Abstract
Burkholderia pseudomallei, the causative agent of melioidosis, contains a large pathogen genome (7.2 Mb) with ∼2,000 genes of putative or unknown function. Interactions with potential hosts and environmental factors may induce rapid adaptations in these B. pseudomallei genes, which can be discerned through evolutionary analysis of multiple B. pseudomallei genomes. Here we show that several previously uncharacterized B. pseudomallei genes bearing genetic signatures of rapid adaptation (positive selection) can induce diverse cellular phenotypes when expressed in mammalian cells. Notably, several of these phenotypes are plausibly related to virulence, including multinuclear giant cell formation, apoptosis, and autophagy induction. Specifically, we show that BPSS0180, a type VI cluster-associated gene, is capable of inducing autophagy in both phagocytic and nonphagocytic mammalian cells. Following infection of macrophages, a B. pseudomallei mutant disrupted in BPSS0180 exhibited significantly decreased colocalization with LC3 and impaired intracellular survival; these phenotypes were rescued by introduction of an intact BPSS0180 gene. The results suggest that BPSS0180 may be a novel inducer of host cell autophagy that contributes to B. pseudomallei intracellular growth. More generally, our study highlights the utility of applying evolutionary principles to microbial genomes to identify novel virulence genes.
INTRODUCTION
Burkholderia pseudomallei is the causative agent of melioidosis, an often-fatal infectious disease of humans and animals that is prevalent in Southeast Asia and Northern Australia (1). The B. pseudomallei genome represents one of the most complex microbial pathogen genomes ever sequenced, with over 5,700 genes that likely contribute to B. pseudomallei's ability to survive in diverse and harsh environments (2). While B. pseudomallei is normally regarded as a soil saprophyte, it has been proposed that adaptations incurred in B. pseudomallei in response to selective pressures in its natural reservoir (soil) may have indirectly contributed to its ability to colonize and thrive in mammalian hosts, making B. pseudomallei a useful model system for the study of “accidental virulence.” However, a significant fraction of the B. pseudomallei genome still remains to be functionally annotated beyond in silico predictions—for example, almost 33% of B. pseudomallei genes still carry “hypothetical” or “putative” functions. There is thus a need for approaches to rapidly prioritize functionally interesting B. pseudomallei genes relevant to mammalian virulence for further analysis and study.
Previous research has demonstrated that B. pseudomallei is an intracellular pathogen that can utilize several strategies to survive within host cells, including the induction of actin-based motility, multinucleate giant cell (MNGC) formation, endosome escape, and evasion and exploitation of host cell autophagic pathways (1, 3). Particularly relevant to this study is autophagy, a eukaryotic cellular process that functions to remove proteins and organelles from the cell (4). Recent evidence suggests that autophagy is a key component of innate immune defenses used by host cells against several intracellular pathogens (5). In previous studies, autophagy has been shown to inhibit the intracellular survival of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and group A Streptococcus (6, 7). However, despite its conventional role as a host defense mechanism against some pathogens, other intracellular pathogens have developed mechanisms to evade autophagic recognition and in some cases even to subvert and manipulate autophagy signaling for their own benefit (8, 9). For example, Brucella abortus, Coxiella burnetii, and Legionella pneumophila have all developed specific molecular strategies to adapt the host autophagy machinery for invasion and replication (10–12). In the case of B. pseudomallei, previous studies have demonstrated that treating B. pseudomallei-infected RAW264.7 macrophages with rapamycin, a known autophagy inducer, increased B. pseudomallei colocalization with LC3 (a marker of autophagy) and decreased intracellular survival (13). Further analysis using electron microscopy to determine the cellular compartment in which B. pseudomallei organisms were located revealed that the bacteria were subject to LC3-associated phagocytosis (14) and that B. pseudomallei cells which escape phagosomes are not targeted by canonical autophagy. However, little is known about specific B. pseudomallei genes that may affect autophagy pathways in host cells or their involvement in the B. pseudomallei intracellular life cycle.
We previously reported a comparative genomic analysis of 11 B. pseudomallei genomes, identifying genes possessing genetic signatures of rapid adaptation (positive selection), an evolutionary process where beneficial traits and alleles are selected for in the population due to environmental pressures. In DNA sequence data, genes exhibiting positive selection can be broadly identified by comparing the rates of nonsynonymous to synonymous polymorphisms. We hypothesized that these positively selected genes, while overtly responding to environmental pressures encountered by B. pseudomallei in soil, might indirectly facilitate the colonization of mammalian hosts (15). Preliminary analysis supported the notion that some of these positively selected genes might interact with host cellular pathways. In this study, we extended this functional analysis to an expanded repertoire of positively selected B. pseudomallei genes. We found that many of the positively selected genes elicited intriguing phenotypes when expressed in mammalian cells, several of which were plausibly related to virulence (e.g., MNGC formation). Among these genes, we highlighted BPSS0180 as a gene whose expression is capable of inducing autophagy in both phagocytic and nonphagocytic cells. Subsequent analysis of BPSS0180 mutants suggested that BPSS0180 may contribute to the intracellular survival of B. pseudomallei in mammalian hosts. These results suggest that B. pseudomallei may have evolved certain genes to capitalize on the host autophagic process for microbial survival.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Identifying B. pseudomallei genes under positive selection.
To identify positively selected genes in B. pseudomallei, homologous gene sequences from 11 B. pseudomallei genomes were aligned and analyzed (15) using the maximum likelihood pipeline implemented in PAML 4.0 (16). Two different likelihood ratio (LR) models (M1a-M2a or M7-M8) were employed (16, 17). If a gene model incorporating positive selection had a higher likelihood score than that of a null model without positive selection, this was regarded as evidence for positive selection. Using this approach, 211 genes were commonly identified by both models as being positively selected (15). For this study, we chose 26 positively selected genes among the originally identified 211 genes, using criteria described in Results and Discussion (Table 1). In addition, we also included 4 genes (BPSL1598, BPSS0144, BPSS0410, and BPSS2306) as controls. These genes did not meet the criteria for positive selection and were otherwise randomly selected from the B. pseudomallei genome (Table 1).
Table 1.
Subcellular localization of positively selected B. pseudomallei proteins
| Protein category | Category no. | Sanger ID | Functional annotation | Functional annotation of Nandi et al. (15) | Ka/Ks | P value | Subcellular localization pattern |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Putative exported proteins | 1 | BPSL0388 | Hypothetical protein | Putative exported protein | 16.78923 | 1.57E−04 | Dispersed with clusters throughout the cell |
| 2 | BPSL0701 | Putative exported protein | Hypothetical protein | 5.40184 | 1.81E−04 | Dispersed with clusters throughout the cell | |
| 3 | BPSL0837 | Arabinose efflux permease | Putative transporter protein | 17.34757 | 2.34E−06 | Cytoplasm | |
| 4 | BPSL2755 | Putative exported protein | Hypothetical protein | 27.38346 | 7.67E−04 | Dispersed with clusters throughout the cell | |
| T3SS-associated proteins | 5 | BPSS1503 | Uncharacterized protein conserved in bacteria | Hypothetical protein | 46.81391 | 3.25E−04 | Dispersed with clusters throughout the cell |
| 6 | BPSS1504 | Uncharacterized low-complexity proteins | Hypothetical protein | 12.92541 | 6.64E−06 | Dispersed with clusters throughout the cell | |
| 7 | BPSS1552 | Type III secretion system protein | Type III secretion system protein | 302.7963 | 2.93E−21 | Dispersed with clusters throughout the cell | |
| T6SS-associated proteins | 8 | BPSS0180 | Uncharacterized protein conserved in bacteria | Hypothetical protein | 13.44259 | 2.18E−10 | Punctate (predominately in the cytoplasm) |
| Proteins with genes located in genomic islands | 9 | BPSL0579 | Hypothetical protein | Hypothetical protein | 4.34889 | 6.21E−06 | Dispersed with clusters throughout the cell |
| Virulence-related lipoproteins | 10 | BPSS0415 | Putative lipoprotein | Lipoprotein | 8.25162 | 2.11E−06 | Dispersed with clusters throughout the cell |
| 11 | BPSS0752 | Putative lipoprotein (UniProtKB/TrEMBL accession no. Q63MA8) | Lipoprotein | 161.5491 | 1.05E−08 | Dispersed with clusters throughout the cell | |
| Capsule and outer membrane proteins | 12 | BPSS0096 | Outer membrane protein and related peptidoglycan-associated (lipo)proteins | OmpA family protein | 21.33664 | 2.16E−06 | Dispersed with clusters throughout the cell |
| Proteins involved in quorum sensing | 13 | BPSS1570 | N-Acyl-l-homoserine lactone synthetase | N-Acylhomoserine lactone synthase | 325.5811 | 6.36E−15 | Dispersed with clusters throughout the cell |
| Virulence-related enzymes | 14 | BPSL1591 | Saccharopine dehydrogenase and related proteins | Hypothetical protein | 281.5625 | 1.51E−30 | Dispersed with clusters throughout the cell |
| 15 | BPSL2084 | O-Methyltransferase involved in polyketide biosynthesis | Putative bifunctional protein | 23.87113 | 2.90E−04 | Dispersed with clusters throughout the cell | |
| 16 | BPSL2198 | Predicted esterase of the alpha-beta hydrolase superfamily | Putative exported phospholipase | 684.0606 | 1.69E−20 | Perinuclear | |
| 17 | BPSL2074 | Glycosidases | Putative alpha-amylase-related protein | 22.3514 | 1.78E−05 | Nucleus | |
| 18 | BPSL2362 | Collagenase and related proteases | Hypothetical protein | 14.87154 | 1.97E−06 | Dispersed with clusters throughout the cell | |
| 19 | BPSL3041 | NAD-dependent aldehyde dehydrogenases | Phenylacetic acid degradation oxidoreductase | 30.96521 | 9.52E−06 | Dispersed with clusters throughout the cell | |
| 20 | BPSL3229 | Lysophospholipase L1 and related esterases | Hypothetical protein | 94.41791 | 3.96E−23 | Dispersed with clusters throughout the cell | |
| 21 | BPSL3337 | Predicted hydrolases or acyltransferases (alpha/beta hydrolase superfamily) | Putative hydrolase | 142.4119 | 3.34E−11 | Dispersed with clusters throughout the cell | |
| 22 | BPSS0452 | DNA polymerase IV (family X) | Phosphoesterase | 181.4097 | 4.34E−50 | Nucleus | |
| 23 | BPSS0945 | Membrane proteins related to metalloendopeptidases | Peptidase | 30.67755 | 6.09E−06 | Nucleus | |
| 24 | BPSS1010 | Putative halogenase (UniProtKB/TrEMBL accession no. Q63LK5) | Halogenase | 29.58273 | 3.07E−15 | Dispersed with clusters throughout the cell | |
| 25 | BPSS1973 | Predicted protease | Hypothetical protein | 412.251 | 6.73E−32 | Dispersed with clusters throughout the cell | |
| 26 | BPSS2102 | Serine/threonine protein kinase | Protein kinase | 20.72486 | 1.07E−06 | Dispersed with clusters throughout the cell | |
| Randomly selected proteins (controls) | 27 | BPSL1598 | Putative transport-related membrane protein | Small conductance mechanosensitive channel | Dispersed with clusters throughout the cell | ||
| 28 | BPSS0144 | Amylase | Glucoamylase and related glucosyl hydrolases | Dispersed with clusters throughout the cell | |||
| 29 | BPSS0410 | Hypothetical protein | Hypothetical protein | Dispersed with clusters throughout the cell | |||
| 30 | BPSS2306 | Porin protein | Outer membrane protein | Dispersed with clusters throughout the cell |
Bacterial strains and cell culture.
B. pseudomallei strains K96243 and Bp22 and BPSS0180 mutants were cultured in Luria-Bertani (LB) broth at 37°C. Escherichia coli strain SM10 λpir was used as a conjugative donor of the λpir-dependent suicide replicon pDM4 (18). RAW264.7 macrophage cells stably expressing GFP-LC3 have been described previously (13). HeLa cells (a gift of Edwin Cheung, Genome Institute of Singapore, Singapore) and RAW264.7 cells (purchased from ATCC) were maintained at 37°C in 5% CO2 with 1% penicillin-streptomycin supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco/Invitrogen).
Genomic DNA isolation and plasmid construction.
Genomic DNAs were isolated from B. pseudomallei K96243 and Bp22 by using a QIAamp DNA minikit (Qiagen) according to the manufacturer's protocol. The mammalian expression vector Vivid Colors pcDNA6.2/N-EmGFP-GW/TOPO and the pcDNA3.1/V5-His TOPO TA expression system (Invitrogen) were used to clone and express the positively selected genes. Sequence integrity of constructs was confirmed by Sanger sequencing analysis. A list of primers used for PCR amplification is provided in Table S1 in the supplemental material.
Mutagenesis of BPSS0180.
A BPSS0180 deletion mutant was derived by double-crossover allelic exchange following approaches used previously in our laboratory (19). Briefly, two pairs of primers were used to amplify an upstream fragment flanked by XbaI and BglII sites (5′GGGTCTAGACCGCTGCCGATCCACGTGAC and 5′GGGAGATCTCATCGACGGGCGCCATCCAG) and a downstream fragment flanked by BglII and XbaI sites (5′GGGAGATCTACGATTTGCACGCGCAGCAG and 5′GGGTCTAGACCGGATCGCGCTCAGTTCGA). Those two fragments, together with a tetA(C) cassette flanked by BglII sites, were ligated together into the pBluescript KS phagemid. The mutagenesis construct was excised by XbaI digestion and ligated into the XbaI site of pDM4 (18). This pDM4 construct was transformed into E. coli and then transferred into B. pseudomallei by conjugation as previously described (19). Verification of the deletion in the B. pseudomallei genome was achieved by PCR and subsequent DNA sequencing.
Complementation of the bpss0190 mutant strain.
A DNA fragment spanning the entire BPSS0180 open reading frame was amplified by PCR and then ligated into pBHR1 (20). Fidelity of the complementing gene was confirmed by nucleotide sequencing. The resulting plasmid was introduced into E. coli S17-1 λpir and transferred into the BPSS0810 deletion mutant strain by conjugation. Transconjugants were selected by exhibiting resistance to (i) tetracycline (25 μg/ml) and kanamycin (1 mg/ml) for the BPSS0180 mutant carrying the pBHR1-BPSS0180 complementation plasmid (strain ΔBPSS0180-BPSS0180comp); (ii) tetracycline (25 μg/ml), kanamycin (1 mg/ml), and chloramphenicol (50 μg/ml) for the BPSS0180 mutant carrying the pBHR1 empty vector (strain ΔBPSS0180-EV); and (iii) kanamycin (1 mg/ml) and chloramphenicol (50 μg/ml) for wild-type B. pseudomallei carrying the pBHR1 empty vector. The last two strains served as a control group. During infection of RAW264.7 cells, ceftazidime (90 μg/ml) was added into the culture medium to eliminate extracellular bacteria, as the plasmid-bearing wild-type strains exhibit kanamycin resistance.
Intracellular survival assays.
Murine macrophage RAW264.7 cells were seeded in 24-well plates at 106 cells/well 15 h prior to B. pseudomallei infection. B. pseudomallei strains were grown overnight in the appropriate medium, and on the day of infection, they were reinoculated into fresh medium and grown to mid-log phase before infection. Infections were performed at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 10. After 1 h at 37°C, extracellular bacteria were killed by replacing the medium with fresh medium containing 900 μg/ml kanamycin and 90 μg/ml ceftazidime. At 2, 4, and 6 h postinfection, the cells were washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) 3 times and then lysed with 0.5% saponin to release intracellular bacteria. Serial dilutions of the cell lysate were then plated on LB agar, and CFU were enumerated after 2 days. Relative intracellular survival rates (%) are presented by normalizing CFU numbers to those at 2 h postinfection (set at 100%).
DNA transfection and confocal microscopy analysis.
HeLa cells were grown on poly-l-lysine-coated glass coverslips (BD Bioscience) to 70 to 80% confluence and then transfected using FuGENE HD reagent (Roche) according to the manufacturer's protocol for 24 h. After transfection, cells were washed with PBS and fixed with 3.7% paraformaldehyde for 15 min at room temperature. Cells were washed with PBS and covered with mounting medium containing ProLong Gold antifade reagent (Invitrogen) and DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) to facilitate nucleus counting. Cells were visualized using a Zeiss LSM 150 inverted confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM) and analyzed using Zeiss LSM Image Browser software (Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany). For actin staining, cells were stained with Alexa Fluor 555- and Alexa Fluor 488-phalloidin (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer's protocol. For LC3 colocalization studies, HeLa or RAW264.7 cells were incubated with primary anti-LC3 antibodies (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer's instructions, followed by Alexa Fluor 594-conjugated secondary goat anti-rabbit IgG (1:1,500). For LAMP1 staining, HeLa cells were transfected with a construct encoding green fluorescent protein (GFP)-tagged BPSS0180 or with empty vector controls and then treated with rapamycin. Cells were then incubated with primary anti-LAMP1 antibody followed by Alexa Fluor 594-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG secondary antibodies (Invitrogen) (1:1,500). To measure B. pseudomallei colocalization with LC3, RAW264.7 cells stably expressing GFP-LC3 were infected with B. pseudomallei on coverslips in the wells of 24-well plates. After 4 washes with PBS, infected cells were fixed with methanol for 10 min and treated with blocking buffer (1.5% bovine serum albumin [BSA], 0.2% Triton X-100 in PBS) for 1 h at room temperature. Coverslips were then incubated with a rabbit anti-B. pseudomallei outer membrane protein (OMP) serum (10) (1:500 dilution in blocking buffer) for 2 h at room temperature, followed by 3 PBS washes. Secondary antibody staining was performed using a Texas Red-conjugated goat anti-rabbit immunoglobulin (Ig) antibody (Molecular Probes) diluted 1:1,000 in blocking buffer for 2 h at room temperature. Nuclear staining was performed using 0.1 mg/ml DAPI for 5 min at room temperature. Coverslips were mounted immediately using Permafluor aqueous mounting medium (Immunotech) before cells were visualized under a CLSM (Olympus FV500). Image processing was performed using Olympus FluoView TIEMPO software. Image analysis was performed using the public software ImageJ.
Western blotting.
To examine levels of LC3 expression, cells (rapamycin treated, DNA transfected) seeded in 6-well plates were washed with PBS and lysed by addition of cell lysis buffer (Roche) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Samples were boiled and proteins separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) using 12% precast polyacrylamide gels (Bio-Rad). Proteins were then electrotransferred onto PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride) membranes (Bio-Rad). Membranes were incubated with rabbit anti-LC3 and rabbit anti-actin (Thermo Fisher Scientific) primary antibodies (1:500), and after blocking and washing, the membranes were then incubated with goat anti-rabbit IgG secondary antibodies (1:1,000). Membranes were washed and protein bands visualized using either TMB (3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine) substrate or ECL reagents (SuperSignal West Femto chemiluminescence substrate; Pierce). Quantification was performed using ImageJ software.
Statistical analysis.
For quantitative analysis, at least 100 cells or bacteria were counted for each condition in all experiments. Pairwise comparisons between sample sets were performed using Student's t test. Values are expressed as means ± standard errors of the means (SEM). P values of <0.05 are considered to be statistically significant.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Cellular assay for positively selected B. pseudomallei genes.
We previously reported a comparative genomic analysis of 11 B. pseudomallei genomes, identifying 211 genes exhibiting signatures of positive selection (15). These positively selected genes were widely dispersed across diverse functions, including metabolic processes, membrane functions, signal transduction, and gene expression regulation. To functionally characterize these genes, we selected 26 genes from the initial set of 211 that met one of the following criteria: (i) genes which have been reported as putative virulence factors in the published literature (e.g., BPSS1552), (ii) genes encoding virulence-related proteins (e.g., BPSL2198), or (iii) genes encoding orthologs of known virulence factors or with subgenic sequence homologies with virulence factors (e.g., BPSS0415). We also included genes encoding putative exported, transporter, or outer membrane proteins, genes located in or in close proximity to type III or VI secretion system gene clusters, genes associated with genomic islands, and genes related to bacterial lipoproteins (Table 1). Of these 26 positively selected genes, 4 were previously uncharacterized and/or “hypothetical” proteins based upon original genome annotations (2). In addition, we also included 4 randomly selected genes (BPSL1598, BPSS0144, BPSS0410, and BPSS2306) which did not exhibit signatures of positive selection, as controls (Table 1).
Infection of mammalian cells by microbial pathogens typically involves the hijacking of eukaryotic cellular pathways by bacterial effector proteins. Previous research has shown that different effector proteins can target distinct host subcellular compartments, where they interact with specific intracellular host pathways (21, 22). As such, identifying bacterial proteins that traffic to specific subcellular locations in host cells may provide important clues regarding their function during infection. We hypothesized that determining the subcellular localization of the positively selected gene products in mammalian cell compartments might provide important clues to understanding their function. To investigate this possibility, we expressed the 30 chosen genes (26 positively selected genes and 4 controls) (Table 1) as GFP-tagged variants in HeLa cells. We detected GFP signals in many different subcellular compartments (Table 1; Fig. 1 provides representative examples). Gene products belonging to category 1 were dispersed as clusters throughout the cell (Fig. 1, row I), while gene products in category 2 were distributed in the cytoplasm but not the nucleus (Fig. 1, row II). Gene products in category 3 were associated with perinuclear expression (Fig. 1, row III), while gene products belonging to category 4 were exclusively nuclear (Fig. 1, row IV). Gene products in category 5 were associated with punctate or dot-like structures suggestive of autophagosomes (Fig. 1, row V). In contrast, the gene products for all four control genes were associated with small discrete cytoplasmic clusters distributed throughout the cytosol, without any specific subcellular localization pattern (Table 2). We recognize that these subcellular localization results should be interpreted with an element of caution, as some of these proteins might not be produced in their true physiologic context. Nevertheless, these results do indicate that B. pseudomallei genes selected by this evolutionary approach are associated with diverse subcellular localization patterns.
Fig 1.
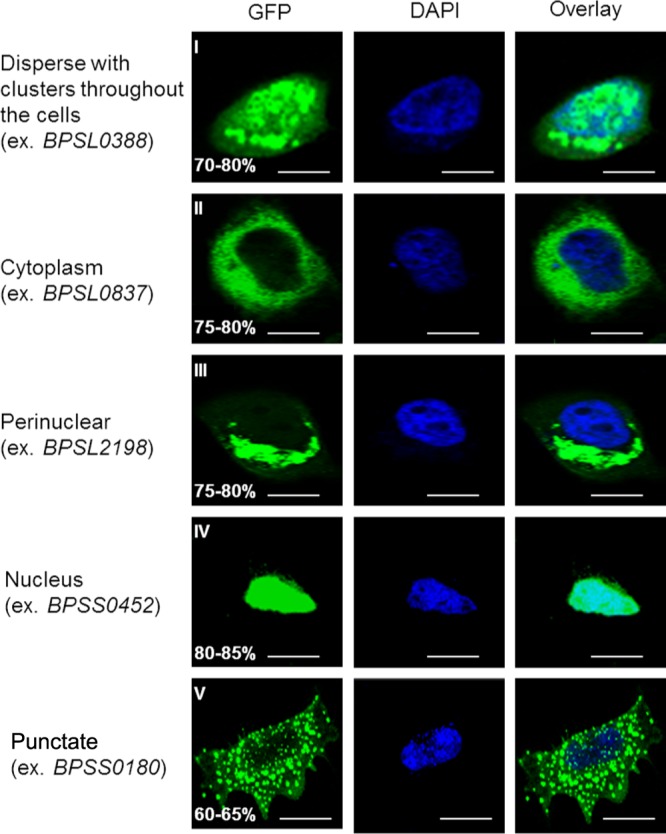
Subcellular localization patterns of proteins encoded by positively selected genes. Representative confocal images of HeLa cells transfected with individual positively selected genes (expressed as GFP fusion proteins [green]) are shown. Cells transfected with positively selected genes exhibited five different types of GFP fusion subcellular localization patterns (I to V). Percentages indicate the proportions of transfected cells with the indicated subcellular localization patterns (n = 100). Results were obtained from three independent experiments. Bars, 10 μm.
Positively selected B. pseudomallei genes induce distinct cellular phenotypes.
Besides differences in subcellular localization, we found that expression of the positively selected B. pseudomallei genes in mammalian cells also induced distinct cellular phenotypes. Intriguingly, several of these phenotypes were reminiscent of cellular phenotypes known to occur in host cells upon B. pseudomallei infection. A few interesting examples are now presented.
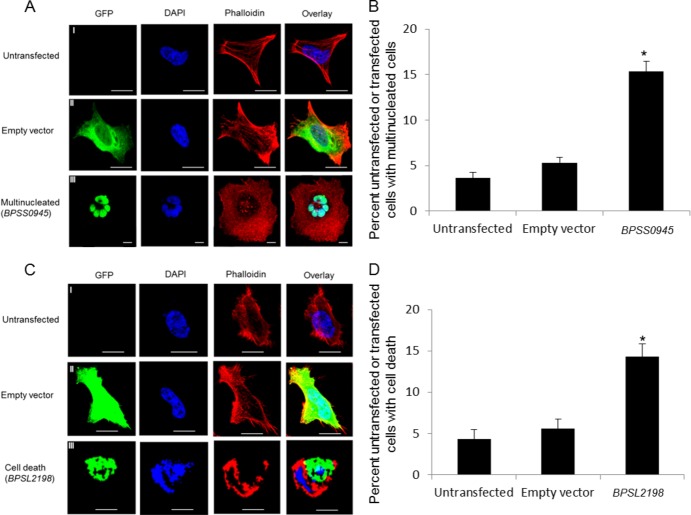
Expression of the GFP-tagged BPSS0945 protein, a predicted peptidase, resulted in a significant (P < 0.05) increase in MNGC formation (15%) compared to that in untransfected cells (3%) or cells transfected with empty vector controls (5%) (Fig. 2A and B). This finding may relate to the ability of B. pseudomallei to induce cell-to-cell fusion facilitating pathogen spread across host cells (23). The GFP-tagged BPSS0945 protein was localized to the nucleus (Fig. 2A; category 4 in Table 1). Interestingly, BPSS0945 sequence analysis revealed the presence of a twin-arginine signal peptide sequence often found in exported proteins (24), the presence of 12 domains related to cell division and chromosome partitioning, and a region exhibiting low homology to human microtubule-associated serine/threonine kinase-like (MASTL) protein. A recent study demonstrated that MASTL plays a key role in M phase, facilitating mitotic entry, anaphase, and cytokinesis (25). These analyses suggest that BPSS0945 may play an important role in MNGC formation.
Fig 2.
Positively selected genes implicated in conferral of different host cell phenotypes. (A) Representative confocal images of untransfected HeLa cells or cells transfected with empty vector (GFP only) or BPSS0945 (GFP tagged). Cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained for nuclei (DAPI; blue) and actin (Phalloidin; red). Untransfected cells or cells transfected with empty vector (rows I and II) did not exhibit any host cell phenotypes. Cells transfected with BPSS0945 exhibited multinucleate giant cell formation (row III). Bars, 10 μm. (B) Quantitative analysis of multinucleate giant cell formation in untransfected cells or cells transfected with empty vector or BPSS0945. Values on the y axis are presented as percentages of the total number of transfected cells (n = 100), obtained from three independent experiments. The asterisk indicates a P value of <0.05 relative to untransfected or empty vector-transfected cells. (C) Cells transfected with BPSL2198 exhibited cell death (row III), in contrast to untransfected cells (row I) or empty vector-transfected cells (row II). Bars, 10 μm. (D) Quantitative analysis of cell death induction in untransfected cells or cells transfected with empty vector or BPSL2198. Values are presented as percentages of the total number of transfected cells (n = 100), obtained from three independent experiments. The asterisk indicates a P value of <0.05 relative to untransfected or empty vector-transfected cells.
Similarly, cells transfected with GFP-tagged BPSL2198 protein, a putative exported phospholipase, exhibited a significant increase (P < 0.05) in nuclear disintegration and cell death in 23% of transected cells, compared to 6% of untransfected cells or 8% of cells transfected with empty vector (Fig. 2C and D). The BPSL2198 protein was localized to the nuclear periphery (category IV). Phospholipases cleave phospholipids, and during infection, many act to disrupt the host cell plasma membrane, leading to host cell lysis or cytotoxicity (26). Sequence analysis of BPSL2198 also revealed a twin-arginine signal peptide sequence and a patatin-like phospholipase domain which is also present in ExoU, a cytotoxin with phospholipase A2 activity found in Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and a known virulence factor (27).
No specific phenotypes were observed in cells transfected with any of the four negative-control genes, which did not exhibit signatures of positive selection. These results, considered alongside the BPSS0180 data described below, suggest that a subset of positively selected genes in B. pseudomallei may functionally contribute to different virulence phenotypes associated with melioidosis.
The BPSS0180 protein, a T6SS protein, induces green puncta that colocalize with the autophagy marker LC3.
The majority (65%) of cells transfected with GFP-tagged BPSS0180 protein exhibited significant green puncta or dot-like structures (category 5) (Fig. 1, row V). BPSS0180 encodes a hypothetical protein but is localized within a type VI secretion system (T6SS) cluster, a recently discovered secretion system essential for virulence in many intracellular bacterial pathogens (28). Notably, T6SS cluster 4, where BPSS0180 resides, is present in both B. pseudomallei and its related pathogenic relative Burkholderia mallei but absent in Burkholderia thailandensis, a closely related Burkholderia species generally considered nonpathogenic to mammals (29). A homology search of BPSS0180 within the B. pseudomallei K96243 genome revealed the presence of three other paralogs (BPSS0110, BPSS2101, and BPSL3100), while a homology search across other microbial genomes revealed that BPSS0180 homologs are also found in other bacterial T6SSs, such as those of Salmonella spp.
Hypothesizing that BPSS0180 might be involved in autophagy induction, we used three different approaches to establish if the green punctate structures induced by the GFP-tagged BPSS0180 protein in HeLa cells might represent autophagy. First, we colabeled cells transfected with GFP-tagged BPSS0180 with LysoTracker, a marker of lysosomes and acidic compartments. We observed colocalization of the punctate structures with LysoTracker (see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material), indicating that the punctate structures induced by BPSS0180 are acidic vesicles consistent with autophagolysosomes (30).
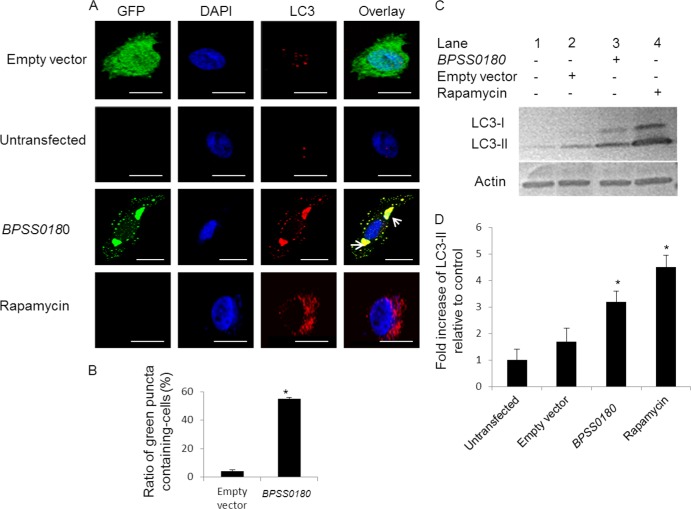
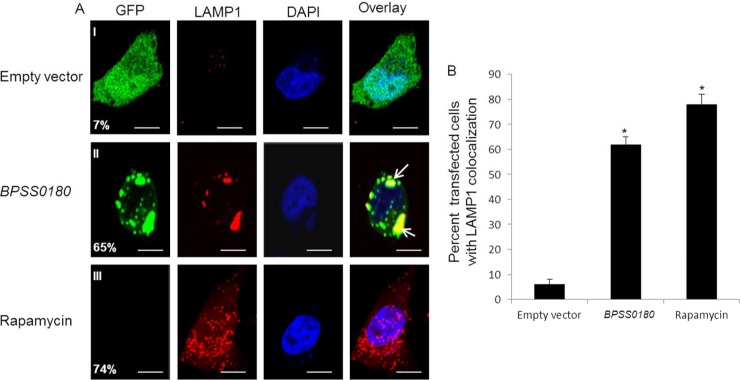
Second, we costained the transfected HeLa cells with anti-LC3 antibodies, as LC3 is a marker of autophagy (31, 32). As a positive control, we observed increased levels of LC3 colocalization with autophagosomes in cells treated with rapamycin, a known inducer of autophagosome formation (Fig. 3). Similarly, we found that cells transfected with GFP-tagged BPSS0180 protein exhibited a significant increase in the percentage of green puncta (35%) colocalizing with LC3 compared to cells transfected with GFP-only vector controls (3%) (Fig. 3). To support the immunofluorescence results, we then measured the conversion of LC3-I to LC3-II by Western blotting to assess if BPSS0180 transfection could stimulate autophagy in host cells: conversion of the cytosolic form of LC3 (LC3-I) to the autophagosomal membrane-associated form (LC3-II) is accepted as a specific indicator of autophagosome formation (30–32). We confirmed an increase in LC3-I-to-LC3-II conversion in HeLa cells after rapamycin treatment (Fig. 3C, lane 4). Likewise, transfecting HeLa cells with GFP-tagged BPSS0180 protein also led to an increase in LC3-II levels (Fig. 3C, lane 3) compared to those in uninfected cells or cells transfected with empty vector controls (Fig. 3C, lanes 1 and 2). Third, GFP-tagged BPSS0180-induced vesicles also showed colocalization with LAMP1 (lysosome-associated membrane glycoprotein 1) (Fig. 4), a lysosomal membrane protein delivered to the autophagosome during maturation (33). Collectively, these results indicate that BPSS0180 expression may induce autophagy in HeLa cells.
Fig 3.
BPSS0180 induces autophagy in HeLa cells. (A) Representative confocal images of HeLa cells transfected with empty vector (green) or GFP-tagged BPSS0180 (green), untransfected cells (untreated), and cells treated with rapamycin. Cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained for nuclei (blue) or LC3 (red). Arrows indicate colocalization of punctate structures with LC3, defined by the presence of green punctate structures in BPSS0180-transfected cells (green) which were fully overlaid by intense red. Bars, 10 μm. (B) Quantitative analysis of green puncta induced by empty vector or BPSS0180 in HeLa cells. (C) Western blots. (Top) LC3 expression of HeLa cells transfected with empty vector or BPSS0180, untransfected cells (untreated), or cells treated with rapamycin. (Bottom) Actin as a loading control. (D) Fold increases in LC3-II were determined by densitometric quantitative comparison of each LC3-II band to the same band in untransfected control cells (lane 2). Each band was normalized against the actin control band. Asterisks indicate P values of <0.05 relative to untransfected control cells.
Fig 4.
BPSS0180-induced puncta colocalize with the lysosome marker LAMP1. (A) Representative confocal images of HeLa cells transfected with empty vector (green) or GFP-tagged BPSS0180 (green) or left untransfected and treated with rapamycin. Cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained for nuclei (blue) and LAMP1 (red), a marker of lysosomes. Arrows indicate cells with punctate structures colocalizing with LAMP1. Colocalization of puncta with LAMP1 was defined by the proportion of green puncta overlapping regions of anti-LAMP1 staining. Bars, 10 μm. (B) Quantitative analysis of cells with LAMP1 punctate structures. Asterisks indicate P values of <0.05 relative to cells transfected with empty vector.
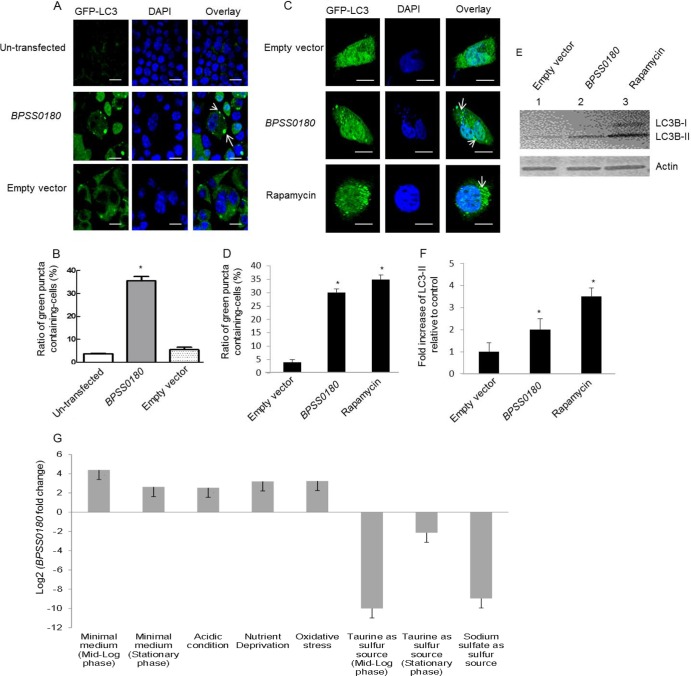
To investigate if the ability of BPSS0180 to induce autophagy is cell type specific, we then expressed GFP-tagged BPSS0180 protein in RAW264.7 macrophage cells. Similar to the case in HeLa cells, extensive colocalization of LC3 with green puncta induced by GFP-tagged BPSS0180 protein was observed in the RAW264.7 cells (see Fig. S2 in the supplemental material), suggesting that BPSS0180 likely induces autophagy in a cell-independent manner. Moreover, to exclude the possibility that the GFP-tagged BPSS0180 construct may be associated with autophagy induction as a consequence of the GFP tag, we then transfected phagocytic (RAW264.7) and nonphagocytic (HeLa) cells, stably and transiently expressing GFP-LC3, respectively, with constructs encoding the non-GFP-tagged BPSS0180 protein. Compared to control cells, the number of cells exhibiting puncta (marked by GFP-LC3) increased significantly when cells were treated with rapamycin (35%) (Fig. 5C and D) or expressed the non-GFP-tagged BPSS0180 protein (30 to 35%) (Fig. 5A to D). We also observed increased conversion of LC3-I to LC3-II in HeLa cells either treated with rapamycin (Fig. 5E, lane 3) or transfected with the non-GFP-tagged BPSS0180 protein (Fig. 5E, lane 1). These results suggest that induction of autophagy by BPSS0180 is independent of its fusion with a GFP tag.
Fig 5.
Plasmid-independent induction of autophagy by BPSS0180 in phagocytic and nonphagocytic cells and BPSS0180 transcriptional regulation. (A) Representative confocal images of RAW264.7 (phagocytic) cells stably expressing GFP-LC3 and transfected with empty vector (pCI-neo) or a construct encoding the BPSS0180 protein or left untransfected. Cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained for nuclei (blue). Arrows indicate cells with GFP-LC3-labeled puncta. Bars, 10 μm. (B) Quantitative analysis of cells with GFP-LC3-labeled puncta. (C) Representative confocal images of HeLa (nonphagocytic) cells transiently expressing GFP-LC3 and transfected with empty vector (pcDNA 3.1/V5-His-TOPO) or His-tagged BPSS0180 or treated with rapamycin. Cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained for nuclei (blue). Arrows indicate cells with GFP-LC3-labeled puncta. Bars, 10 μm. (D) Quantitative analysis of cells with GFP-LC3-labeled puncta. Asterisks indicate P values of <0.05 relative to cells transfected with empty vector or without transfection. (E) Western blots. (Top) LC3 expression of HeLa cells transfected with empty vector or BPSS0180 or treated with rapamycin. (Bottom) Actin as a loading control. (F) Fold increases in LC3-II were determined by densitometric quantitative comparison of each LC3-II band to the same band in the cells transfected with empty vector (lane 1 in panel E). Each band was normalized against the actin control band. Asterisks indicate P values of <0.05 relative to cells transfected with empty vector. (G) Graph depicting BPSS0180 expression across various perturbations (listed below the graph). See Table S2 in the supplemental material for details of experimental and reference conditions. All BPSS0180 expression alterations represent differential regulation, as indicated by a change of ≥2-fold (absolute log2 BPSS0180 fold change of >1) and pass the threshold level of statistical significance (P < 0.001).
To gain insights into potential physiological conditions that might trigger BPSS0180 expression in B. pseudomallei, we consulted an in-house microarray database of B. pseudomallei cells grown under diverse conditions. We observed that BPSS0180 was highly upregulated under starvation conditions (Fig. 5G) and downregulated in nutrient-rich medium where taurine or sodium sulfate was used as a sulfur source. Because autophagy is induced in response to nutrient starvation, these differential expression patterns are consistent with BPSS0180 playing a plausible role in inducing autophagy.
BPSS0180 is required for autophagy induction and contributes to intracellular survival of B. pseudomallei.
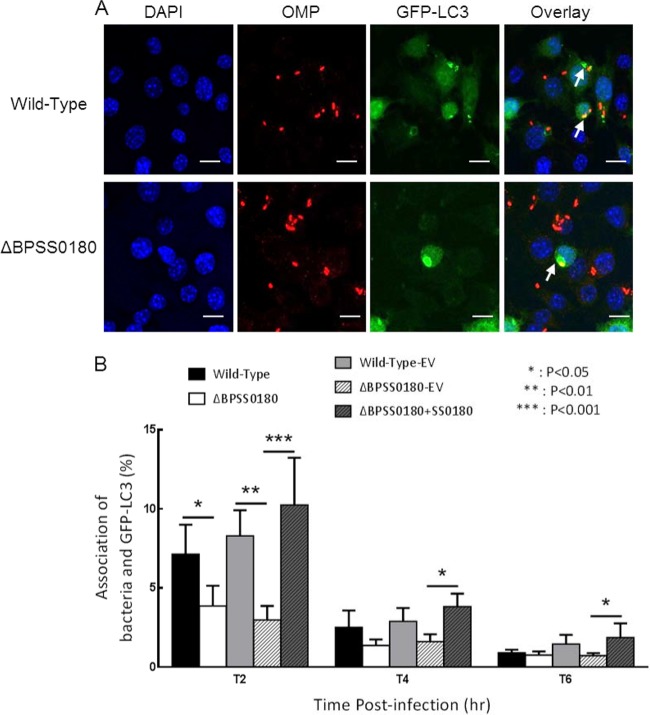
To further analyze the requirement for BPSS0180 in LC3 colocalization of B. pseudomallei, we constructed an in-frame BPSS0180 deletion mutant by allelic exchange using the λpir-dependent vector pDM4 (34). We analyzed the colocalization of GFP-LC3 with either wild-type or BPSS0180 mutant bacteria at different time points following infection of RAW264.7 cells stably expressing GFP-LC3 (Fig. 6A). Using fluorescence microscopy analysis, we observed that BPSS0180 mutant bacteria showed decreased colocalization with LC3 compared to that of the wild type (Fig. 6A). A quantitative analysis confirmed that colocalization of BPSS0180 mutants with LC3 was significantly decreased at 4 h postinfection (Fig. 6B). Complementation of the mutant phenotypes was attempted by expression of a gene cassette amplified by PCR and expressed in pBHR1. Colocalization of mutant bacteria with GFP-LC3 was restored to wild-type levels by the expression of intact BPSS0180 (Fig. 6B). These results suggest that BPSS0180 is involved in autophagy induction.
Fig 6.
Colocalization of bacteria and LC3 in B. pseudomallei-infected RAW264.7 cells expressing GFP-LC3. (A) Confocal images of RAW264.7 cells stably expressing GFP-LC3 (green) and infected with wild-type or BPSS0180 mutant B. pseudomallei. Cells were fixed at 4 h, permeabilized, incubated with rabbit anti-B. pseudomallei outer membrane serum and Texas Red-conjugated goat anti-rabbit immunoglobulin (Ig) antibody (Molecular Probes) for B. pseudomallei detection (red) (10), and stained with DAPI for detection of nuclei (blue). Arrows indicate bacteria colocalizing with GFP-LC3, defined by the presence of labeled B. pseudomallei (red) fully overlaid by an intense green fluorescent ring. Bars, 10 μm. (B) Cells were infected with either wild-type bacteria (Wild-Type), the BPSS0180 mutant (ΔBPSS0180), wild-type bacteria with empty pBHR1 vector (Wild-Type-EV), the BPSS0180 mutant with empty pBHR1 vector (ΔBPSS0180-EV), or the BPSS0180 mutant with a vector-borne BPSS0180 gene cassette (ΔBPSS0180+SS0180). Error bars indicate the standard errors of the means (SEM) for 4 individual experiments, with analysis by two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA).
Moreover, while the BPSS0180 mutant grew normally in vitro (data not shown), the BPSS0180 mutants displayed significantly reduced intracellular survival compared to wild-type bacteria at 6 h postinfection (Fig. 7A). Survival data, presented as relative survival normalized to the 2-h postinfection time point, show that the decreased survival of mutant bacteria at 6 h postinfection was largely restored to that of wild-type bacteria by the expression of BPSS0180 (Fig. 7B). Thus, these results suggest that BPSS0180 may contribute to the intracellular survival of B. pseudomallei.
Fig 7.
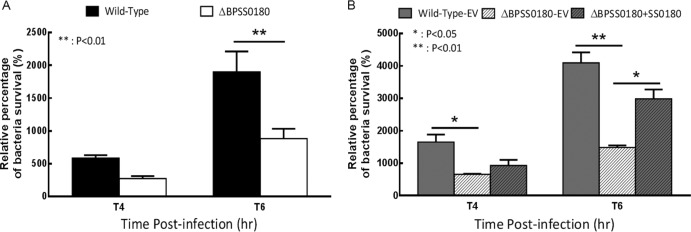
Intracellular survival of B. pseudomallei strains in RAW264.7 cells. Cells were infected with either wild-type bacteria (Wild-Type) or the BPSS0180 mutant (ΔBPSS0180) (A) or with wild-type bacteria with empty pBHR1 vector (Wild-Type-EV), the BPSS0180 mutant with empty pBHR1 vector (ΔBPSS0180-EV), or the BPSS0180 mutant with a vector-borne BPSS0180 gene cassette (ΔBPSS0180+SS0180) (B). Results are presented as relative survival (%) normalized to the CFU at 2 h postinfection. Error bars indicate the standard errors of the means (SEM), with analysis by two-way ANOVA.
Autophagy is a catabolic pathway used by cells to respond to various stresses, including nutrient deprivation (35). The autophagic apparatus also plays an important protective role against several intracellular pathogens, preventing their replication and invasion (6, 7). This is achieved either by using autophagosomes to engulf bacterium-containing phagosomes (36) or by the direct sequestration of bacteria from the cytosol into autophagosomes (37) and subsequent recruitment of LC3 to the bacterium-containing phagosomes, which stimulates phagosome maturation (38). However, certain pathogens, such as Brucella abortus, Coxiella burnetii, and Legionella pneumophila, have evolved mechanisms to subvert autophagic pathways for their own benefit, for example, by creating replication niches within autophagosomes, where they can multiply and survive (10–12).
In the case of B. pseudomallei intracellular infection, we have previously shown that B. pseudomallei organisms are present primarily as either free bacteria in the host cytoplasm or within single-membrane phagosomes. Indeed, in our hands, only 1 of 500 B. pseudomallei organisms in cells were observed within a double-membrane compartment that might be considered an autophagosome (14). These findings demonstrate that B. pseudomallei is likely not efficiently targeted by canonical double-membrane autophagosomes via direct sequestration of free bacteria in cytosol (37) or engulfment of bacterium-containing phagosomes (36) and that canonical autophagy is rarely involved in the clearance of B. pseudomallei (14). In contrast to canonical autophagy, we found that LC3 is recruited to B. pseudomallei-containing phagosomes (14), suggesting that LAP (LC3-associated phagocytosis) (38), rather than canonical autophagy, is the mechanism which macrophage cells use in defense against B. pseudomallei infection (14). Interestingly, we also found that mere retention of bacteria within phagosomes is insufficient for LAP to occur, as heat-killed B. pseudomallei showed dramatically reduced colocalization with LC3 (14). This last observation suggests that LAP induction is likely to require another bacterial factor(s) produced by, or present on, live bacteria (14). Because BPSS0180 is associated with a type VI secretion system, we speculate that BPSS0180 may encode a structural or secreted protein that triggers B. pseudomallei-induced autophagy. Some recent studies have shown that bacterial proteins can induce autophagy: for example, the cell membrane-associated lipoprotein LpqH of Mycobacterium tuberculosis has been reported to activate autophagy in human monocytes (39), listeriolysin O (LLO) secreted by Listeria monocytogenes can induce autophagy during infection (40), and VopQ, a type III secretion system effector secreted by Vibrio parahaemolyticus, is necessary and sufficient for autophagy induction during infection (41). However, in the first two examples, it is antibacterial autophagy that is induced (39, 40), and in the third case, autophagy contributes to a novel mechanism to manipulate the host cellular response to infection which is not directly targeted to the infecting bacteria (41) but seems to be associated with suppression of the NLRC4 inflammasome (42). Our results suggest that BPSS0180 does not induce either antibacterial autophagy or LC3 recruitment to B. pseudomallei-containing phagosomes (LAP), as in mutant bacteria lacking BPSS0180 the colocalization of bacteria with LC3 is decreased. Our hypothesis is that BPSS0180 induces canonical autophagy targeted to host cellular components in order to provide a survival advantage to B. pseudomallei through increased production of host nutrient resources, facilitating its intracellular replication. However, a detailed understanding of the cellular localization and biochemical function of the BPSS0180 protein remains unknown, and further studies are warranted to determine its specific role in intracellular survival.
In conclusion, in this study we identified the BPSS0180 protein, an uncharacterized protein of B. pseudomallei that is subject to positive selection and has the ability to induce autophagy in mammalian cells. BPSS0180 mutants demonstrated reduced intracellular survival, suggesting that BPSS0810 may contribute to B. pseudomallei virulence. It is possible that BPSS0180 may induce canonical autophagy targeted to host cellular components rather than to intracellular bacteria, which in principle might provide a survival advantage to B. pseudomallei through increased production of host nutrient resources for intracellular replication. More generally, our results suggest that undertaking an evolutionary analysis of multiple pathogen genomes may reveal novel targets regulating pathogenesis in B. pseudomallei and other recently emerging pathogens.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by a core grant to the Genome Institute of Singapore from the Agency for Science, Technology, and Research of Singapore (P.T.) and by funding provided by the Australian Research Council (B.A. and R.J.D.).
Footnotes
Published ahead of print 4 October 2013
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JB.00718-13.
REFERENCES
- 1.Wiersinga WJ, van der Poll T, White NJ, Day NP, Peacock SJ. 2006. Melioidosis: insights into the pathogenicity of Burkholderia pseudomallei. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 4:272–282 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Holden MT, Titball RW, Peacock SJ, Cerdeño-Tárraga AM, Atkins T, Crossman LC, Pitt T, Churcher C, Mungall K, Bentley SD, Sebaihia M, Thomson NR, Bason N, Beacham IR, Brooks K, Brown KA, Brown NF, Challis GL, Cherevach I, Chillingworth T, Cronin A, Crossett B, Davis P, DeShazer D, Feltwell T, Fraser A, Hance Z, Hauser H, Holroyd S, Jagels K, Keith KE, Maddison M, Moule S, Price C, Quail MA, Rabbinowitsch E, Rutherford K, Sanders M, Simmonds M, Songsivilai S, Stevens K, Tumapa S, Vesaratchavest M, Whitehead S, Yeats C, Barrell BG, Oyston PC, Parkhill J. 2004. Genomic plasticity of the causative agent of melioidosis, Burkholderia pseudomallei. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101:14240–14245 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Allwood EM, Devenish RJ, Prescott M, Adler B, Boyce JD. 2011. Strategies for intracellular survival of Burkholderia pseudomallei. Front. Microbiol. 2:170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Rabinowitz JD, White 2010. Autophagy and metabolism. Science 330:1344–1348 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Levine B, Mizushima N, Virgin HW. 2011. Autophagy in immunity and inflammation. Nature 469:323–335 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Orvedahl A, Levine B. 2009. Eating the enemy within: autophagy in infectious diseases. Cell Death Differ. 16:57–69 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Knodler LA, Celli J. 2011. Eating the strangers within: host control of intracellular bacteria via xenophagy. Cell. Microbiol. 13:1319–1327 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Deretic V, Levine B. 2009. Autophagy, immunity, and microbial adaptations. Cell Host Microbe 5:527–549 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ogawa M, Mimuro H, Yoshikawa Y, Ashida H, Sasakawa C. 2011. Manipulation of autophagy by bacteria for their own benefit. Microbiol. Immunol. 55:459–471 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Celli J, de Chastellier C, Franchini DM, Pizarro Cerda J, Moreno E, Gorvel JP. 2003. Brucella evades macrophage killing via VirB-dependent sustained interactions with the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Exp. Med. 198:545–556 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kirkegaard K, Taylor MP, Jackson WT. 2004. Cellular autophagy: surrender, avoidance and subversion by microorganisms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2:301–314 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Amer AO, Swanson MS. 2005. Autophagy is an immediate macrophage response to Legionella pneumophila. Cell. Microbiol. 7:765–778 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Cullinane M, Gong L, Li X, Lazar-Adler N, Tra T, Wolvetang E, Prescott M, Boyce JD, Devenish RJ, Adler B. 2008. Stimulation of autophagy suppresses the intracellular survival of Burkholderia pseudomallei in mammalian cell lines. Autophagy 4:744–753 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gong L, Cullinane M, Treerat P, Ramm G, Prescott M, Adler B, Boyce JD, Devenish RJ. 2011. The Burkholderia pseudomallei type III secretion system and BopA are required for evasion of LC3-associated phagocytosis. PLoS One 6:e17852. 10.1371/journal.pone.0017852 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Nandi T, Ong C, Singh AP, Boddey J, Atkins T, Sarkar-Tyson M, Essex-Lopresti AE, Chua HH, Pearson T, Kreisberg JF, Nilsson C, Ariyaratne P, Ronning C, Losada L, Ruan Y, Sung WK, Woods D, Titball RW, Beacham I, Peak I, Keim P, Nierman WC, Tan P. 2010. A genomic survey of positive selection in Burkholderia pseudomallei provides insights into the evolution of accidental virulence. PLoS Pathog. 6:e1000845. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000845 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yang Z. 2007. PAML 4: phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol. Biol Evol. 24:1586–1591 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Anisimova M, Bielawski JP, Yang Z. 2001. Accuracy and power of the likelihood ratio test in detecting adaptive molecular evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 18:1585–1592 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Milton DL, O'Toole R, Horstedt P, Wolf-Watz H. 1996. Flagellin A is essential for the virulence of Vibrio anguillarum. J. Bacteriol. 178:1310–1319 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.D'Cruze T, Gong L, Treerat P, Ramm G, Boyce JD, Prescott M, Adler B, Devenish RJ. 2011. Role for the Burkholderia pseudomallei type three secretion system cluster 1 bpscN gene in virulence. Infect. Immun. 79:3659–3664 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Warawa J, Woods DE. 2005. Type III secretion system cluster 3 is required for maximal virulence of Burkholderia pseudomallei in a hamster infection model. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 242:101–108 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Finlay BB, Cossart P. 1997. Exploitation of mammalian host cell functions by bacterial pathogens. Science 276:718–725 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bhavsar AP, Guttman JA, Finlay BB. 2007. Manipulation of host-cell pathways by bacterial pathogens. Nature 449:827–834 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kespichayawattana W, Rattanachetkul S, Wanun T, Utaisincharoen P, Sirisinha S. 2000. Burkholderia pseudomallei induces cell fusion and actin-associated membrane protrusion: a possible mechanism for cell-to-cell spreading. Infect. Immun. 68:5377–5384 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.De Buck E, Lammertyn E, Anné J. 2008. The importance of the twin-arginine translocation pathway for bacterial virulence. Trends Microbiol. 16:442–453 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Voets E, Wolthuis RM. 2010. MASTL is the human orthologue of Greatwall kinase that facilitates mitotic entry, anaphase and cytokinesis. Cell Cycle 9:3591–3601 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Istivan TS, Coloe PJ. 2006. Phospholipase A in Gram-negative bacteria and its role in pathogenesis. Microbiology 152:1263–1274 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Phillips RM, Six DA, Dennis EA, Ghosh P. 2003. In vivo phospholipase activity of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa cytotoxin ExoU and protection of mammalian cells with phospholipase A2 inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 278:41326–41332 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Shalom G, Shaw JG, Thomas MS. 2007. In vivo expression technology identifies a type VI secretion system locus in Burkholderia pseudomallei that is induced upon invasion of macrophages. Microbiology 153:2689–2699 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Schell MA, Ulrich RL, Ribot WJ, Brueggemann EE, Hines HB, Chen D, Lipscomb L, Kim HS, Mrázek J, Nierman WC, Deshazer D. 2007. Type VI secretion is a major virulence determinant in Burkholderia mallei. Mol. Microbiol. 64:1466–1485 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Ueno T, Yamamoto A, Kirisako T, Noda T, Kominami E, Ohsumi Y, Yoshimori T. 2000. LC3, a mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome membranes after processing. EMBO J. 19:5720–5728 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bampton ET, Goemans CG, Niranjan D, Mizushima N, Tolkovsky AM. 2005. The dynamics of autophagy visualized in live cells: from autophagosome formation to fusion with endo/lysosomes. Autophagy 1:23–36 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Mizushima N, Yoshimori T, Levine B. 2010. Methods in mammalian autophagy research. Cell 140:313–326 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Huynh KK, Eskelinen EL, Scott CC, Malevanets A, Saftig P, Grinstein S. 2007. LAMP proteins are required for fusion of lysosomes with phagosomes. EMBO J. 26:313–324 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.de Lorenzo V, Herrero M, Jakubzik U, Timmis KN. 1990. Mini-Tn5 transposon derivatives for insertion mutagenesis, promoter probing, and chromosomal insertion of cloned DNA in gram-negative eubacteria. J. Bacteriol. 172:6568–6572 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Yorimitsu T, Klionsky DJ. 2005. Autophagy: molecular machinery for self-eating. Cell Death Differ. 2:1542–1552 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Gutierrez MG, Master SS, Singh SB, Taylor GA, Colombo MI, Deretic V. 2004. Autophagy is a defense mechanism inhibiting BCG and Mycobacterium tuberculosis survival in infected macrophages. Cell 119:753–766 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ogawa M, Yoshimori T, Suzuki T, Sagara H, Mizushima N, Sasakawa C. 2005. Escape of intracellular Shigella from autophagy. Science 307:727–731 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sanjuan MA, Dillon CP, Tait SW, Moshiach S, Dorsey F, Connell S, Komatsu M, Tanaka K, Cleveland JL, Withoff S, Green DR. 2007. Toll-like receptor signalling in macrophages links the autophagy pathway to phagocytosis. Nature 450:1253–1257 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Shin DM, Yuk JM, Lee HM, Lee SH, Son JW, Harding CV, Kim JM, Modlin RL, Jo EK. 2010. Mycobacterial lipoprotein activates autophagy via TLR2/1/CD14 and a functional vitamin D receptor signalling. Cell. Microbiol. 12:1648–1665 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Meyer-Morse N, Robbins JR, Rae CS, Mochegova SN, Swanson MS, Zhao Z, Virgin HW, Portnoy D. 2010. Listeriolysin O is necessary and sufficient to induce autophagy during Listeria monocytogenes infection. PLoS One 5:e8610. 10.1371/journal.pone.0008610 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Burdette DL, Seemann J, Orth K. 2009. Vibrio VopQ induces PI3-kinase-independent autophagy and antagonizes phagocytosis. Mol. Microbiol. 73:639–649 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Higa N, Toma C, Koizumi Y, Nakasone N, Nohara T, Masumoto J, Kodama T, Iida T, Suzuki T. 2013. Vibrio parahaemolyticus effector proteins suppress inflammasome activation by interfering with host autophagy signaling. PLoS Pathog. 9:e1003142. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003142 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.