Abstract
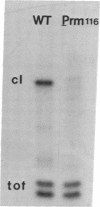
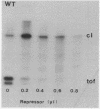
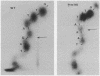
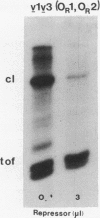
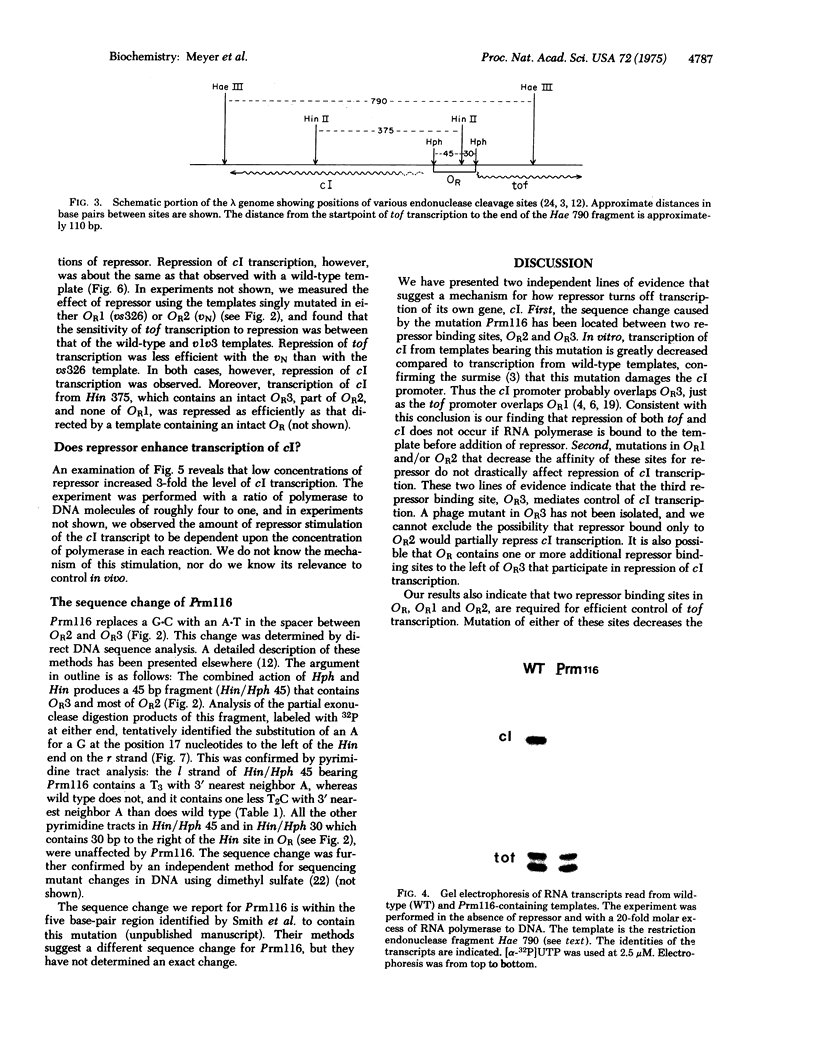
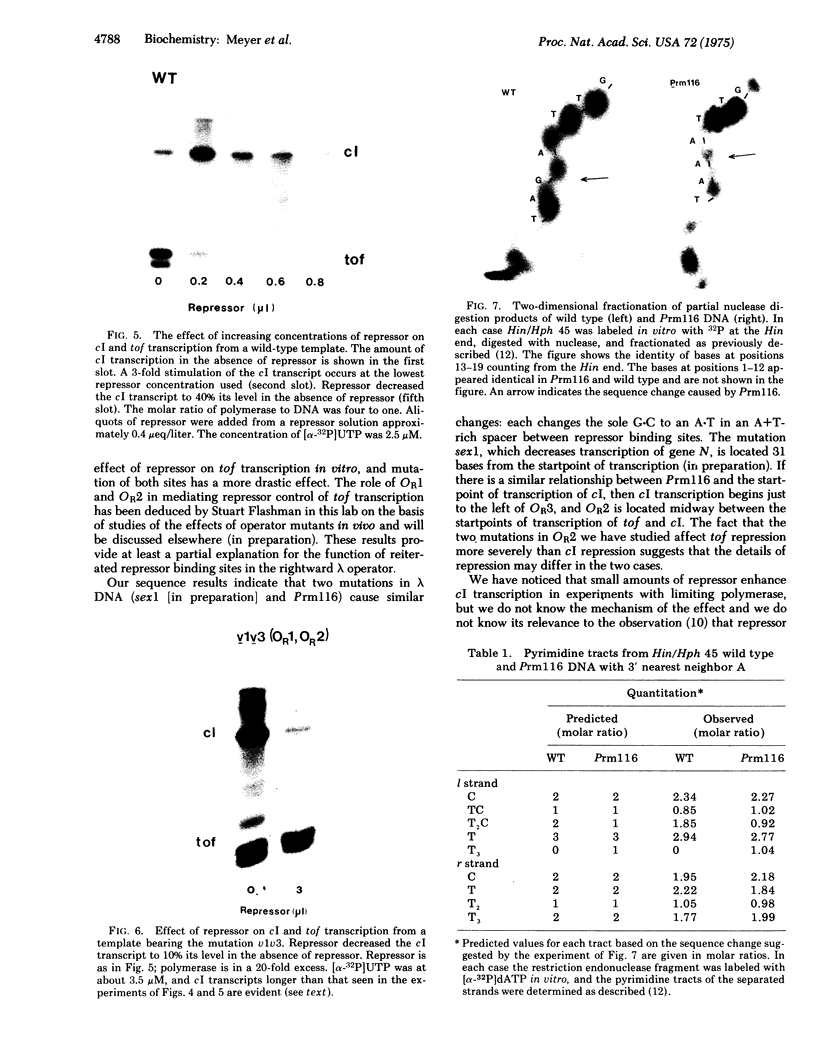
We report transcription in vitro of the lambda repressor gene, cI, using specific restriction endonuclease fragments as templates. This transcription is repressed by lambda repressor. Moreover, we report the sequence change caused by a cI promoter mutation. This change is located between two repressor binding sites in the rightward operator (OR). Transcription studies using mutant templates indicate that repressor bound to two sites in OR regulates transcription of gene tof, and repressor bound to the remaining site(s) controls transcription of cI.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allet B., Solem R. Separation and analysis of promoter sites in bacteriophage lambda DNA by specific endonucleases. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 5;85(4):475–484. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90310-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Dahlberg J. E. RNA synthesis startpoints in bacteriophage lambda: are the promoter and operator transcribed? Nat New Biol. 1972 Jun 21;237(77):227–232. doi: 10.1038/newbio237227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dottin R. P., Cutler L. S., Pearson M. L. Repression and autogenous stimulation in vitro by bacteriophage lambda repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):804–808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizels N. M. The nucleotide sequence of the lactose messenger ribonucleic acid transcribed from the UV5 promoter mutant of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3585–3589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., van deSande H. Chain length determination of small double- and single-stranded DNA molecules by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1975 Aug 26;14(17):3787–3794. doi: 10.1021/bi00688a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Ptashne M., Backman K., Kield D., Flashman S., Jeffrey A., Maurer R. Recognition sequences of repressor and polymerase in the operators of bacteriophage lambda. Cell. 1975 Jun;5(2):109–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Ptashne M., Maurer R. Control elements in the DNA of bacteriophage lambda. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:857–868. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Ptashne M. Multiple repressor binding at the operators in bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1531–1535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Ptashne M. Structure of the lambda operators. Nature. 1973 Nov 16;246(5429):133–136. doi: 10.1038/246133a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer R., Maniatis T., Ptashne M. Promoters are in the operators in phage lambda. Nature. 1974 May 17;249(454):221–223. doi: 10.1038/249221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordal G. W., Kaiser A. D. Mutations in the right operator of bacteriophage lambda: evidence for operator-promoter interpenetration. J Mol Biol. 1973 Oct 5;79(4):709–722. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Hopkins N. The operators controlled by the lambda phage repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1282–1287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichardt L. F. Control of bacteriophage lambda repressor synthesis: regulation of the maintenance pathway of the cro and cI products. J Mol Biol. 1975 Apr 5;93(2):289–309. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90133-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. W. Termination factor for RNA synthesis. Nature. 1969 Dec 20;224(5225):1168–1174. doi: 10.1038/2241168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R. A., Ptashne M. In vitro repression of RNA synthesis by purified lambda phage repressor. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 17;230(11):76–80. doi: 10.1038/newbio230076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K., Hradecna Z., Szybalski W. Asymmetric distribution of the transcribing regions on the complementary strands of coliphage lambda DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1618–1625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomizawa J., Ogawa T. Effect of ultraviolet irradiation on bacteriophage lambda immunity. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jan 28;23(2):247–263. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz A., Pirrotta V. Sequence of the PR promoter of phage lambda. Nature. 1975 Mar 13;254(5496):118–121. doi: 10.1038/254118a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen K. M., Gussin G. N. Genetic characterization of a prm- mutant of bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1973 Nov;56(1):300–312. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90308-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]