Abstract
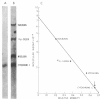
Escherichia coli ribosomes washed with 1 M NH4Cl were found to function as acceptor for leucine and phenylalanine in the reaction catalyzed by leucyl, phenylalanyl-tRNA:protein transferase. When isolated subunits were acylated with [14C]phenylalanine and reisolated by gradient centrifugation, the recovered 30S particles had a specific radioactivity nearly 30 times that of similarly treated 50S particles. Autoradiography of gels, which contained protein from acylated 30S particles, that had been subjected to electrophoresis in 8 M urea and in sodium dodecyl sulfate, suggested that acceptor activity was largely due to a single protein with a molecular weight of about 12,000. Leucine and phenylalanine residues that had been transferred to ribosomal protein were reactive with fluorodinitrobenzene and were released as leucyl- or phenylalanylarginine after treatment with trypsin.
The results indicate that leucyl, phenylalanyl-tRNA: protein transferase catalyzes the addition of these amino acids to an NH2-terminal arginine residue of a specific ribosomal protein on the 30S subunit.
Keywords: subunits, gel electrophoresis, gradient centrifugation, E. coli
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FRAENKEL-CONRAT H., HARRIS J. I., LEVY A. L. Recent developments in techniques for terminal and sequence studies in peptides and proteins. Methods Biochem Anal. 1955;2:359–425. doi: 10.1002/9780470110188.ch12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosclaude F., Mercier J. C., Ribadeau-Dumas B. Structure primaire de la caséine alpha-s1 bovine. Localisation des peptides trypsiques dans les fragments obtenus par hydrolyse trypsique de la caséine maléylée. Eur J Biochem. 1970 May 1;14(1):98–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00266.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki K., Sabol S., Wahba A. J., Ochoa S. Translation of the genetic message. VII. Role of initiation factors in formation of the chain initiation complex with Escherichia coli ribosomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 May;125(2):542–547. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90612-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAJI A., KAJI H., NOVELLI G. D. SOLUBLE AMINO ACID-INCORPORATING SYSTEM. II. SOLUBLE NATURE OF THE SYSTEM AND THE CHARACTERIZATION OF THE RADIOACTIVE PRODUCT. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1192–1197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz M. J., Soffer R. L. Enzymatic modification of proteins. 3. Purification and properties of a leucyl, phenylalanyl transfer ribonucleic acid protein transferase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1970 Apr 25;245(8):2066–2073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz M. J., Soffer R. L. Enzymatic modification of proteins. VI. Site of acylation of bovine serum albumin in the leucine, phenylalanine-transfer reaction. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 25;246(14):4431–4438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANS R. J., NOVELLI G. D. A convenient, rapid and sensitive method for measuring the incorporation of radioactive amino acids into protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1960 Nov;3:540–543. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(60)90171-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANS R. J., NOVELLI G. D. A convenient, rapid and sensitive method for measuring the incorporation of radioactive amino acids into protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1960 Nov;3:540–543. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(60)90171-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHAEI J. H., NIRENBERG M. W. Characteristics and stabilization of DNAase-sensitive protein synthesis in E. coli extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Oct 15;47:1580–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.10.1580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momose K., Kaji A. Soluble amino acid-incorporating system. 3. Further studies on the product and its relation to the ribosomal system for incorporation. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 25;241(14):3294–3307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otaka E., Osawa S. The incorporation of amino acids into proteins of chloramphenicol particles in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Apr 18;119(1):146–159. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soffer R. L. Enzymatic modification of proteins. II. Purification and properties of the arginyl transfer ribonucleic acid-protein transferase from rabbit liver cytoplasm. J Biol Chem. 1970 Feb 25;245(4):731–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soffer R. L. Enzymatic modification of proteins. V. Protein acceptor specificity in the arginine-transfer reaction. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1602–1606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soffer R. L., Horinishi H., Leibowitz M. J. The aminoacyl tRNA-protein transferases. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:529–533. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub P., Nomura M. Structure and function of Escherichia coli ribosomes. I. Partial fractionation of the functionally active ribosomal proteins and reconstitution of artificial subribosomal particles. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jun 28;34(3):575–593. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90182-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLER J. P. THE NH2-TERMINAL RESIDUES OF THE PROTEINS FROM CELL-FREE EXTRACTS OF E. COLI. J Mol Biol. 1963 Nov;7:483–496. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80096-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]