Abstract
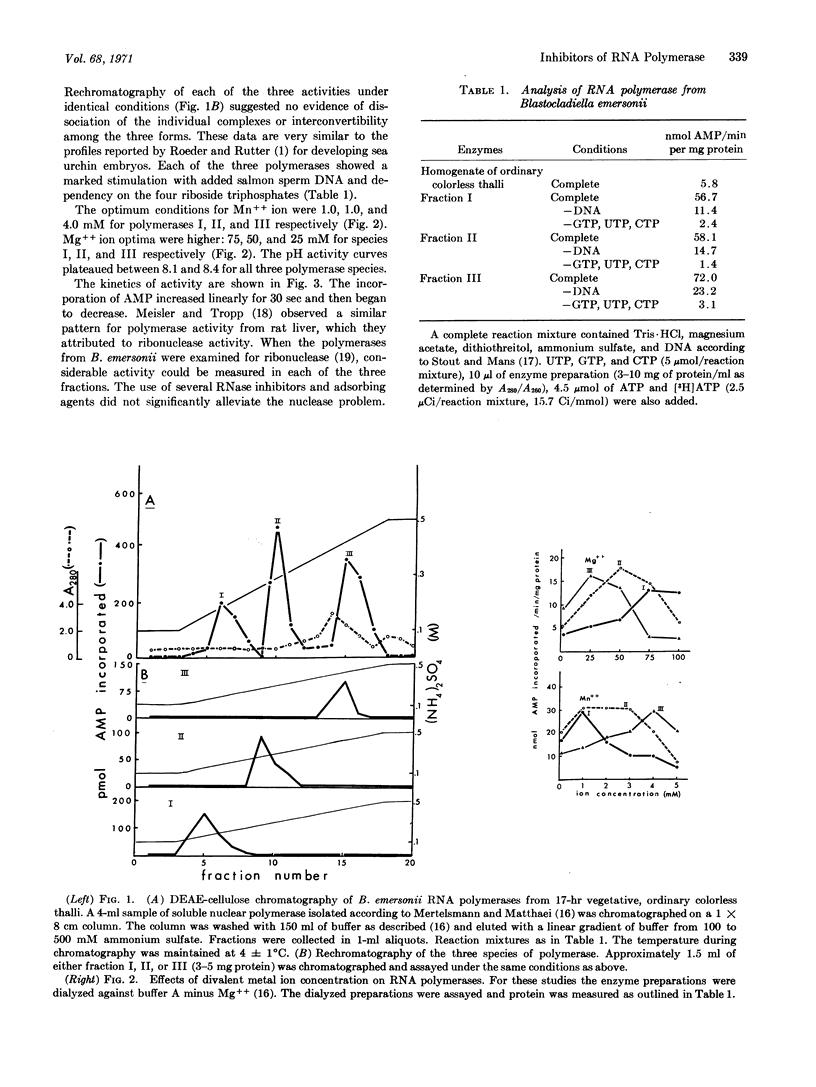
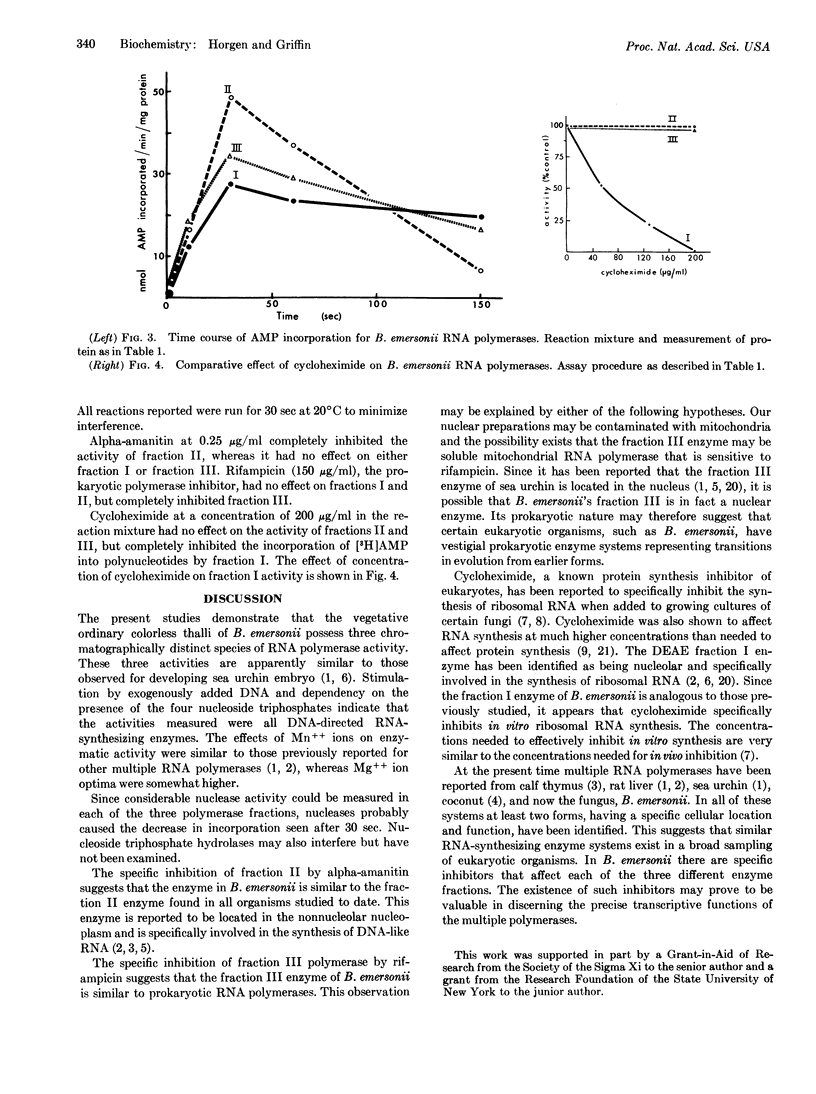
Specific inhibitors of each of the three RNA polymerases of Blastocladiella emersonii have been found. Cycloheximide specifically inhibited the in vitro activity of the DEAE-fraction I enzyme, alpha-amanitin specifically inhibited the DEAE-fraction II enzyme, and rifampicin specifically inhibited the fraction III enzyme. DNA stimulation and dependency on the four riboside triphosphates were shown to be characteristic of each of the three fractions. Optimum concentrations of magnesium ions required were shown to differ among the three fractions and to be somewhat higher than optimum concentrations of manganese ions. The effect of pH on activity was essentially identical for each of the three fractions. Kinetic experiments and nuclease assays indicated the presence of some interfering substances in the partially purified RNA polymerase fractions.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker F. F. A method for rapid isolation of large quantities of uncontaminated hepatocyte nuclei displaying vigorous RNA polymerase activity: normal and regenerating liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):380–382. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90593-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIALA E. S., DAVIS F. F. PREFERENTIAL INHIBITION OF SYNTHESIS AND METHYLATION OF RIBOSOMAL RNA IN NEUROSPORA CRASSA BY ACTIDIONE. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jan 4;18:115–118. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90892-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haidle C. W., Storck R. Inhibition by cycloheximide of protein and RNA synthesis in Mucor rouxii. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jan 24;22(2):175–180. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90428-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann G., Honikel K. O., Knüsel F., Nüesch J. The specific inhibition of the DNA-directed RNA synthesis by rifamycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;145(3):843–844. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90147-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horgen P. A., Griffin D. H. Cytochrome Oxidase Activity in Blastocladiella emersonii. Plant Physiol. 1969 Nov;44(11):1590–1593. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.11.1590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob S. T., Sajdel E. M., Munro H. N. Different responses of soluble whole nuclear RNA polymerase and soluble nucleolar RNA polymerase to divalent cations and to inhibition by alpha-amanitin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Feb 20;38(4):765–770. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90647-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedinger C., Gniazdowski M., Mandel J. L., Jr, Gissinger F., Chambon P. Alpha-amanitin: a specific inhibitor of one of two DNA-pendent RNA polymerase activities from calf thymus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jan 6;38(1):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindell T. J., Weinberg F., Morris P. W., Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Specific inhibition of nuclear RNA polymerase II by alpha-amanitin. Science. 1970 Oct 23;170(3956):447–449. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3956.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisler A. I., Tropp B. E. Studies on ribonucleic acid synthesis in nuclei isolated from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Feb 18;174(2):476–490. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90277-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertelsmann R., Matthaei H. Isolation and purification of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from nuclei of human placenta. (Nucleoside triphosphate: ribonucleic acid nucleotidyl transferase, e.c.2.7.7.6.). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Oct 10;33(1):136–139. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90267-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondal H., Mandal R. K., Biswas B. B. Factors and rifampicin influencing RNA polymerase isolated from chromatin of eukaryotic cell. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Sep 10;40(5):1194–1200. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90922-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Multiple forms of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in eukaryotic organisms. Nature. 1969 Oct 18;224(5216):234–237. doi: 10.1038/224234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Multiple ribonucleic acid polymerases and ribonucleic acid synthesis during sea urchin development. Biochemistry. 1970 Jun 9;9(12):2543–2553. doi: 10.1021/bi00814a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Specific nucleolar and nucleoplasmic RNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Mar;65(3):675–682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.3.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straat P. A., Ts'o P. O. Ribonucleic acid polymerase from Micrococcus luteus (Micrococcus lysodeikticus). IV. Effect of rifampicin and oligomers on the homopolymer-directed reaction. Biochemistry. 1970 Feb 17;9(4):926–931. doi: 10.1021/bi00806a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taber R. L., Jr, Vincent W. S. Effects of cycloheximide on ribosomal RNA synthesis in yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Feb 21;34(4):488–494. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90408-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrli W., Nüesch J., Knüsel F., Staehelin M. Action of rifamycins on RNA polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 18;157(1):215–217. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90285-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kloet S. R. Accumulation of RNA with a DNA like base composition in Saccharomyces carlsbergensis in the presence of cycloheximide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 May 18;19(5):582–586. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90378-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


