Abstract
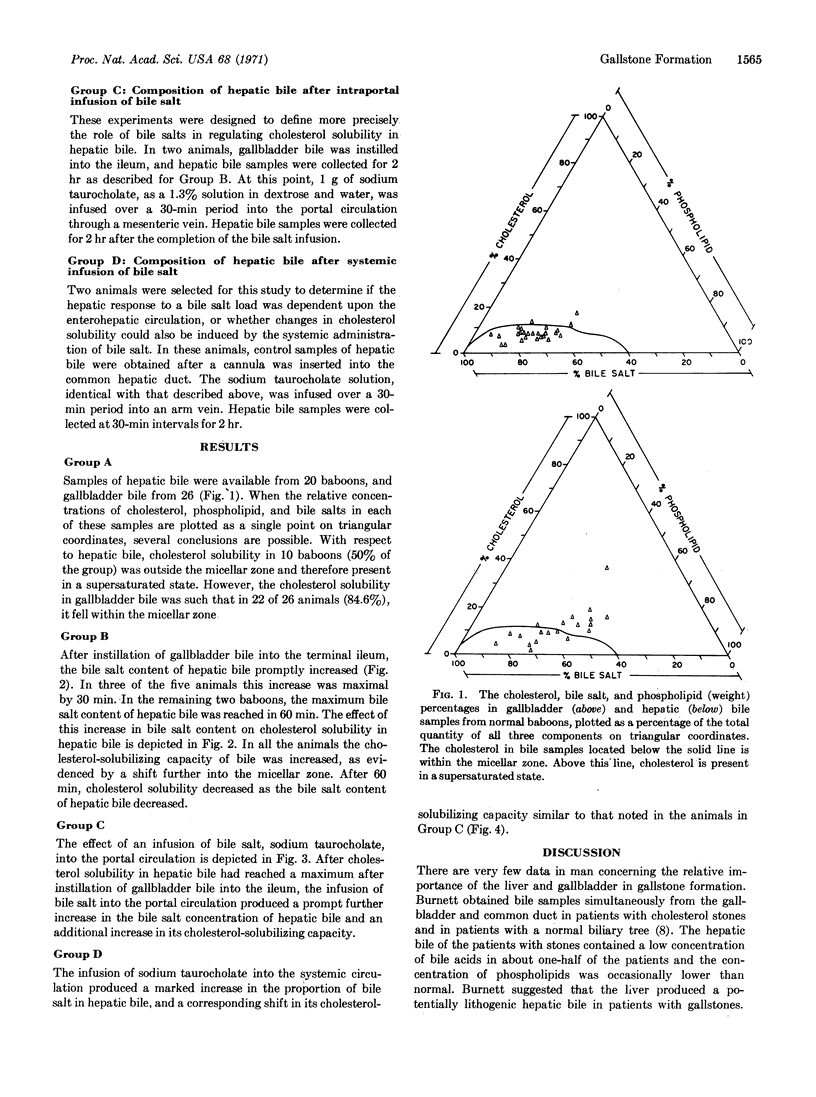
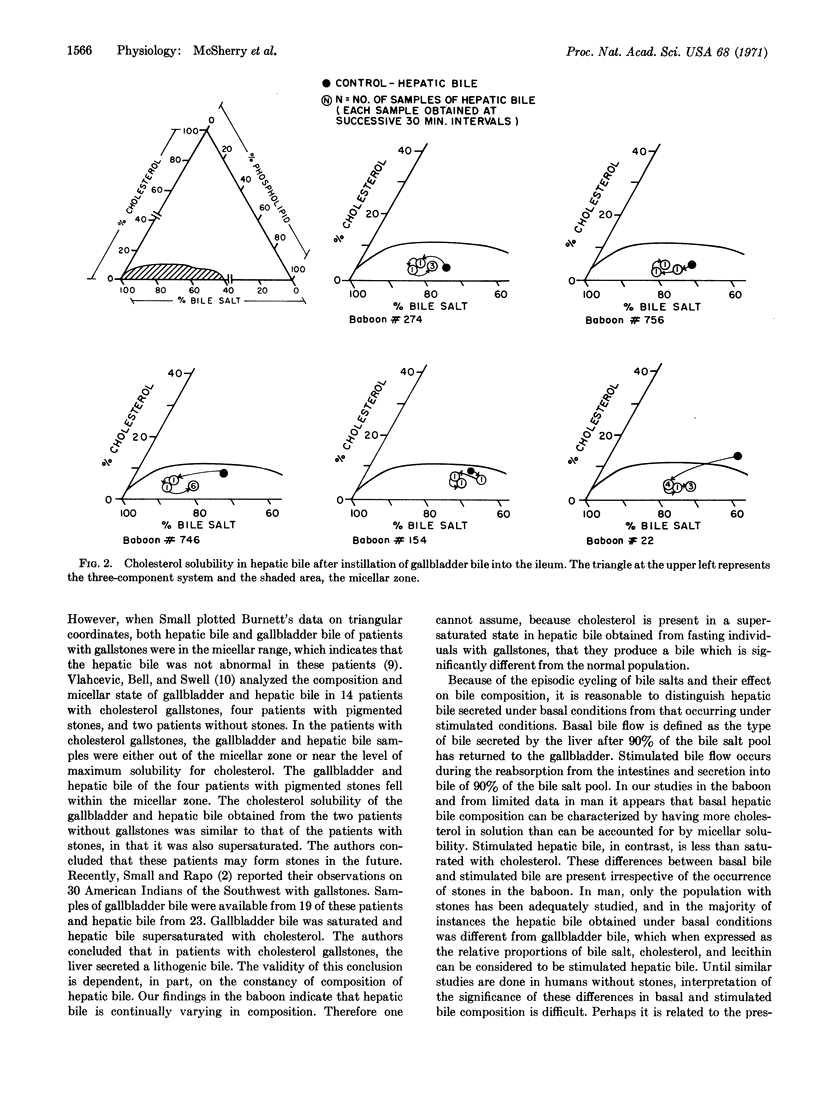
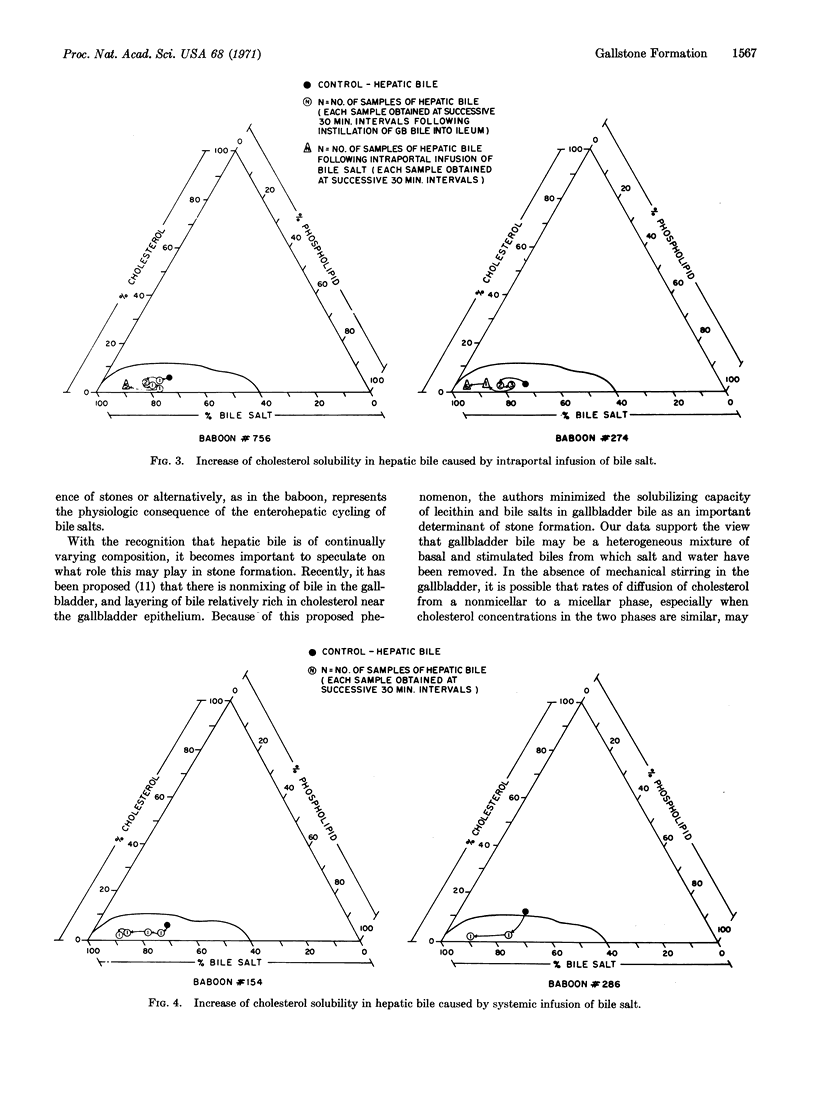
The baboon, Papio, has been found to be a model for the study of the pathogenesis of cholesterol cholelithiasis in man. Studies of the physiologic variations in hepatic bile composition indicate a cyclic pattern to the proportions of cholesterol, lecithin, and bile salt in hepatic bile. During reabsorption of the bile salt pool from the intestines (stimulated flow), hepatic bile is characteristically undersaturated with cholesterol. After reabsorption of the bile salt pool (basal flow), hepatic bile is characteristically supersaturated with cholesterol. This typical pattern of basal and stimulated hepatic bile occurs irrespective of the presence of cholesterol stones in the baboon. Recognition of these two types of hepatic bile and their interrelationship during admixture in the gallbladder provides new insight into the pathogenesis of gallstone formation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Admirand W. H., Small D. M. The physicochemical basis of cholesterol gallstone formation in man. J Clin Invest. 1968 May;47(5):1043–1052. doi: 10.1172/JCI105794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali S. S., Javitt N. B. Quantitative estimation os bile salts in serum. Can J Biochem. 1970 Sep;48(9):1054–1057. doi: 10.1139/o70-166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cussler E. L., Evans D. F., DePalma R. G. A model for gallbladder function and cholesterol gallstone formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):400–407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dam H., Kruse I., Kallehauge H. E., Hartkopp O. E., Jensen M. K. Studies on human bile. I. Composition of bladder bile from cholelithiasis patients and surgical patients with normal bile compared with data for bladder bile of hamsters on different diets. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1966;18(4):385–404. doi: 10.3109/00365516609113159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn F., McSherry C. K. The baboon and experimental cholelithiasis. Arch Surg. 1970 Jan;100(1):105–108. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1970.01340190107025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javitt N. B., Emerman S. Effect of sodium taurolithocholate on bile flow and bile acid exeretion. J Clin Invest. 1968 May;47(5):1002–1014. doi: 10.1172/JCI105790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSherry C. K., Javitt N. B., De Carvalho J. M., Glenn F. Cholesterol gallstones and the chemical composition of bile in baboons. Ann Surg. 1971 Apr;173(4):569–577. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197104000-00014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. M. Gallstones. N Engl J Med. 1968 Sep 12;279(11):588–593. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196809122791106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. M., Rapo S. Source of abnormal bile in patients with cholesterol gallstones. N Engl J Med. 1970 Jul 9;283(2):53–57. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197007092830201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlahcevic Z. R., Bell C., Jr, Swell L. Significance of the liver in the production of lithogenic bile in man. Gastroenterology. 1970 Jul;59(1):62–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


