Abstract
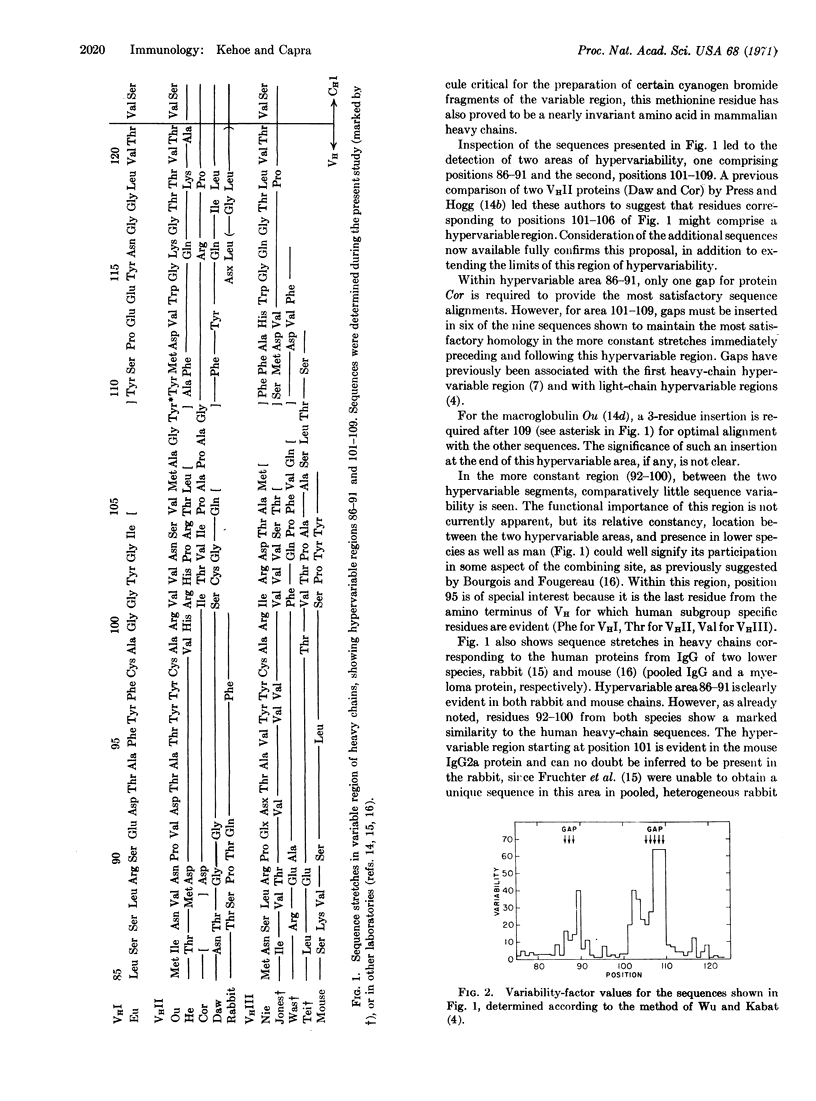
Cyanogen bromide fragments were isolated from the heavy chains of three human IgG myeloma proteins of the VHIII subgroup, sequenced by an automated method, and localized to the variable region. Inspection of these sequences, together with corresponding stretches from both human and animal proteins (studied in other laboratories) led to the detection of two additional hypervariable regions characteristic of the VH segment of immunoglobulin heavy chains. These areas of hypervariability, involving heavy-chain residues 86-91 and 101-109, were separated by a region of relative constancy. The close relationship of these two hypervariable regions, and the previously described first heavy-chain hypervariable region (residues 31-37), to the first heavy-chain disulphide bridge implies that the three hypervariable areas might be in close steric approximation in native immunoglobulin molecules.
Examination of the sequences of the terminal portion of VH of all these proteins (the segment from residue 95 to the beginning of homology region CHl) revealed that no subgroup-specific residues could be identified in this area. Thus, heavy-chain subgroup distinctions may not extend through the entire variable region.
Keywords: myeloma proteins, antigen-antibody specificity, human, amino acid sequences
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bourgois Alain, Fougereau Michel. Partial amino acid sequence of the variable region of a mouse gammaG2a immunoglobulin heavy chain. Evidence for the existence of a third sub-group of variability for the heavy chain pool. FEBS Lett. 1970 Jun 27;8(5):265–268. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80283-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Kunkel H. G. Amino acid sequence similarities in two human anti gamma globulin antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):87–92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. A., Pflumm M. N., Rutishauser U., Edelman G. M. Subgroups of amino acid sequences in the variable regions of immunoglobulin heavy chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Nov;64(3):997–1003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.3.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fruchter R. G., Jackson S. A., Mole L. E., Porter R. R. Sequence studies of the Fd section of the heavy chain of rabbit immunoglobulin G. Biochem J. 1970 Jan;116(2):249–259. doi: 10.1042/bj1160249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS E., WITKOP B. Nonenzymatic cleavage of peptide bonds: the methionine residues in bovine pancreatic ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jun;237:1856–1860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Metzger H. Affinity labeling of a mouse myeloma protein which binds nitrophenyl ligands. Sequence and position of a labeled tryptic peptide. Biochemistry. 1970 Sep 29;9(20):3862–3871. doi: 10.1021/bi00822a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., Talmage D. W. Mechanism of antibody diversity: germ line basis for variability. Science. 1970 Apr 17;168(3929):325–334. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3929.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabat E. A. Heterogeneity and structure of antibody-combining sites. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1970 Feb 13;169(1):43–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1970.tb55978.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabat E. A. Unique features of the variable regions of Bence Jones proteins and their possible relation to antibody complementarity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):613–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler H., Shimizu A., Paul C., Moore V., Putnam F. W. Three variable-gene pools common to IgM, IgG and IgA immunoglobulins. Nature. 1970 Sep 26;227(5265):1318–1320. doi: 10.1038/2271318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C. Linked groups of residues in immunoglobulin k chains. Nature. 1967 Oct 28;216(5113):330–332. doi: 10.1038/216330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponstingl H., Schwarz J., Reichel W., Hilschmann N. Die Primärstruktur eines monoklonalen gamma-1-Immunoglobulins (Myelomprotein NIE). I. Aminosäuresequenz des variablen Teils der H-Kette, Subgruppen variabler Teile. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1970 Dec;351(12):1591–1594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Press E. M., Hogg N. M. The amino acid sequences of the Fd fragments of two human gamma-1 heavy chains. Biochem J. 1970 May;117(4):641–660. doi: 10.1042/bj1170641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. C., Fudenberg H. H., Pink J. R. Heavy-chain variable regions in normal and pathological immunolobulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1143–1146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T., Kabat E. A. An analysis of the sequences of the variable regions of Bence Jones proteins and myeloma light chains and their implications for antibody complementarity. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):211–250. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



