Abstract
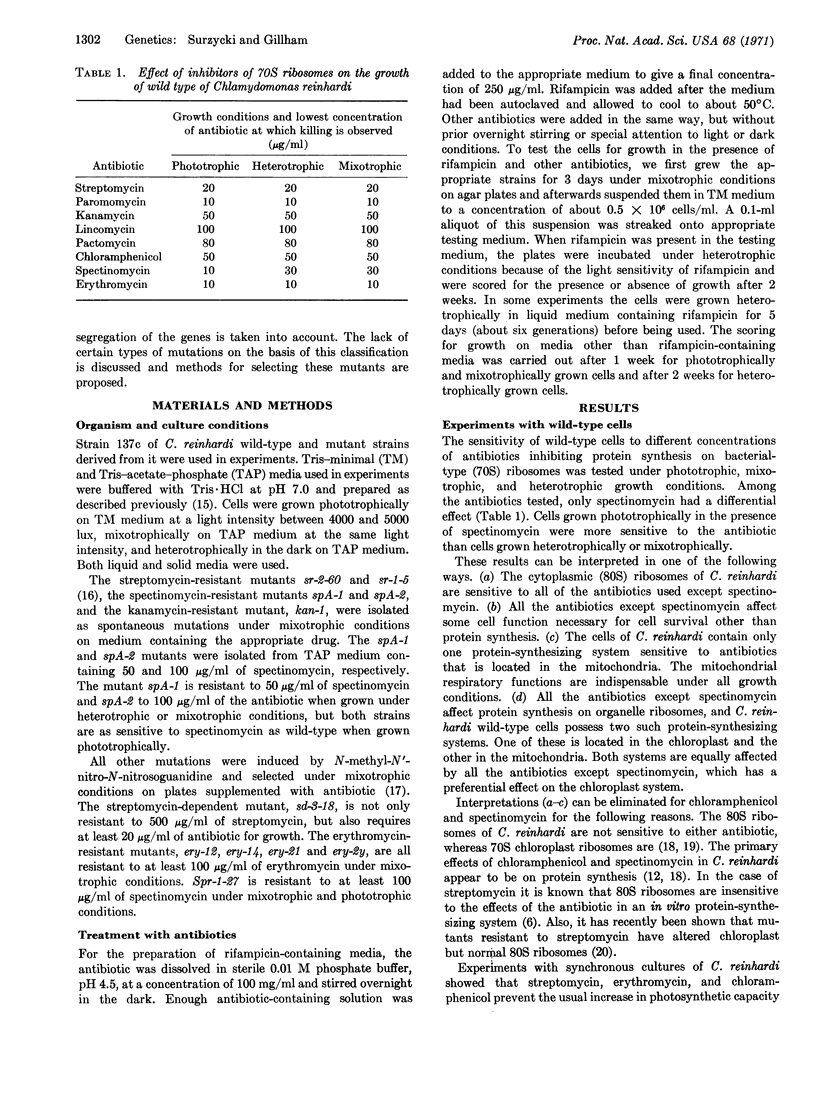
A new method for classifying Mendelian and non-Mendelian antibiotic-resistant mutants in Chlamydomonas reinhardi is proposed. This classification takes into account the cellular site of expression of the resistant phenotype, the location of genetic information for resistance in the cell, and the pattern of inheritance of the different mutants. The classification is consistent with the idea that C. reinhardi contains three protein-synthesizing systems, two of which are sensitive to antibacterial antibiotics and located in the chloroplast and mitochondria, respectively. The information for resistance can be coded either in the chloroplast, the mitochondria, or the nucleus. A new experimental approach to the problem of cellular localization of mutations to antibiotic resistance is prescribed and used for the classification of known resistant mutations.
Keywords: protein-synthesizing systems, antibiotics
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. J., Moll B., Surzycki S. J., Levine R. P. Genetic transcription and translation specifying chloroplast components in Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Biochemistry. 1971 Feb 16;10(4):692–701. doi: 10.1021/bi00780a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang K. S. Physical conservation of parental cytoplasmic DNA through meiosis in Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 May;60(1):194–200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.1.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen D., Deutsch J., Netter P., Petrochilo E., Slonimski P. P. Mitochondrial genetics. I. Methodology and phenomenology. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1970;24:449–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillham N. W., Boynton J. E., Burkholder B. Mutations altering chloroplast ribosome phenotype in Chlamydomonas. I. Non-mendelian mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):1026–1033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.1026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillham N. W. Induction of chromosomal and nonchromosomal mutations in Chlamydomonas reinhardi with N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine. Genetics. 1965 Sep;52(3):529–537. doi: 10.1093/genetics/52.3.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoober J. K., Blobel G. Characterization of the chloroplastic and cytoplasmic ribosomes of Chlamydomonas reinhardi. J Mol Biol. 1969 Apr 14;41(1):121–138. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90130-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAGER R. Genetic systems in Chlamydomonas. Science. 1960 Nov 18;132(3438):1459–1465. doi: 10.1126/science.132.3438.1459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sager R., Ramanis Z. A genetic map of non-Mandelian genes in Chlamydomonas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Mar;65(3):593–600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.3.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmer O., Arnold C. G. Uber die Zahl der Kopien eines ausserkaryotischen Gens bei Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;107(4):366–371. doi: 10.1007/BF00441198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmer O., Arnold C. G. Untersuchungen zur Lokalisation eines ausserkaryotischen Gens bei Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Arch Mikrobiol. 1969;66(2):199–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surzycki S. J. Genetic functions of the chloroplast of Chlamydomonas reinhardi: effect of rifampin on chloroplast DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1327–1334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


