Abstract
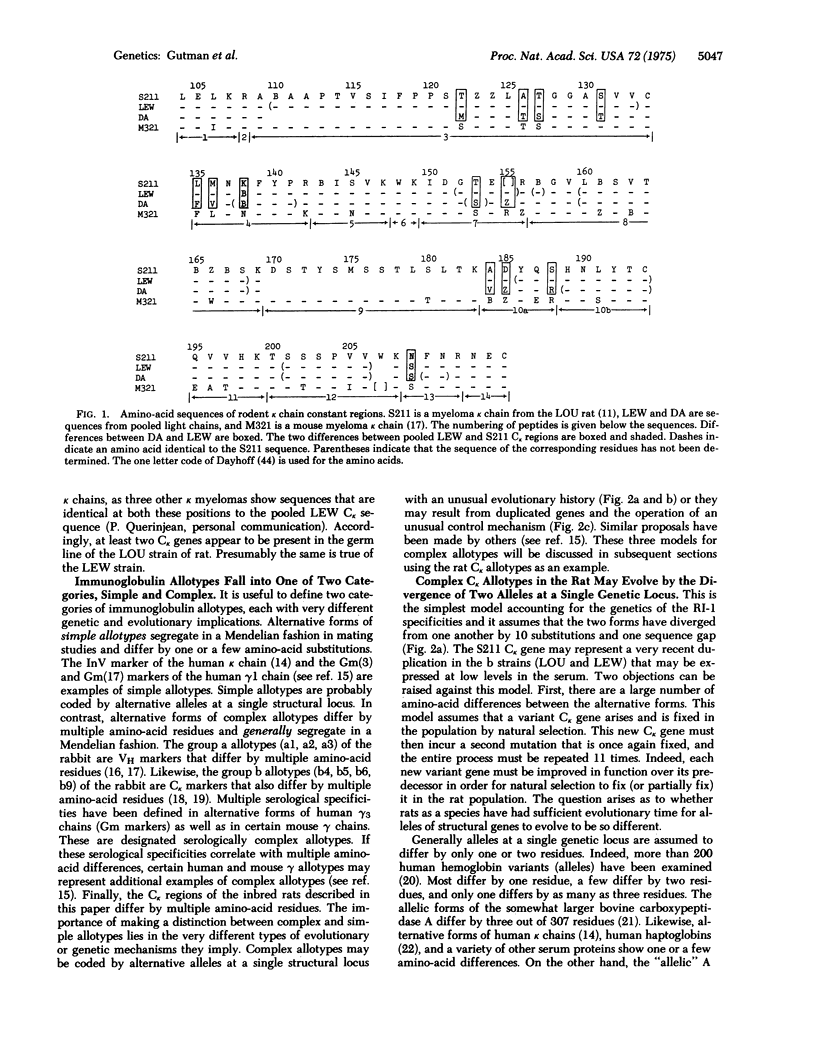
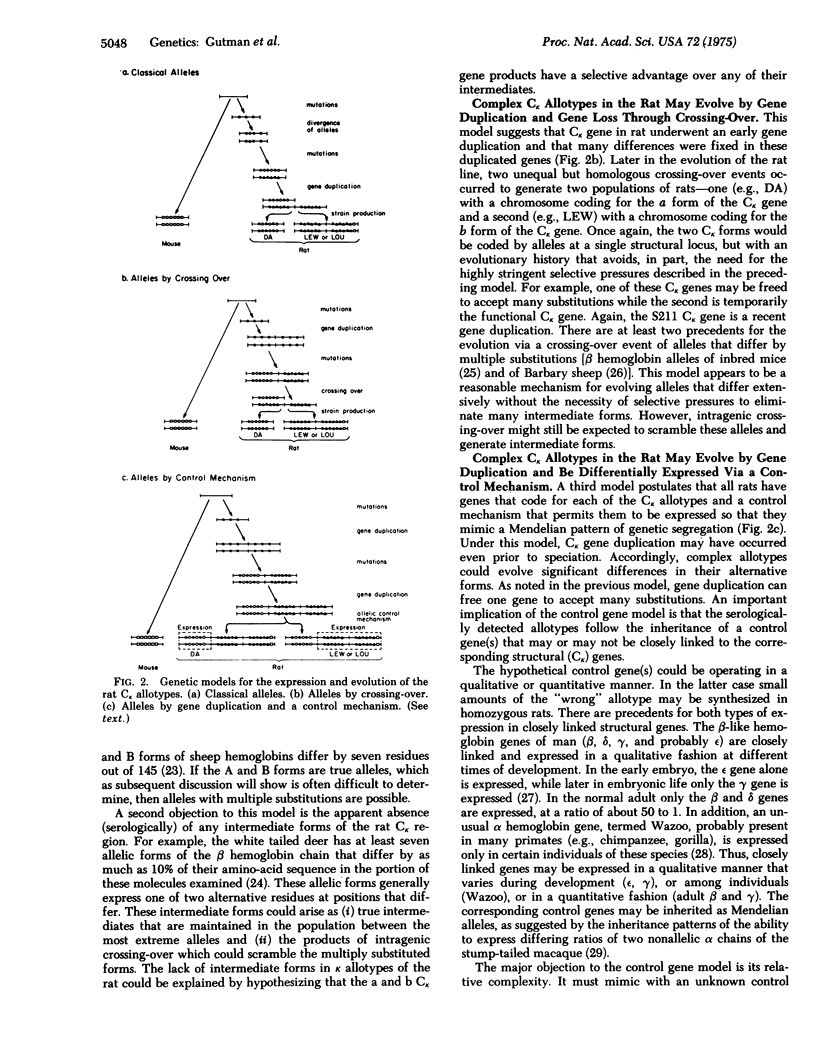
Immunoglobulin kappa chains from various inbred strains of rats have two serologically detectable forms that segregate in a Mendelian fashion (allotypes a and b of the RI-I locus). Partial amino-acid sequences from the constant regions of these two forms have been compared. Of the 81 residues of the constant region studied, 10 amino-acid substitutions as well as one size difference (sequence gap) were found. This large number of sequence differences among alternative forms of the kappa allotype raises provocative questions as to the genetic and evolutionary implications of these light chain allotypes. We designate allotypes whose alternative forms differ at multiple residue positions as complex allotypes. There are basically two genetic models that might explain complex allotypes. First, these allotypes are alleles of a single structural gene with an unusual evolutionary history. Second, all rats have genes that code for each of the light chain allotypes and a control mechanism that permits them to be expressed so that they mimic a Mendelian pattern of segregation. We discuss evidence from other immunoglobulin systems that is compatible with this second model.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appella E., Rejnek J., Reisfeld R. A. Variations at the carboxyl-terminal amino acid sequence of rabbit light chains with b4, b5 and b6 allotypic specificities. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):473–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90289-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benacerraf B., McDevitt H. O. Histocompatibility-linked immune response genes. Science. 1972 Jan 21;175(4019):273–279. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4019.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. A., Dixon G. H. Amino-acid sequence of alpha chains of human haptoglobins. Nature. 1968 May 25;218(5143):736–741. doi: 10.1038/218736a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosma M. J., Bosma G. C. Congenic mouse strains: the expression of a hidden immunoglobulin allotype in a congenic partner strain of BALB-c mice. J Exp Med. 1974 Mar 1;139(3):512–527. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.3.512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer S. H., Hathaway P., Pascasio F., Bordley J., Orton C., Naughton M. A. Differences in the amino acid sequences of tryptic peptides from three sheep hemoglobin beta chains. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 10;242(9):2211–2232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer S. H., Noyes A. N., Boyer M. L., Marr K. Hemoglobin 3 chains in apes. Primary structures and the presumptive nature of back mutation in a normally silent gene. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 10;248(3):992–1003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnet F. M. "Self-recognition" in colonial marine forms and flowering plants in relation to the evolution of immunity. Nature. 1971 Jul 23;232(5308):230–235. doi: 10.1038/232230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gally J. A., Edelman G. M. The genetic control of immunoglobulin synthesis. Annu Rev Genet. 1972;6:1–46. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.06.120172.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman J. G. Hemoglobin Beta chain structural variation in mice: evolutionary and functional implications. Science. 1972 Nov 24;178(4063):873–874. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4063.873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluecksohn-Waelsch S., Erickson R. P. The T-locus of the mouse: implications for mechanisms of development. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1970;5:281–316. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfliesh R. M. Constant-region cysteine-containing peptides of b4 and b9 rabbit kappa-chains isolated by a new diagonal mapping procedure. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):910–912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman G. A., Weissman I. L. Inheritance and strain distribution of a rat immunoglobulin allotype. J Immunol. 1971 Nov;107(5):1390–1393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris H., Hopkinson D. A., Robson E. B. The incidence of rare alleles determining electrophoretic variants: data on 43 enzyme loci in man. Ann Hum Genet. 1974 Jan;37(3):237–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1974.tb01832.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman T. H. The in vivo production of hemoglobin C in ruminants. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Nov 29;241(0):549–555. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb21911.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohne D. E. Evolution of higher-organism DNA. Q Rev Biophys. 1970 Aug;3(3):327–375. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500004765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks P. A., Rifkind R. A. Protein synthesis: its control in erythropoiesis. Science. 1972 Mar 3;175(4025):955–961. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4025.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKean D., Potter M., Hood L. Mouse immunoglobulin chains. Partial amino acid sequence of a kappa chain. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb;12(4):749–759. doi: 10.1021/bi00728a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mole L. E., Jackson S. A., Porter R. R., Wilkinson J. M. Allotypically related sequences in the Fd fragment of rabbit immunoglobulin heavy chains. Biochem J. 1971 Sep;124(2):301–318. doi: 10.1042/bj1240301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudgett M., Fraser B. A., Kindt T. J. Nonallelic behavior of rabbit variable-region allotypes. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1448–1452. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nezlin R. S., Vengerova T. I., Rokhlin O. V., Machulla H. K. Allotypic marker of kappa light chains of rat immunoglobulins localized in the constant region of the chain. Immunochemistry. 1974 Aug;11(8):517–518. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(74)90160-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poljak R. J., Amzel L. M., Avey H. P., Chen B. L., Phizackerley R. P., Saul F. Three-dimensional structure of the Fab' fragment of a human immunoglobulin at 2,8-A resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3305–3310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pétra P. H., Bradshaw R. A., Walsh K. A., Neurath H. Identification of the amino acid replacements characterizing the allotypic forms of bovine carboxypeptidase A. Biochemistry. 1969 Jul;8(7):2762–2768. doi: 10.1021/bi00835a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivat L., Gilbert D., Ropartz C. Immunoglobulin allotypic specificities in mixed leucocyte cultures. Immunology. 1973 Jun;24(6):1041–1049. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rokhlin O. V., Nezlin R. S. RL allotypes of light chains of rat immunoglobulins: ratio in heterozygous rats and distribution among inbred and random-bred rats. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(2):209–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01249.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rokhlin O. V., Nezlin R. S. RL allotypes of light chains of rat immunoglobulins: ratio in heterozygous rats and distribution among inbred and random-bred rats. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(2):209–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01249.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rokhlin O. V., Vengerova T. I., Nezlin R. S. RL allotypes of light chains of rat immunoglobulins. Immunochemistry. 1971 Jun;8(6):525–538. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90404-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMPSON G. G. The nature and origin of supraspecific taxa. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1959;24:255–271. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1959.024.01.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarich V. M., Wilson A. C. Generation time and genomic evolution in primates. Science. 1973 Mar 16;179(4078):1144–1147. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4078.1144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starace V., Querinjean P. The primary structure of a rat kappa Bence Jones protein: phylogenetic relationships of V- and C-region genes. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):59–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strosberg A. D., Hamers-Casterman C., Van der Loo W., Hamers R. A rabbit with the allotypic phenotype: ala2a3 b4b5b6. J Immunol. 1974 Oct;113(4):1313–1318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. J., Easley C. W. Sickling phenomena of deer. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Nov 29;241(0):594–604. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb21916.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry W. D., Hood L. E., Steinberg A. G. Genetics of immunoglobulin kappa-chains: chemical analysis of normal human light chains of differing Inv types. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 May;63(1):71–77. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vengerova T. I., Rokhlin O. V., Nezlin R. S. Chemical differences between two allotypic variants of light chains of rat immunoglobulins. Peptide mapping and cyanogen bromide cleavage. Immunochemistry. 1972 Dec;9(12):1239–1245. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90298-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. M. Variation in the N-terminal sequence of heavy chains of immunoglobulin G from rabbits of different allotype. Biochem J. 1969 Apr;112(2):173–185. doi: 10.1042/bj1120173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


