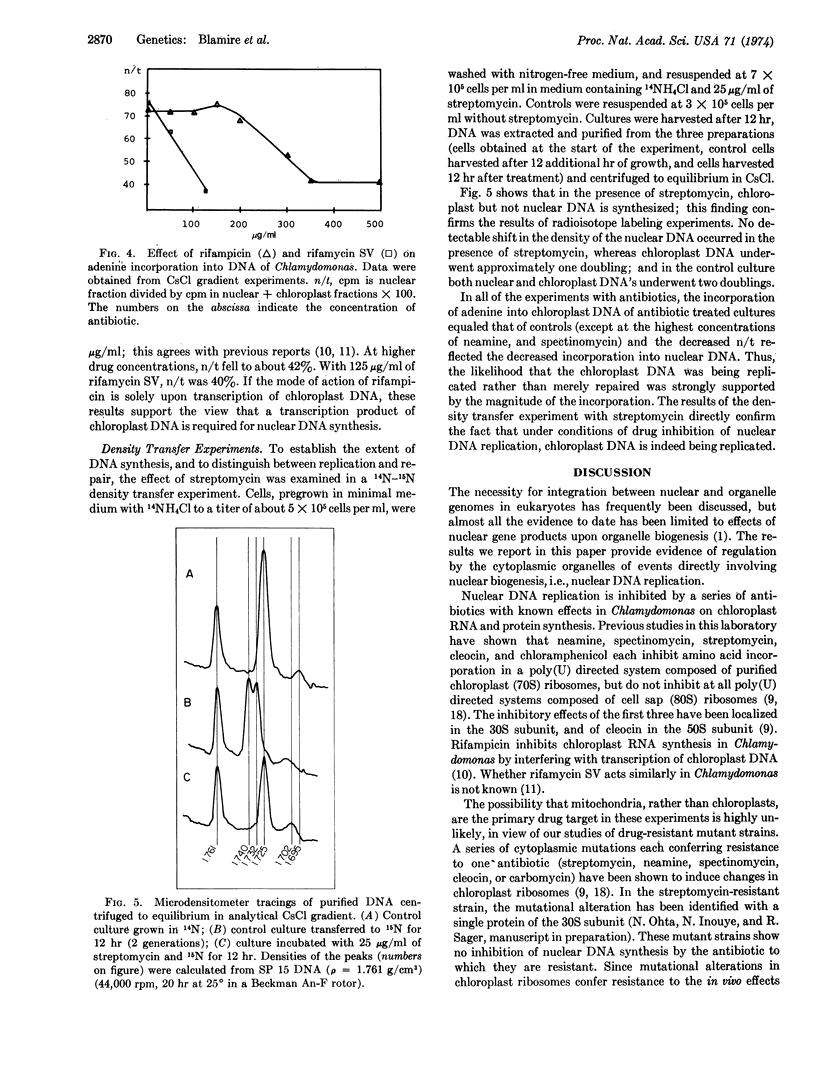

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barath Z., Küntzel H. Cooperation of mitochondrial and nuclear genes specifying the mitochondrial genetic apparatus in Neurospora crassa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1371–1374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang K. S., Sueoka N. Replication of chloroplast DNA in Chlamydomonas reinhardi during vegetative cell cycle: its mode and regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1506–1513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman L. I., Goldring E. S., Marmur J. Preferential synthesis of yeast mitochondrial DNA in the absence of protein synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1969 Dec 28;46(3):367–376. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90182-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoober J. K., Stegeman W. J. Control of the synthesis of a major polypeptide of chloroplast membranes in Chlamydomonas reinhardi. J Cell Biol. 1973 Jan;56(1):1–12. doi: 10.1083/jcb.56.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meselson M., Stahl F. W., Vinograd J. EQUILIBRIUM SEDIMENTATION OF MACROMOLECULES IN DENSITY GRADIENTS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1957 Jul 15;43(7):581–588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.43.7.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman P. S., Mahler H. R. Molecular consequences of ethidium bromide mutagenesis. Nat New Biol. 1971 May 5;231(18):12–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pica-Mattoccia L., Attardi G. Expression of the mitochondrial genome in HeLa cells. IX. Replication of mitochondrial DNA in relationship to cell cycle in HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 Mar 14;64(2):465–484. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90511-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riva S., Silvestri L. G. Rifamycins: a general view. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1972;26:199–224. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.26.100172.001215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAGER R., GRANICK S. Nutritional studies with Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1953 Oct 14;56(5):831–838. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1953.tb30261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlanger G., Sager R. Localization of five antibiotic resistances at the subunit level in chloroplast ribosomes of Chlamydomonas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1715–1719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlanger G., Sager R., Ramanis Z. Mutation of a cytoplasmic gene in Chlamydomonas alters chlorplast ribosome function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3551–3555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schor S., Siekevitz P., Palade G. E. Cyclic Changes in Thylakoid Membranes of Synchronized Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 May;66(1):174–180. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.1.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D., Tauro P., Schweizer E., Halvorson H. O. The replication of mitochondrial DNA during the cell cycle in Saccharomyces lactis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):936–942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surzycki S. J. Genetic functions of the chloroplast of Chlamydomonas reinhardi: effect of rifampin on chloroplast DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1327–1334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swinton D. C., Hanawalt P. C. In vivo specific labeling of Chlamydomonas chloroplast DNA. J Cell Biol. 1972 Sep;54(3):592–597. doi: 10.1083/jcb.54.3.592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weislogel P. O., Butow R. A. Low temperature and chloramphenicol induction of respiratory deficiency in a cold-sensitive mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):52–58. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R., Sager R. Denaturation and the renaturation kinetics of chloroplast DNA from Chlamydomonas reinhardi. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jun 14;58(2):611–622. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90375-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson D. H., Maroudas N. G., Wilkie D. Induction of the cytoplasmic petite mutation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by the antibacterial antibiotics erythromycin and chloramphenicol. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;111(3):209–223. doi: 10.1007/BF00433106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


