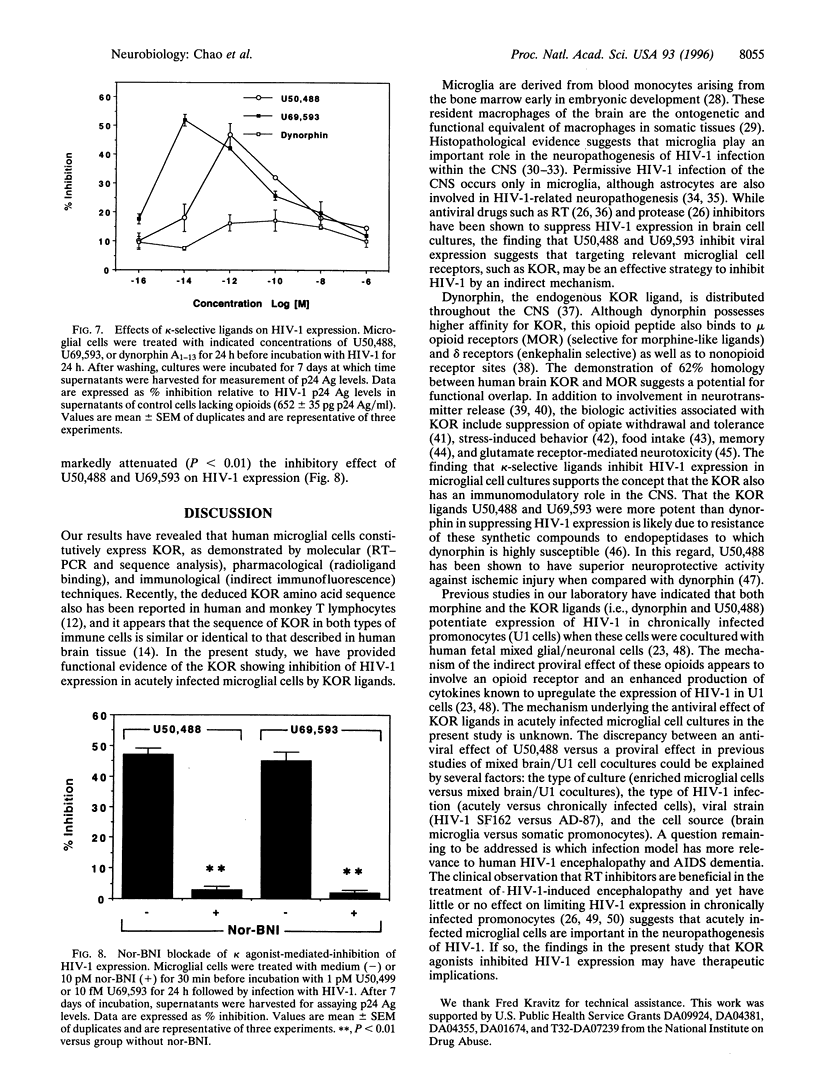
Abstract
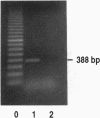
Microglial cells, the resident macrophages of the brain, play an important role in the neuropathogenesis of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1), and recent studies suggest that opioid peptides regulate the function of macrophages from somatic tissues. We report herein the presence of kappa opioid receptors (KORs) in human fetal microglia and inhibition of HIV-1 expression in acutely infected microglial cell cultures treated with KOR ligands. Using reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and sequencing analyses, we found that mRNA for the KOR was constitutively expressed in microglia and determined that the nucleotide sequence of the open reading frame was identical to that of the human brain KOR gene. The expression of KOR in microglial cells was confirmed by membrane binding of [3H]U69,593, a kappa-selective ligand, and by indirect immunofluorescence. Treatment of microglial cell cultures with U50,488 or U69,593 resulted in a dose-dependent inhibition of expression of the monocytotropic HIV-1 SF162 strain. This antiviral effect of the kappa ligands was blocked by the specific KOR antagonist, nor-binaltrophimine. These findings suggest that kappa opioid agonists have immunomodulatory activity in the brain, and that these compounds could have potential in the treatment of HIV-1-associated encephalopathy.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arvidsson U., Riedl M., Chakrabarti S., Vulchanova L., Lee J. H., Nakano A. H., Lin X., Loh H. H., Law P. Y., Wessendorf M. W. The kappa-opioid receptor is primarily postsynaptic: combined immunohistochemical localization of the receptor and endogenous opioids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 23;92(11):5062–5066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.11.5062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwood W. J., Berger J. R., Kaderman R., Tornatore C. S., Major E. O. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection of the brain. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1993 Oct;6(4):339–366. doi: 10.1128/cmr.6.4.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barg J., Belcheva M. M., Rowiński J., Coscia C. J. kappa-Opioid agonist modulation of [3H]thymidine incorporation into DNA: evidence for the involvement of pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein-coupled phosphoinositide turnover. J Neurochem. 1993 Apr;60(4):1505–1511. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03314.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskin D. S., Widmayer M. A., Browning J. L., Heizer M. L., Schmidt W. K. Evaluation of delayed treatment of focal cerebral ischemia with three selective kappa-opioid agonists in cats. Stroke. 1994 Oct;25(10):2047–2054. doi: 10.1161/01.str.25.10.2047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidlack J. M., Saripalli L. D., Lawrence D. M. kappa-Opioid binding sites on a murine lymphoma cell line. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Nov 2;227(3):257–265. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(92)90003-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroleo M. C., Arbitrio M., Melchiorri D., Nisticò G. A reappraisal of the role of the various opioid receptor subtypes in cell-mediated immunity. Neuroimmunomodulation. 1994 Mar-Apr;1(2):141–147. doi: 10.1159/000097148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr D. J., DeCosta B. R., Kim C. H., Jacobson A. E., Guarcello V., Rice K. C., Blalock J. E. Opioid receptors on cells of the immune system: evidence for delta- and kappa-classes. J Endocrinol. 1989 Jul;122(1):161–168. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1220161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr D. J., Serou M. Exogenous and endogenous opioids as biological response modifiers. Immunopharmacology. 1995 Nov;31(1):59–71. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(95)00033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao C. C., Gekker G., Hu S., Peterson P. K. Human microglial cell defense against Toxoplasma gondii. The role of cytokines. J Immunol. 1994 Feb 1;152(3):1246–1252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao C. C., Gekker G., Hu S., Sheng W. S., Portoghese P. S., Peterson P. K. Upregulation of HIV-1 expression in cocultures of chronically infected promonocytes and human brain cells by dynorphin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1995 Aug 25;50(5):715–722. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(95)00176-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang L. F., Chuang T. K., Killam K. F., Jr, Qiu Q., Wang X. R., Lin J. J., Kung H. F., Sheng W., Chao C., Yu L. Expression of kappa opioid receptors in human and monkey lymphocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Apr 26;209(3):1003–1010. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson D. W., Mattiace L. A., Kure K., Hutchins K., Lyman W. D., Brosnan C. F. Microglia in human disease, with an emphasis on acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Lab Invest. 1991 Feb;64(2):135–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson P. S., Hansson E., Rönnbäck L. Delta and kappa opiate receptors in primary astroglial cultures from rat cerebral cortex. Neurochem Res. 1990 Nov;15(11):1123–1126. doi: 10.1007/BF01101714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geleziunas R., Arts E. J., Boulerice F., Goldman H., Wainberg M. A. Effect of 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication in human fetal brain macrophages. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Jun;37(6):1305–1312. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.6.1305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gendelman H. E., Lipton S. A., Tardieu M., Bukrinsky M. I., Nottet H. S. The neuropathogenesis of HIV-1 infection. J Leukoc Biol. 1994 Sep;56(3):389–398. doi: 10.1002/jlb.56.3.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian D. Ameboid microglia as effectors of inflammation in the central nervous system. J Neurosci Res. 1987;18(1):155-71, 132-3. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490180123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh J., Ukai M., Kameyama T. Dynorphin A-(1-13) potently prevents memory dysfunctions induced by transient cerebral ischemia in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Mar 30;234(1):9–15. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90699-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackisch R., Hotz H., Hertting G. No evidence for presynaptic opioid receptors on cholinergic, but presence of kappa-receptors on dopaminergic neurons in the rabbit caudate nucleus: involvement of endogenous opioids. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1993 Sep;348(3):234–241. doi: 10.1007/BF00169150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S., Gendelman H. E., Orenstein J. M., Dal Canto M. C., Pezeshkpour G. H., Yungbluth M., Janotta F., Aksamit A., Martin M. A., Fauci A. S. Detection of AIDS virus in macrophages in brain tissue from AIDS patients with encephalopathy. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1089–1093. doi: 10.1126/science.3016903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. D., Wilding J. P., al-Dokhayel A. A., Bohuon C., Comoy E., Gilbey S. G., Bloom S. R. A role for neuropeptide-Y, dynorphin, and noradrenaline in the central control of food intake after food deprivation. Endocrinology. 1993 Jul;133(1):29–32. doi: 10.1210/endo.133.1.8100519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence D. M., el-Hamouly W., Archer S., Leary J. F., Bidlack J. M. Identification of kappa opioid receptors in the immune system by indirect immunofluorescence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 14;92(4):1062–1066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.4.1062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., Hatch W. C., Liu W., Kress Y., Lyman W. D., Dickson D. W. Productive infection of human fetal microglia by HIV-1. Am J Pathol. 1993 Oct;143(4):1032–1039. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maderspach K., Solomonia R. Glial and neuronal opioid receptors: apparent positive cooperativity observed in intact cultured cells. Brain Res. 1988 Feb 16;441(1-2):41–47. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91381-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour A., Khachaturian H., Lewis M. E., Akil H., Watson S. J. Autoradiographic differentiation of mu, delta, and kappa opioid receptors in the rat forebrain and midbrain. J Neurosci. 1987 Aug;7(8):2445–2464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansson E., Bare L., Yang D. Isolation of a human kappa opioid receptor cDNA from placenta. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Aug 15;202(3):1431–1437. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabeshima T., Katoh A., Wada M., Kameyama T. Stress-induced changes in brain Met-enkephalin, Leu-enkephalin and dynorphin concentrations. Life Sci. 1992;51(3):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90077-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nottet H. S., Jett M., Flanagan C. R., Zhai Q. H., Persidsky Y., Rizzino A., Bernton E. W., Genis P., Baldwin T., Schwartz J. A regulatory role for astrocytes in HIV-1 encephalitis. An overexpression of eicosanoids, platelet-activating factor, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha by activated HIV-1-infected monocytes is attenuated by primary human astrocytes. J Immunol. 1995 Apr 1;154(7):3567–3581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson G. A., Olson R. D., Kastin A. J. Endogenous opiates: 1988. Peptides. 1989 Nov-Dec;10(6):1253–1280. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(89)90020-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Gekker G., Hu S., Anderson W. R., Kravitz F., Portoghese P. S., Balfour H. H., Jr, Chao C. C. Morphine amplifies HIV-1 expression in chronically infected promonocytes cocultured with human brain cells. J Neuroimmunol. 1994 Mar;50(2):167–175. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(94)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Gekker G., Hu S., Chao C. C. Anti-human immunodeficiency virus type 1 activities of U-90152 and U-75875 in human brain cell cultures. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994 Oct;38(10):2465–2468. doi: 10.1128/aac.38.10.2465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli G., Orenstein J. M., Kinter A., Folks T. M., Fauci A. S. Interferon-alpha but not AZT suppresses HIV expression in chronically infected cell lines. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):575–577. doi: 10.1126/science.2470148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radulović J., Miljević C., Djergović D., Vujić V., Antić J., von Hörsten S., Janković B. D. Opioid receptor-mediated suppression of humoral immune response in vivo and in vitro: involvement of kappa opioid receptors. J Neuroimmunol. 1995 Mar;57(1-2):55–62. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(94)00161-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S., Loh H. H., Lee N. M. Dynorphin blocks opioid inhibition of macrophage-colony stimulating factor-induced proliferation of bone marrow cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Sep 24;202(3):355–359. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90278-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt P., Schröder H., Maderspach K., Staak M. Immunohistochemical localization of kappa opioid receptors in the human frontal cortex. Brain Res. 1994 Aug 22;654(2):223–233. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)90483-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipp M. A., Stefano G. B., D'Adamio L., Switzer S. N., Howard F. D., Sinisterra J., Scharrer B., Reinherz E. L. Downregulation of enkephalin-mediated inflammatory responses by CD10/neutral endopeptidase 24.11. Nature. 1990 Sep 27;347(6291):394–396. doi: 10.1038/347394a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skilling S. R., Sun X., Kurtz H. J., Larson A. A. Selective potentiation of NMDA-induced activity and release of excitatory amino acids by dynorphin: possible roles in paralysis and neurotoxicity. Brain Res. 1992 Mar 20;575(2):272–278. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90090-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer D. C., Price R. W. Human immunodeficiency virus and the central nervous system. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1992;46:655–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.46.100192.003255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suarez-Roca H., Maixner W. Activation of kappa opioid receptors by U50488H and morphine enhances the release of substance P from rat trigeminal nucleus slices. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Feb;264(2):648–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo I., Rojavin M., Bussiere J. L., Eisenstein T. K., Adler M. W., Rogers T. J. Suppression of peritoneal macrophage phagocytosis of Candida albicans by opioids. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Nov;267(2):703–706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemori A. E., Loh H. H., Lee N. M. Suppression by dynorphin A and [des-Tyr1]dynorphin A peptides of the expression of opiate withdrawal and tolerance in morphine-dependent mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Jul;266(1):121–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub D. D., Eisenstein T. K., Geller E. B., Adler M. W., Rogers T. J. Immunomodulatory activity of mu- and kappa-selective opioid agonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):360–364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornatore C., Meyers K., Atwood W., Conant K., Major E. Temporal patterns of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transcripts in human fetal astrocytes. J Virol. 1994 Jan;68(1):93–102. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.1.93-102.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef J., Gekker G., Erice A., Peterson P. K., Balfour H. H. Quantitative assay for testing susceptibility of HIV isolates to zidovudine and sCD4 (178)-PE40. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1992 Aug;11(8):715–721. doi: 10.1007/BF01989976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. J., Terman G. W., Chavkin C. Endogenous dynorphins inhibit excitatory neurotransmission and block LTP induction in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993 Jun 3;363(6428):451–454. doi: 10.1038/363451a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. B., Johnson P. S., Wu J. M., Wang W. F., Uhl G. R. Human kappa opiate receptor second extracellular loop elevates dynorphin's affinity for human mu/kappa chimeras. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 21;269(42):25966–25969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins B. A., Dorn H. H., Kelly W. B., Armstrong R. C., Potts B. J., Michaels F., Kufta C. V., Dubois-Dalcq M. Specific tropism of HIV-1 for microglial cells in primary human brain cultures. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):549–553. doi: 10.1126/science.2200125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]