Abstract
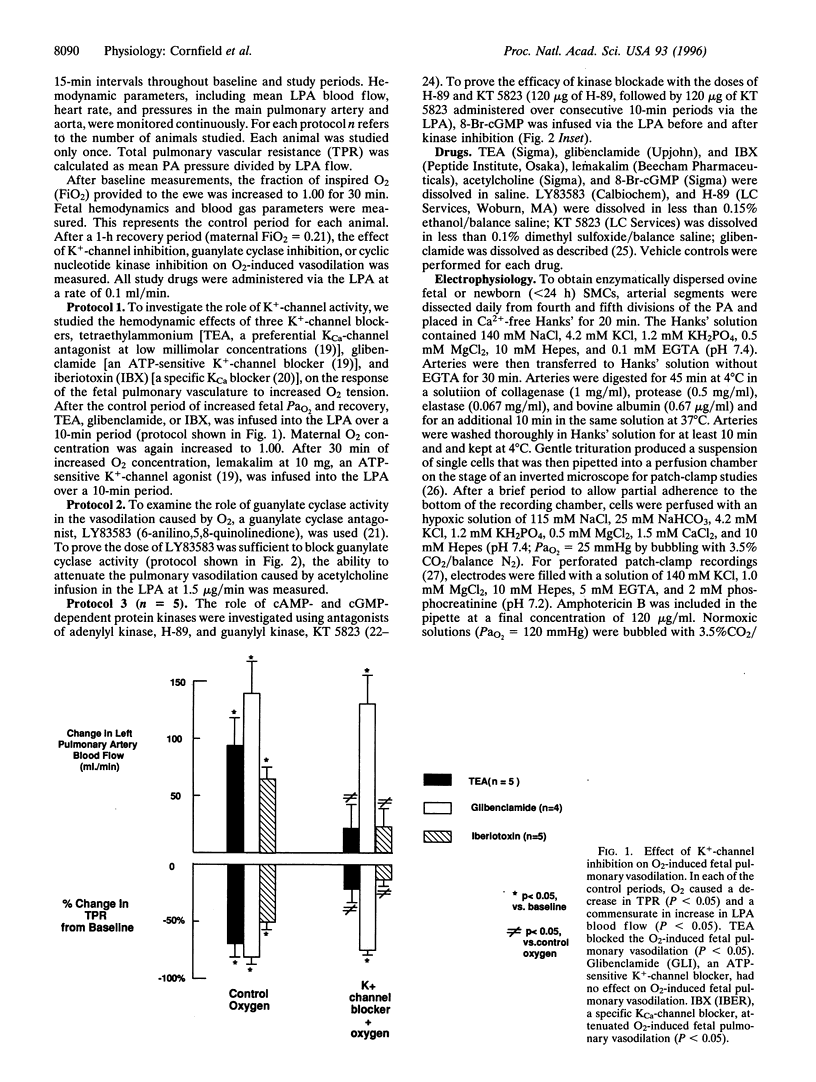
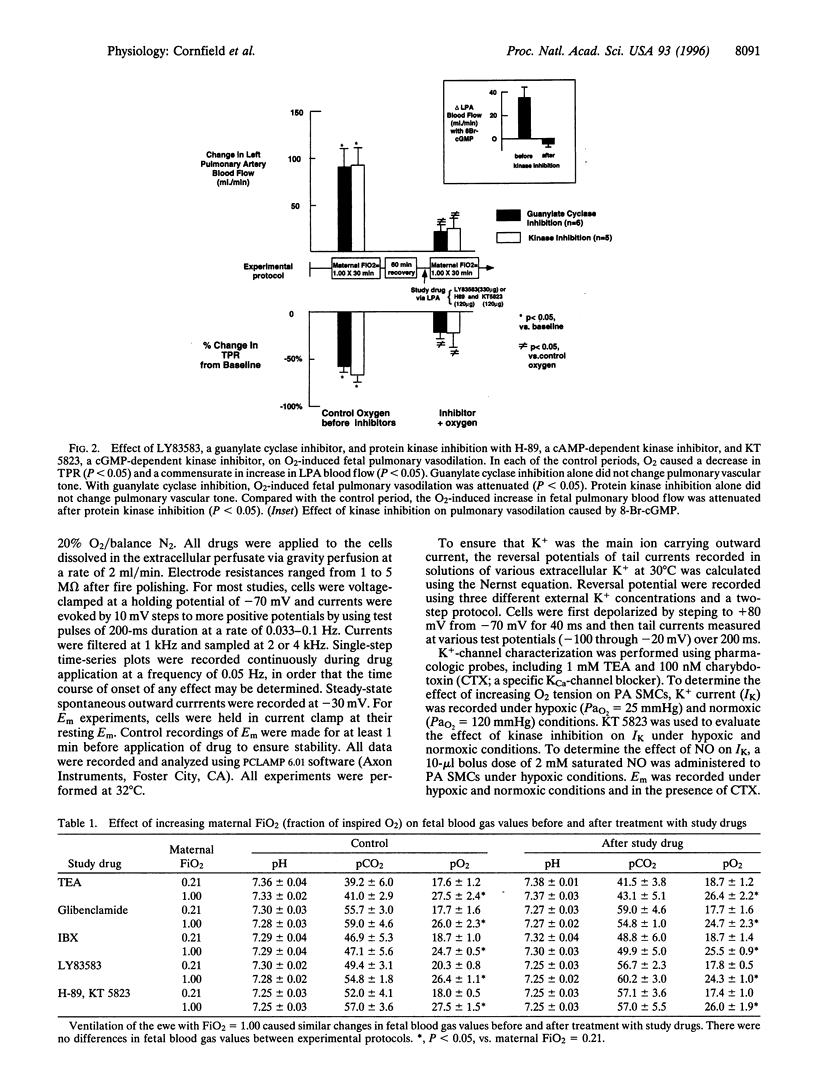
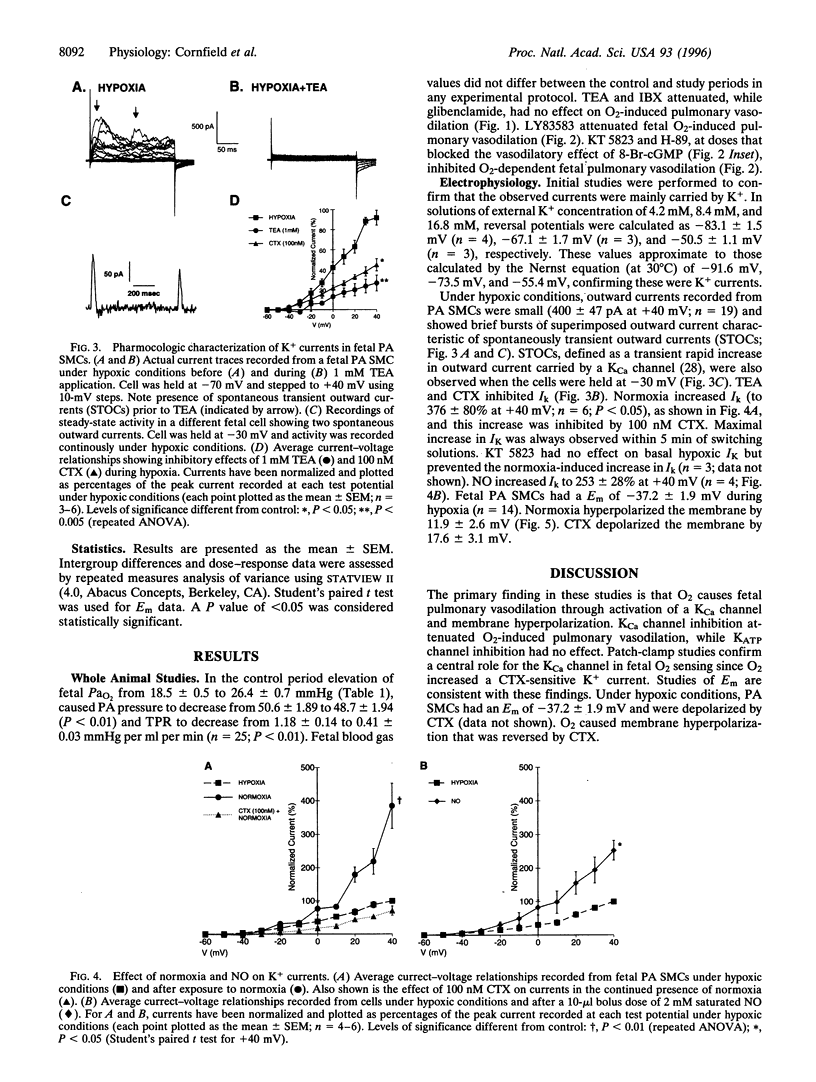
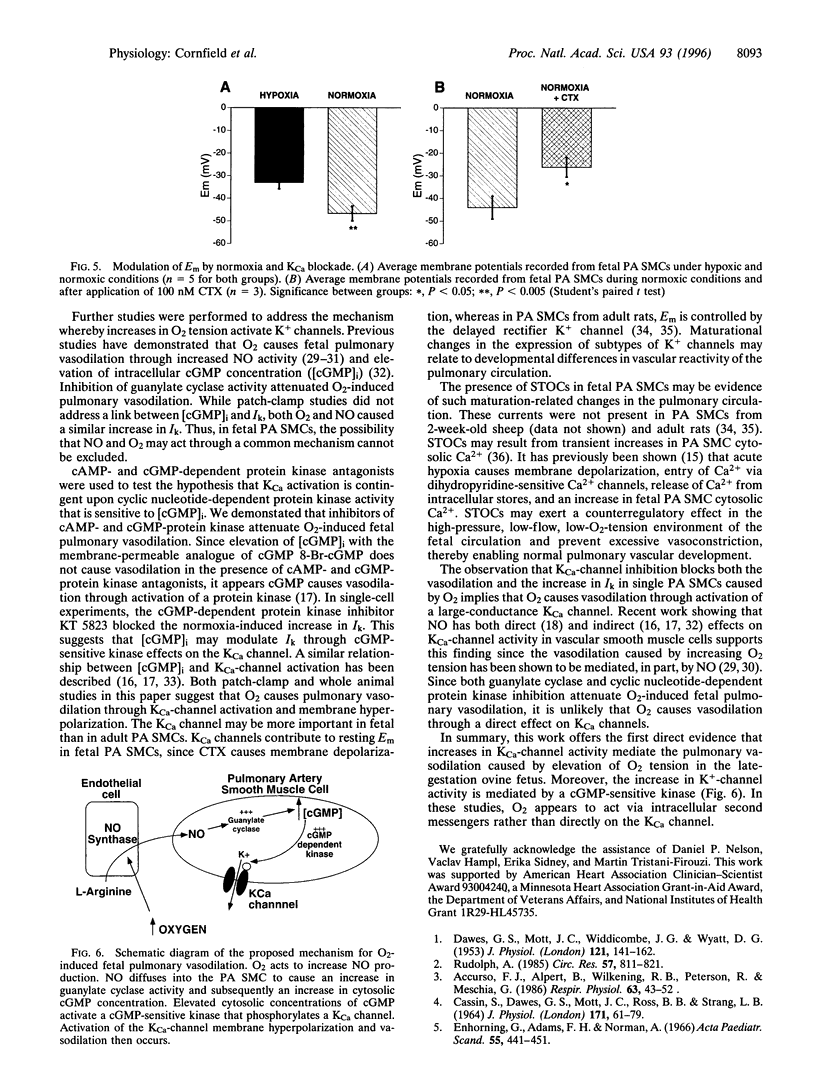
At birth, pulmonary vasodilation occurs as air-breathing life begins. The mechanism of O2-induced pulmonary vasodilation is unknown. We proposed that O2 causes fetal pulmonary vasodilation through activation of a calcium-dependent potassium channel (KCa) via a cyclic nucleotide-dependent kinase. We tested this hypothesis in hemodynamic studies in acutely prepared fetal lambs and in patch-clamp studies on resistance fetal pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. Fetal O2 tension (PaO2) was increased by ventilating the ewe with 100% O2, causing fetal total pulmonary resistance to decrease from 1.18 +/- 0.14 to 0.41 +/- 0.03 mmHg per ml per min. Tetraethylammonium and iberiotoxin, preferential KCa-channel inhibitors, attenuated O2-induced fetal pulmonary vasodilation, while glibenclamide, an ATP-sensitive K+-channel antagonist, had no effect. Treatment with either a guanylate cyclase antagonist (LY83583) or cyclic nucleotide-dependent kinase inhibitors (H-89 and KT 5823) significantly attenuated O2-induced fetal pulmonary vasodilation. Under hypoxic conditions (PaO2 = 25 mmHg), whole-cell K+-channel currents (Ik) were small and were inhibited by 1 mM tetraethylammonium or 100 nM charybdotoxin (CTX; a specific KCa-channel blocker). Normoxia (PaO2 = 120 mmHg) increased Ik by more than 300%, and this was reversed by 100 nM CTX. Nitric oxide also increased Ik. Resting membrane potential was -37.2 +/- 1.9 mV and cells depolarized on exposure to CTX, while hyperpolarizing in normoxia. We conclude that O2 causes fetal pulmonary vasodilation by stimulating a cyclic nucleotide-dependent kinase, resulting in KCa-channel activation, membrane hyperpolarization, and vasodilation.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abman S. H., Chatfield B. A., Hall S. L., McMurtry I. F. Role of endothelium-derived relaxing factor during transition of pulmonary circulation at birth. Am J Physiol. 1990 Dec;259(6 Pt 2):H1921–H1927. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.259.6.H1921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Accurso F. J., Alpert B., Wilkening R. B., Petersen R. G., Meschia G. Time-dependent response of fetal pulmonary blood flow to an increase in fetal oxygen tension. Respir Physiol. 1986 Jan;63(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(86)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer S. L., Huang J. M., Hampl V., Nelson D. P., Shultz P. J., Weir E. K. Nitric oxide and cGMP cause vasorelaxation by activation of a charybdotoxin-sensitive K channel by cGMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 2;91(16):7583–7587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.16.7583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer S. L., Huang J., Henry T., Peterson D., Weir E. K. A redox-based O2 sensor in rat pulmonary vasculature. Circ Res. 1993 Dec;73(6):1100–1112. doi: 10.1161/01.res.73.6.1100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Bolton T. B. Spontaneous transient outward currents in single visceral and vascular smooth muscle cells of the rabbit. J Physiol. 1986 Dec;381:385–406. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolotina V. M., Najibi S., Palacino J. J., Pagano P. J., Cohen R. A. Nitric oxide directly activates calcium-dependent potassium channels in vascular smooth muscle. Nature. 1994 Apr 28;368(6474):850–853. doi: 10.1038/368850a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASSIN S., DAWES G. S., MOTT J. C., ROSS B. B., STRANG L. B. THE VASCULAR RESISTANCE OF THE FOETAL AND NEWLY VENTILATED LUNG OF THE LAMB. J Physiol. 1964 May;171:61–79. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook N. S. The pharmacology of potassium channels and their therapeutic potential. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Jan;9(1):21–28. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90238-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornfield D. N., Chatfield B. A., McQueston J. A., McMurtry I. F., Abman S. H. Effects of birth-related stimuli on L-arginine-dependent pulmonary vasodilation in ovine fetus. Am J Physiol. 1992 May;262(5 Pt 2):H1474–H1481. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.262.5.H1474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornfield D. N., McQueston J. A., McMurtry I. F., Rodman D. M., Abman S. H. Role of ATP-sensitive potassium channels in ovine fetal pulmonary vascular tone. Am J Physiol. 1992 Nov;263(5 Pt 2):H1363–H1368. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.263.5.H1363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornfield D. N., Stevens T., McMurtry I. F., Abman S. H., Rodman D. M. Acute hypoxia causes membrane depolarization and calcium influx in fetal pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1994 Apr;266(4 Pt 1):L469–L475. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1994.266.4.L469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWES G. S., MOTT J. C., WIDDICOMBE J. G., WYATT D. G. Changes in the lungs of the new-born lamb. J Physiol. 1953 Jul;121(1):141–162. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enhörning G., Adams F. H., Norman A. Effect of lung expansion on the fetal lamb circulation. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1966 Sep;55(5):441–451. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1966.tb15234.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galvez A., Gimenez-Gallego G., Reuben J. P., Roy-Contancin L., Feigenbaum P., Kaczorowski G. J., Garcia M. L. Purification and characterization of a unique, potent, peptidyl probe for the high conductance calcium-activated potassium channel from venom of the scorpion Buthus tamulus. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11083–11090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasunuma K., Rodman D. M., McMurtry I. F. Effects of K+ channel blockers on vascular tone in the perfused rat lung. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Oct;144(4):884–887. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/144.4.884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito M., Karachot L. Messengers mediating long-term desensitization in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Neuroreport. 1990 Oct;1(2):129–132. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199010000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin J. G., Murthy K. S., Grider J. R., Makhlouf G. M. Activation of distinct cAMP- and cGMP-dependent pathways by relaxant agents in isolated gastric muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1993 Mar;264(3 Pt 1):G470–G477. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1993.264.3.G470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kase H., Iwahashi K., Nakanishi S., Matsuda Y., Yamada K., Takahashi M., Murakata C., Sato A., Kaneko M. K-252 compounds, novel and potent inhibitors of protein kinase C and cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jan 30;142(2):436–440. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90293-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S. A., Mathews W. R., Meisheri K. D. Role of calcium-activated K+ channels in vasodilation induced by nitroglycerine, acetylcholine and nitric oxide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Dec;267(3):1327–1335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-López J., González C., Ureña J., López-Barneo J. Low pO2 selectively inhibits K channel activity in chemoreceptor cells of the mammalian carotid body. J Gen Physiol. 1989 May;93(5):1001–1015. doi: 10.1085/jgp.93.5.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQueston J. A., Cornfield D. N., McMurtry I. F., Abman S. H. Effects of oxygen and exogenous L-arginine on EDRF activity in fetal pulmonary circulation. Am J Physiol. 1993 Mar;264(3 Pt 2):H865–H871. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1993.264.3.H865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. T., Cheng H., Rubart M., Santana L. F., Bonev A. D., Knot H. J., Lederer W. J. Relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by calcium sparks. Science. 1995 Oct 27;270(5236):633–637. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5236.633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post J. M., Hume J. R., Archer S. L., Weir E. K. Direct role for potassium channel inhibition in hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 1):C882–C890. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.4.C882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae J., Cooper K., Gates P., Watsky M. Low access resistance perforated patch recordings using amphotericin B. J Neurosci Methods. 1991 Mar;37(1):15–26. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(91)90017-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson B. E., Schubert R., Hescheler J., Nelson M. T. cGMP-dependent protein kinase activates Ca-activated K channels in cerebral artery smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jul;265(1 Pt 1):C299–C303. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.1.C299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph A. M. Distribution and regulation of blood flow in the fetal and neonatal lamb. Circ Res. 1985 Dec;57(6):811–821. doi: 10.1161/01.res.57.6.811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. J., Sawyer B. D., Truex L. L., Marshall W. S., Fleisch J. H. LY83583: an agent that lowers intracellular levels of cyclic guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Mar;232(3):764–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaul P. W., Farrar M. A., Zellers T. M. Oxygen modulates endothelium-derived relaxing factor production in fetal pulmonary arteries. Am J Physiol. 1992 Feb;262(2 Pt 2):H355–H364. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.262.2.H355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaul P. W., Wells L. B. Oxygen modulates nitric oxide production selectively in fetal pulmonary endothelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1994 Oct;11(4):432–438. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.11.4.7522486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smirnov S. V., Robertson T. P., Ward J. P., Aaronson P. I. Chronic hypoxia is associated with reduced delayed rectifier K+ current in rat pulmonary artery muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jan;266(1 Pt 2):H365–H370. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1994.266.1.H365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi J., Furukawa K. I., Shigekawa M. Maxi K+ channels are stimulated by cyclic guanosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in canine coronary artery smooth muscle cells. Pflugers Arch. 1993 May;423(3-4):167–172. doi: 10.1007/BF00374390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiktinsky M. H., Morin F. C., 3rd Increasing oxygen tension dilates fetal pulmonary circulation via endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jul;265(1 Pt 2):H376–H380. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1993.265.1.H376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan X. J., Goldman W. F., Tod M. L., Rubin L. J., Blaustein M. P. Hypoxia reduces potassium currents in cultured rat pulmonary but not mesenteric arterial myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1993 Feb;264(2 Pt 1):L116–L123. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1993.264.2.L116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan X. J. Voltage-gated K+ currents regulate resting membrane potential and [Ca2+]i in pulmonary arterial myocytes. Circ Res. 1995 Aug;77(2):370–378. doi: 10.1161/01.res.77.2.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



