Abstract
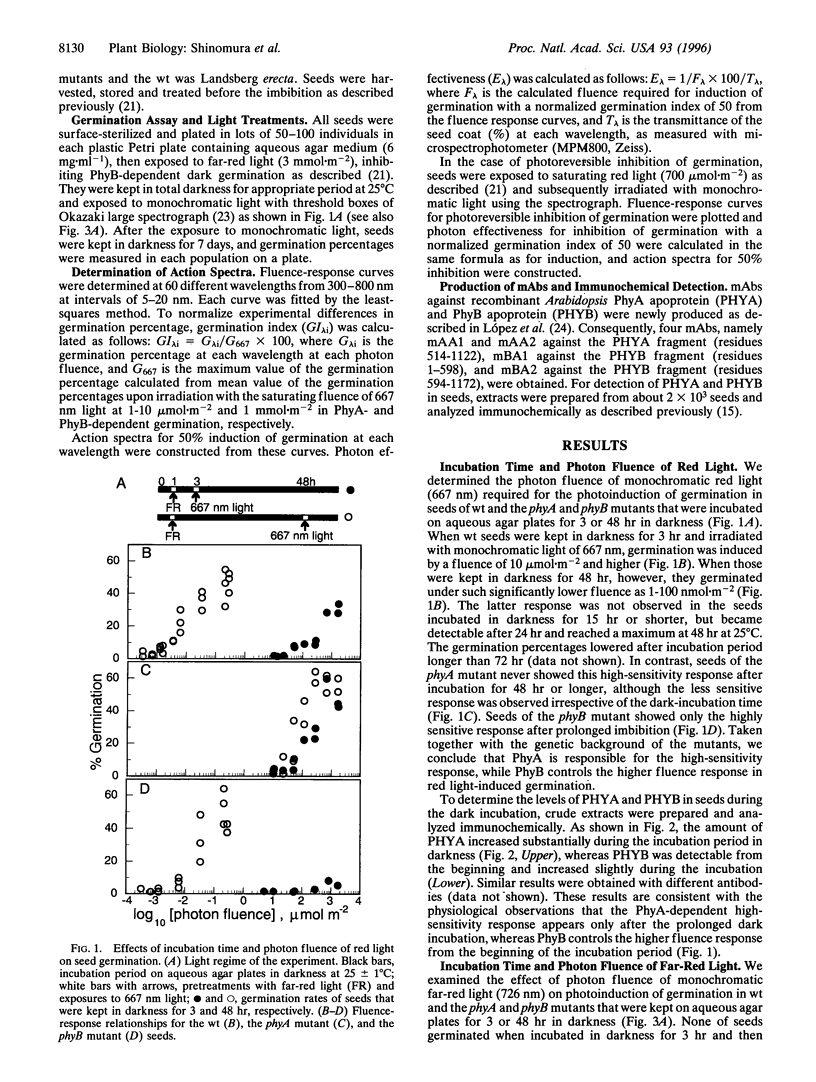
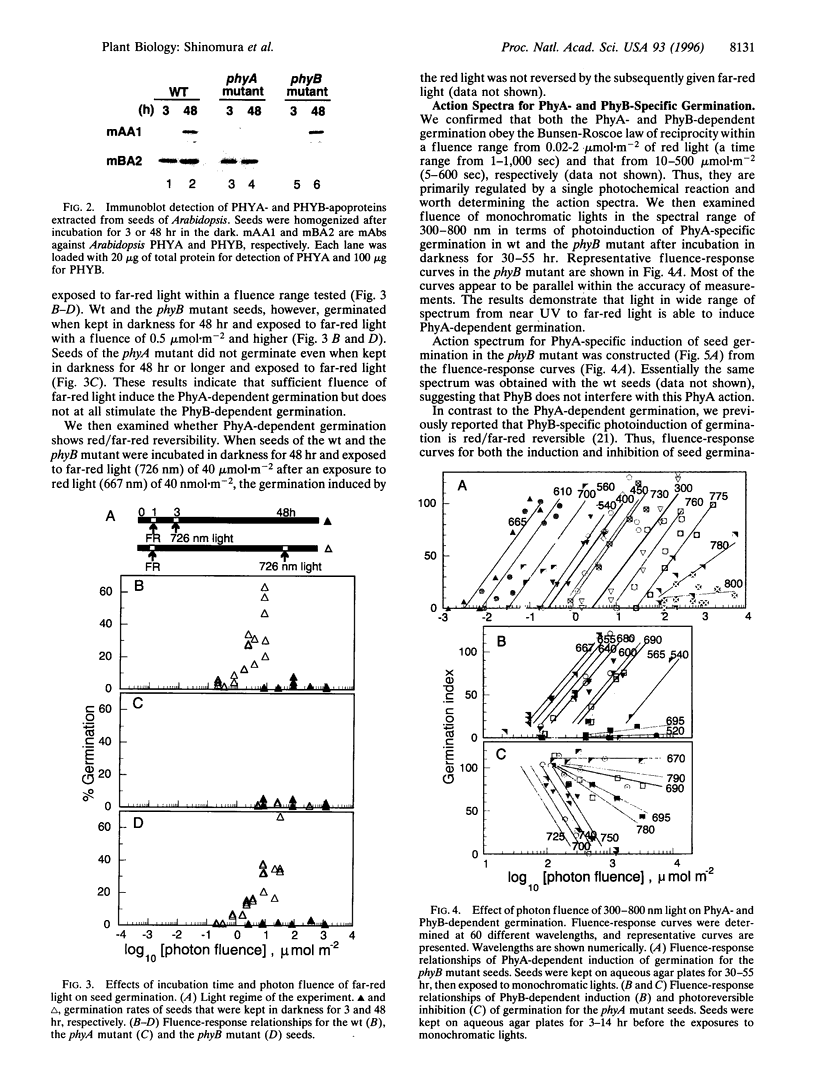
We have examined the seed germination in Arabidopsis thaliana of wild type (wt), and phytochrome A (PhyA)- and B (PhyB)-mutants in terms of incubation time and environmental light effects. Seed germination of the wt and PhyA-null mutant (phyA) was photoreversibly regulated by red and far-red lights of 10-1,000 micromol m-2 when incubated in darkness for 1-14 hr, but no germination occurred in PhyB-null mutant (phyB). When wt seeds and the phyB mutant seeds were incubated in darkness for 48 hr, they synthesized PhyA during dark incubation and germinated upon exposure to red light of 1-100 nmol m-2 and far-red light of 0.5-10 micromol m-2, whereas the phyA mutant showed no such response. The results indicate that the seed germination is regulated by PhyA and PhyB but not by other phytochromes, and the effects of PhyA and PhyB are separable in this assay. We determined action spectra separately for PhyA- and PhyB-specific induction of seed germination at Okazaki large spectrograph. Action spectra for the PhyA response show that monochromatic 300-780 nm lights of very low fluence induced the germination, and this induction was not photoreversible in the range examined. Action spectra for the PhyB response show that germination was photoreversibly regulated by alternate irradiations with light of 0.01-1 mmol m-2 at wavelengths of 540-690 nm and 695-780 nm. The present work clearly demonstrated that PhyA photoirreversibly triggers the germination upon irradiations with ultraviolet, visible and far-red light of very low fluence, while PhyB controls the photoreversible effects of low fluence.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad M., Cashmore A. R. HY4 gene of A. thaliana encodes a protein with characteristics of a blue-light photoreceptor. Nature. 1993 Nov 11;366(6451):162–166. doi: 10.1038/366162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borthwick H. A., Hendricks S. B., Parker M. W., Toole E. H., Toole V. K. A Reversible Photoreaction Controlling Seed Germination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1952 Aug;38(8):662–666. doi: 10.1073/pnas.38.8.662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botto J. F., Sanchez R. A., Whitelam G. C., Casal J. J. Phytochrome A Mediates the Promotion of Seed Germination by Very Low Fluences of Light and Canopy Shade Light in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 1996 Feb;110(2):439–444. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.2.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. L., Norris K. H., Siegelman H. W., Hendricks S. B. DETECTION, ASSAY, AND PRELIMINARY PURIFICATION OF THE PIGMENT CONTROLLING PHOTORESPONSIVE DEVELOPMENT OF PLANTS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 Dec;45(12):1703–1708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.12.1703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chon H. P., Briggs W. R. Effect of red light on the phototropic sensitivity of corn coleoptiles. Plant Physiol. 1966 Dec;41(10):1715–1724. doi: 10.1104/pp.41.10.1715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clack T., Mathews S., Sharrock R. A. The phytochrome apoprotein family in Arabidopsis is encoded by five genes: the sequences and expression of PHYD and PHYE. Plant Mol Biol. 1994 Jun;25(3):413–427. doi: 10.1007/BF00043870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehesh K., Franci C., Parks B. M., Seeley K. A., Short T. W., Tepperman J. M., Quail P. H. Arabidopsis HY8 locus encodes phytochrome A. Plant Cell. 1993 Sep;5(9):1081–1088. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.9.1081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuya M. Molecular properties and biogenesis of phytochrome I and II. Adv Biophys. 1989;25:133–167. doi: 10.1016/0065-227x(89)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Juez E., Nagatani A., Tomizawa K., Deak M., Kern R., Kendrick R. E., Furuya M. The cucumber long hypocotyl mutant lacks a light-stable PHYB-like phytochrome. Plant Cell. 1992 Mar;4(3):241–251. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandoli D. F., Briggs W. R. Phytochrome control of two low-irradiance responses in etiolated oat seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1981 Apr;67(4):733–739. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.4.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagatani A., Reed J. W., Chory J. Isolation and Initial Characterization of Arabidopsis Mutants That Are Deficient in Phytochrome A. Plant Physiol. 1993 May;102(1):269–277. doi: 10.1104/pp.102.1.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks B. M., Quail P. H., Hangarter R. P. Phytochrome A regulates red-light induction of phototropic enhancement in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 1996 Jan;110(1):155–162. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quail P. H., Boylan M. T., Parks B. M., Short T. W., Xu Y., Wagner D. Phytochromes: photosensory perception and signal transduction. Science. 1995 May 5;268(5211):675–680. doi: 10.1126/science.7732376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. W., Nagatani A., Elich T. D., Fagan M., Chory J. Phytochrome A and Phytochrome B Have Overlapping but Distinct Functions in Arabidopsis Development. Plant Physiol. 1994 Apr;104(4):1139–1149. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.4.1139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. W., Nagpal P., Poole D. S., Furuya M., Chory J. Mutations in the gene for the red/far-red light receptor phytochrome B alter cell elongation and physiological responses throughout Arabidopsis development. Plant Cell. 1993 Feb;5(2):147–157. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.2.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharrock R. A., Quail P. H. Novel phytochrome sequences in Arabidopsis thaliana: structure, evolution, and differential expression of a plant regulatory photoreceptor family. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1745–1757. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinomura T., Nagatani A., Chory J., Furuya M. The Induction of Seed Germination in Arabidopsis thaliana Is Regulated Principally by Phytochrome B and Secondarily by Phytochrome A. Plant Physiol. 1994 Feb;104(2):363–371. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.2.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somers D. E., Sharrock R. A., Tepperman J. M., Quail P. H. The hy3 Long Hypocotyl Mutant of Arabidopsis Is Deficient in Phytochrome B. Plant Cell. 1991 Dec;3(12):1263–1274. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.12.1263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderhoef L. N., Quail P. H., Briggs W. R. Red Light-inhibited Mesocotyl Elongation in Maize Seedlings: II. Kinetic and Spectral Studies. Plant Physiol. 1979 Jun;63(6):1062–1067. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.6.1062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitelam G. C., Johnson E., Peng J., Carol P., Anderson M. L., Cowl J. S., Harberd N. P. Phytochrome A null mutants of Arabidopsis display a wild-type phenotype in white light. Plant Cell. 1993 Jul;5(7):757–768. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.7.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman B. K., Briggs W. R. Phototropic Dosage-Response Curves for Oat Coleoptiles. Plant Physiol. 1963 May;38(3):248–253. doi: 10.1104/pp.38.3.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







