Abstract
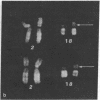
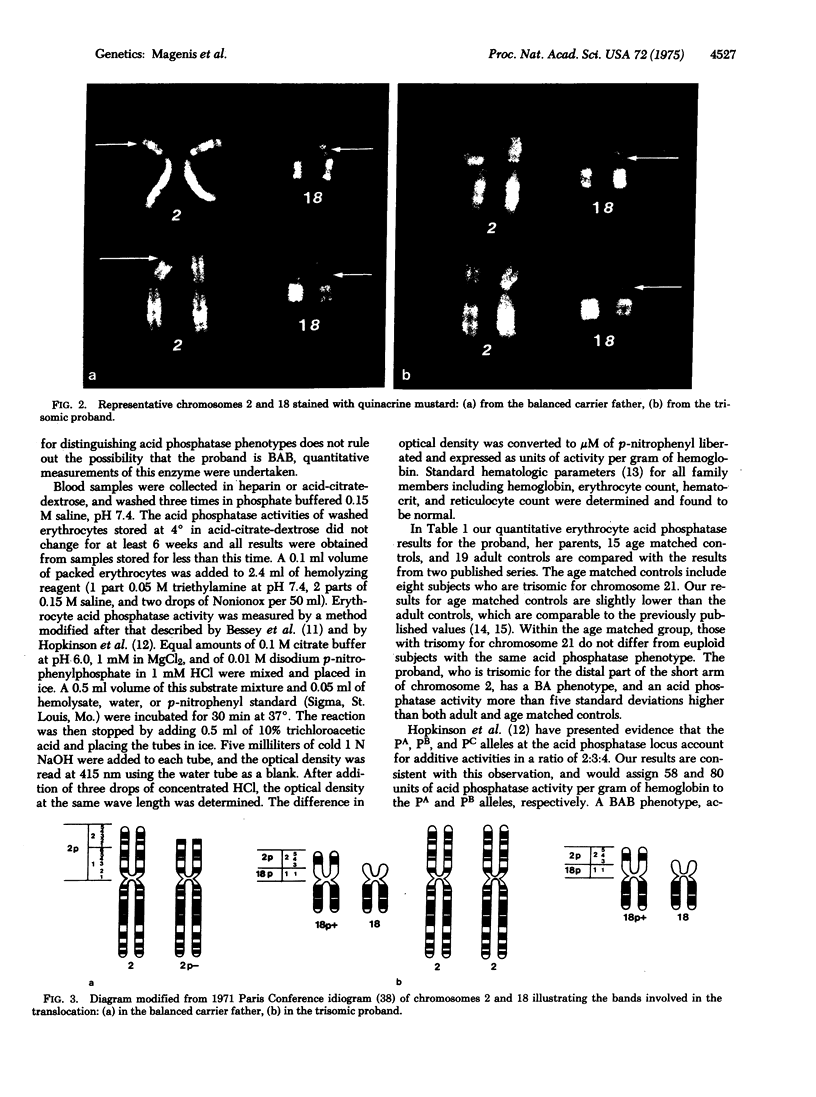
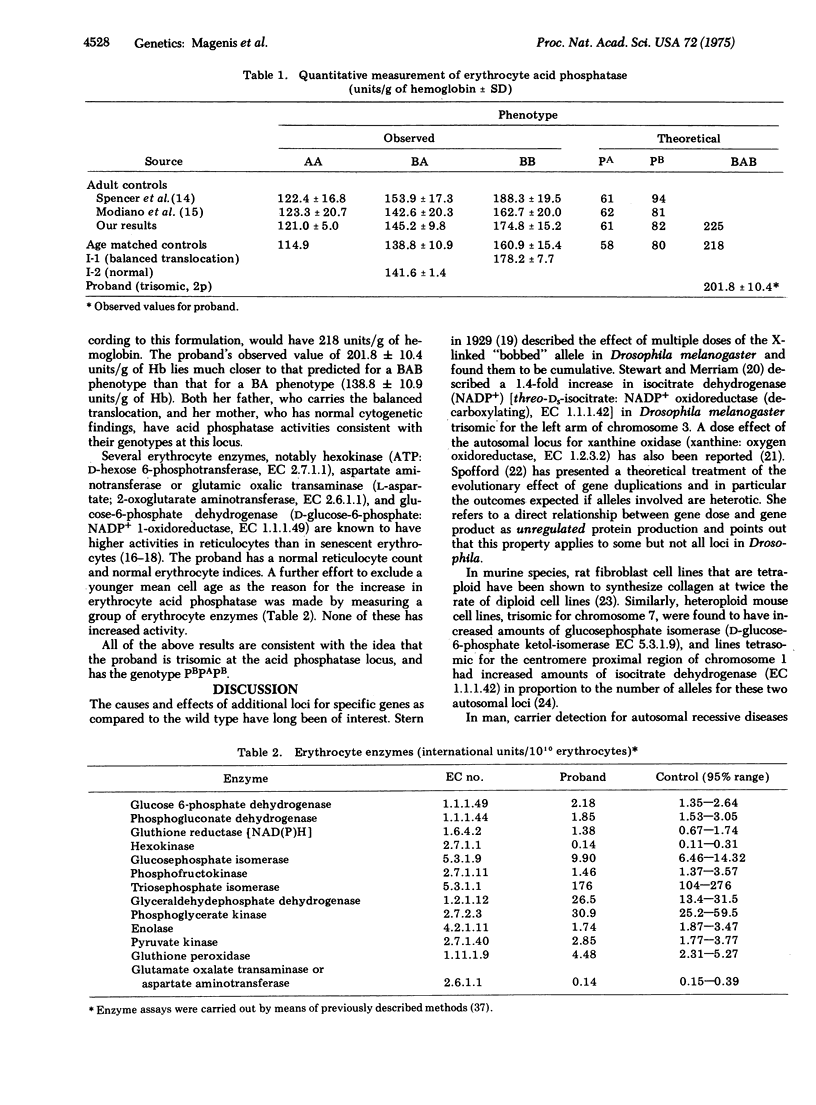
A child, trisomic for the distal short arm of chromosome 2 due to a familial 2/18 translocation, has elevated levels of activity of erythrocyte acid phosphatase [orthophosphoric-monoester phosphohydrolase (acid optimum), 3.1.3.2] Ferguson-Smith et al. [(1973) Nature New Biol. 243, 271-274] previously had found decreased levels of activity and loss of expression of an erythrocyte acid phosphatase allele in a subject who lacked one of the two homologous regions containing the distal three bands of chromosome 2. They suggested that the locus for erythrocyte acid phosphatase is located on that segment. Our findings provide further evidence for this assignment and also suggest an in vivo gene dosage effect of this autosomal locus, which depends on both the type and number of alleles present.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAIKIE A. G., LODER P. B., DEGRUCHY G. C., PITT D. B. PHOSPHOHEXOKINASE ACTIVITY OF ERYTHROCYTES IN MONGOLISM: ANOTHER POSSIBLE MARKER FOR CHROMOSOME 21. Lancet. 1965 Feb 20;1(7382):412–414. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)90007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersson T., Lomakka G., Zech L. The 24 fluorescence patterns of the human metaphase chromosomes - distinguishing characters and variability. Hereditas. 1972;67(1):89–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1971.tb02363.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber R. A. Gene dosage and the expression of electrophoretic patterns in heteroploid mouse cell lines. Genetics. 1973 Jul;74(3):521–531. doi: 10.1093/genetics/74.3.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson-Smith M. A., Newman B. F., Ellis P. M., Thomson D. M., Riley I. D. Assignment by deletion of human red cell acid phosphatase gene locus to the short arm of chromosome 2. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jun 27;243(130):271–274. doi: 10.1038/newbio243271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankenburg W. K., Dodds J. B. The Denver developmental screening test. J Pediatr. 1967 Aug;71(2):181–191. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(67)80070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOPKINSON D. A., SPENCER N., HARRIS H. GENETICAL STUDIES ON HUMAN RED CELL ACID PHOSPHATASE. Am J Hum Genet. 1964 Mar;16:141–154. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karp G. W., Jr, Sutton H. E. Some new phenotypes of human red cell acid phosphatase. Am J Hum Genet. 1967 Jan;19(1):54–62. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAI L., NEVO S., STEINBERG A. G. ACID PHOSPHATASES OF HUMAN RED CELLS: PREDICTED PHENOTYPE CONFORMS TO A GENETIC HYPOTHESIS. Science. 1964 Sep 11;145(3637):1187–1188. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3637.1187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORHEAD P. S., NOWELL P. C., MELLMAN W. J., BATTIPS D. M., HUNGERFORD D. A. Chromosome preparations of leukocytes cultured from human peripheral blood. Exp Cell Res. 1960 Sep;20:613–616. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(60)90138-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mace M. A., Noades J., Robson E. B., Hultén M., Lindsten J., Polani P. E., Jacobs P. A., Buckton K. E. Segregation of ACP1 and MNSs in families with structural rearrangements involving chromosome 2. Ann Hum Genet. 1975 May;38(4):479–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1975.tb00637.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks P. A., Johnson A. B., Hirschberg E. EFFECT OF AGE ON THE ENZYME ACTIVITY IN ERYTHROCYTES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Jun;44(6):529–536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.6.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottolenghi S., Lanyon W. G., Paul J., Williamson R., Weatherall D. J., Clegg J. B., Pritchard J., Pootrakul S., Boon W. H. The severe form of alpha thalassaemia is caused by a haemoglobin gene deletion. Nature. 1974 Oct 4;251(5474):389–392. doi: 10.1038/251389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantelakis S. N., Karaklis A. G., Alexiou D., Vardas E., Valaes T. Red cell enzymes in trisomy 21. Am J Hum Genet. 1970 Mar;22(2):184–193. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priest R. E., Priest J. H. Diploid and tetraploid clonal cells in culture: gene ploidy and synthesis of collagen. Biochem Genet. 1969 Aug;3(4):371–382. doi: 10.1007/BF00485721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SASS M. D., VORSANGER E., SPEAR P. W. ENZYME ACTIVITY AS AN INDICATOR OF RED CELL AGE. Clin Chim Acta. 1964 Jul;10:21–26. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(64)90210-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPENCER N., HOPKINSON D. A., HARRIS H. QUANTITATIVE DIFFERENCES AND GENE DOSAGE IN THE HUMAN RED CELL ACID PHOSPHATASE POLYMORPHISM. Nature. 1964 Jan 18;201:299–300. doi: 10.1038/201299a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sichitiu S., Sinet P. M., Lejeune J., Frézal J. Surdosage de la forme dimérique de l'indophénoloxydase dans la trisomie 21, secondaire au surdosage génique. Humangenetik. 1974 Jun 26;23(1):65–72. doi: 10.1007/BF00295684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll C., Messer J., Vors J. Translocation t(2; 14) équilibrée chez une mère et trisome partielle d'une partie du bras court d'un chromosome no 2 chez deux de ses enfants. Ann Genet. 1974 Sep;17(3):193–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Dozy A., Kan Y. W., Varmus H. E., Lie-Injo L. E., Ganesan J., Todd D. Genetic lesion in homozygous alpha thalassaemia (hydrops fetalis). Nature. 1974 Oct 4;251(5474):392–393. doi: 10.1038/251392a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine W. N., Oski F. A., Paglia D. E., Baughan M. A., Schneider A. S., Naiman J. L. Hereditary hemolytic anemia with hexokinase deficiency. Role of hexokinase in erythrocyte aging. N Engl J Med. 1967 Jan 5;276(1):1–11. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196701052760101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]