Abstract
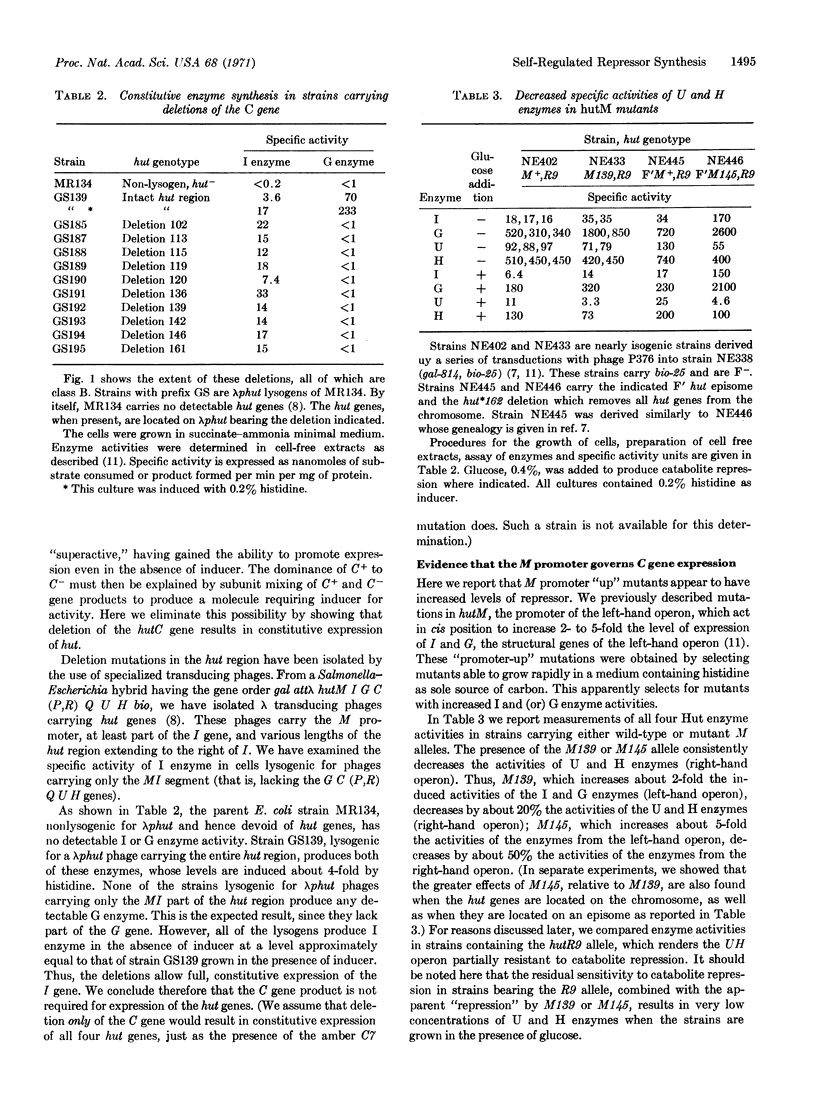
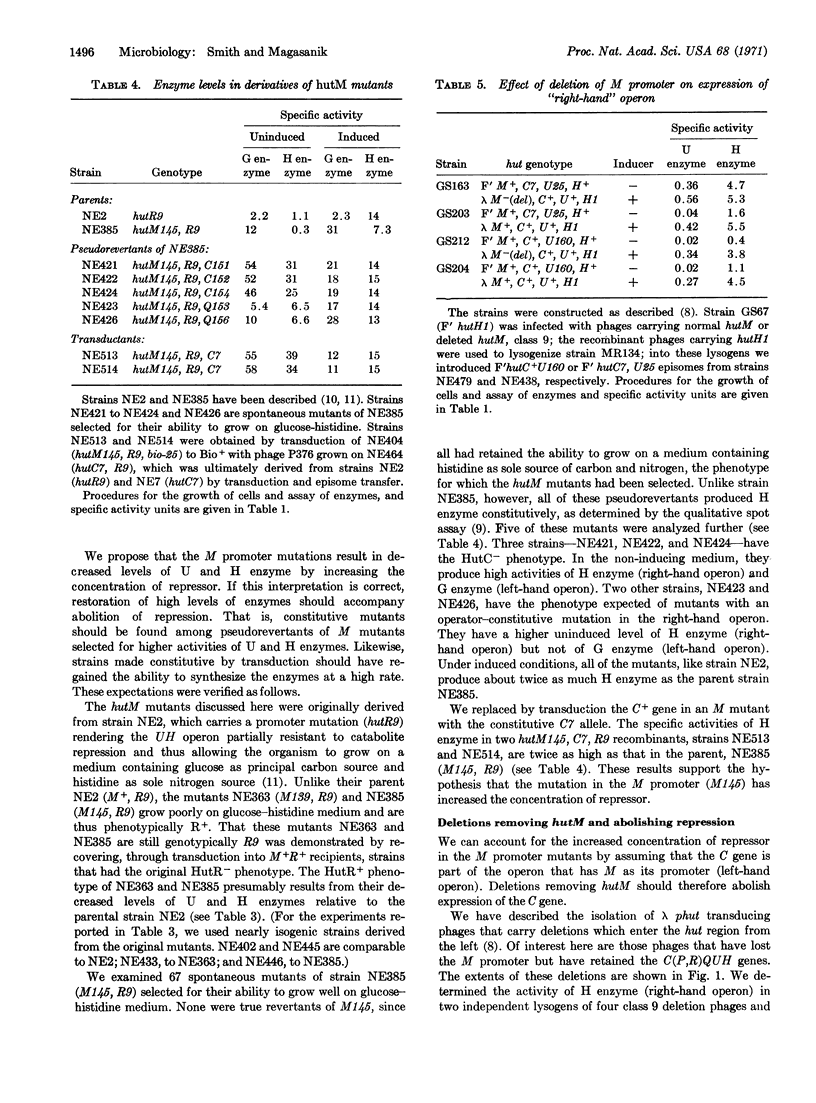
The enzymes mediating histidine utilization, coded by the hut genes, in Salmonella typhimurium are synthesized from two closely-linked operons. Results presented in this paper show that these operons are regulated by a single repressor protein. The hutC gene, coding for this repressor, is part of one of the operons. Since this same operon is sensitive to the repressor, the repressor apparently represses its own synthesis.
Keywords: histidine utilization, phage λ, transduction
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brill W. J., Magasanik B. Genetic and metabolic control of histidase and urocanase in Salmonella typhimurium, strain 15-59. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 10;244(19):5392–5402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen H., Brachet P., Pereira da Silva L., Jacob F. Regulation of repressor expression in lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):855–862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAREN A., OTSUJI N. ISOLATION OF A PROTEIN SPECIFIED BY A REGULATOR GENE. J Mol Biol. 1964 Jun;8:841–852. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80165-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garen A. Sense and nonsense in the genetic code. Three exceptional triplets can serve as both chain-terminating signals and amino acid codons. Science. 1968 Apr 12;160(3824):149–159. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3824.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W., Müller-Hill B. Isolation of the lac repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Dec;56(6):1891–1898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.6.1891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meiss H. K., Brill W. J., Magasanik B. Genetic control of histidine degradation in Salmonella typhimurium, strain LT-2. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 10;244(19):5382–5391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVICK A., MCCOY J. M., SADLER J. R. THE NON-INDUCIBILITY OF REPRESSOR FORMATION. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jun;12:328–330. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80256-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim A. B., Neubauer Z., Calef E. The antirepressor: a new element in the regulation of protein synthesis. Nature. 1970 Apr 4;226(5240):31–32. doi: 10.1038/226031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pero J. Location of the phage lambda gene responsible for turning off lambda-exonuclease synthesis. Virology. 1970 Jan;40(1):65–71. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90379-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R., Halpern Y. S., Magasanik B. Genetic and metabolic control of enzymes responsible for histidine degradation in Salmonella typhimurium. 4-imidazolone-5-propionate amidohydrolase and N-formimino-L-glutamate formiminohydrolase. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3320–3329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R., Magasanik B. The two operons of the histidine utilization system in Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3330–3341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


