Abstract
The reversible unfolding and folding of staphylococcal nuclease in the acid transition has been studied by 220 MHz proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. The values of area, line-width, and chemical shift of each of the imidazole C2 proton resonances of the four histidine residues have been measured in this transition. The change of areas of three histidine resonances and the change of fluorescence of the single tryptophan residue, as a function of pH, appear to follow a single equilibrium. In contrast, a fourth histidine resonance follows a biphasic transition. These findings indicate that local conformational changes can be detected by magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the cooperative transition of the overall structure.
Keywords: histidine, protein structure, acid denaturation, proton, spectroscopy
Full text
PDF
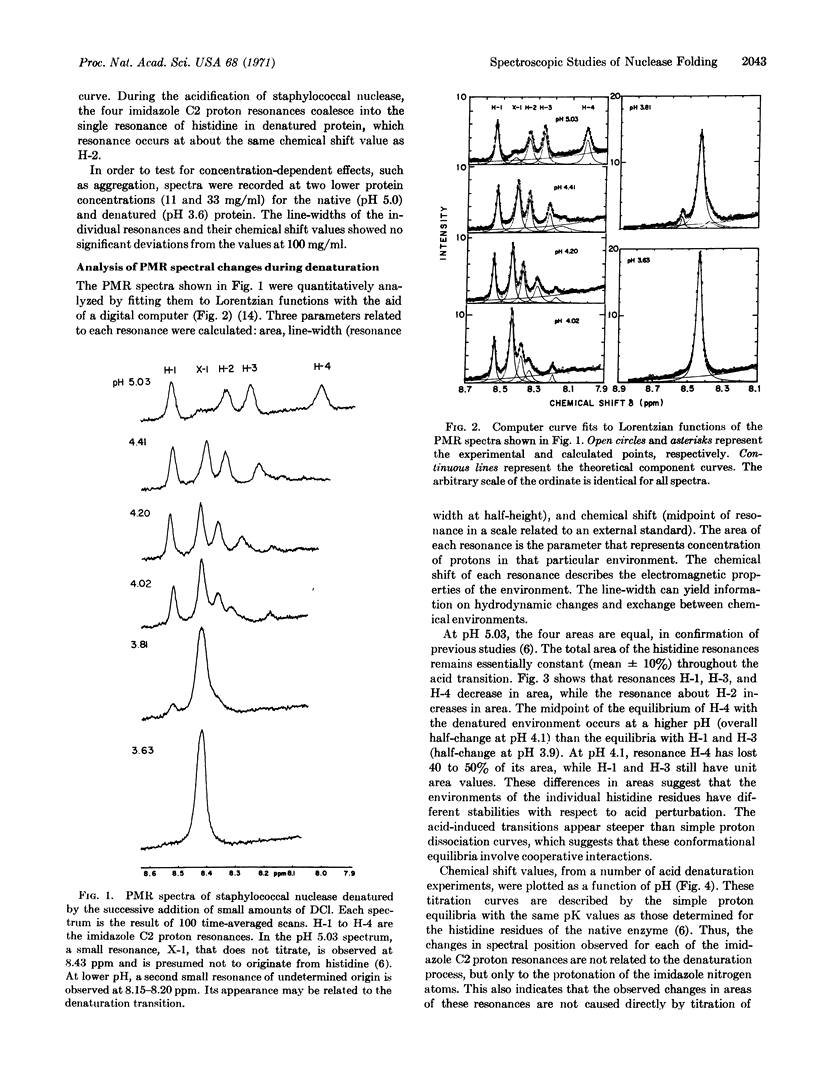
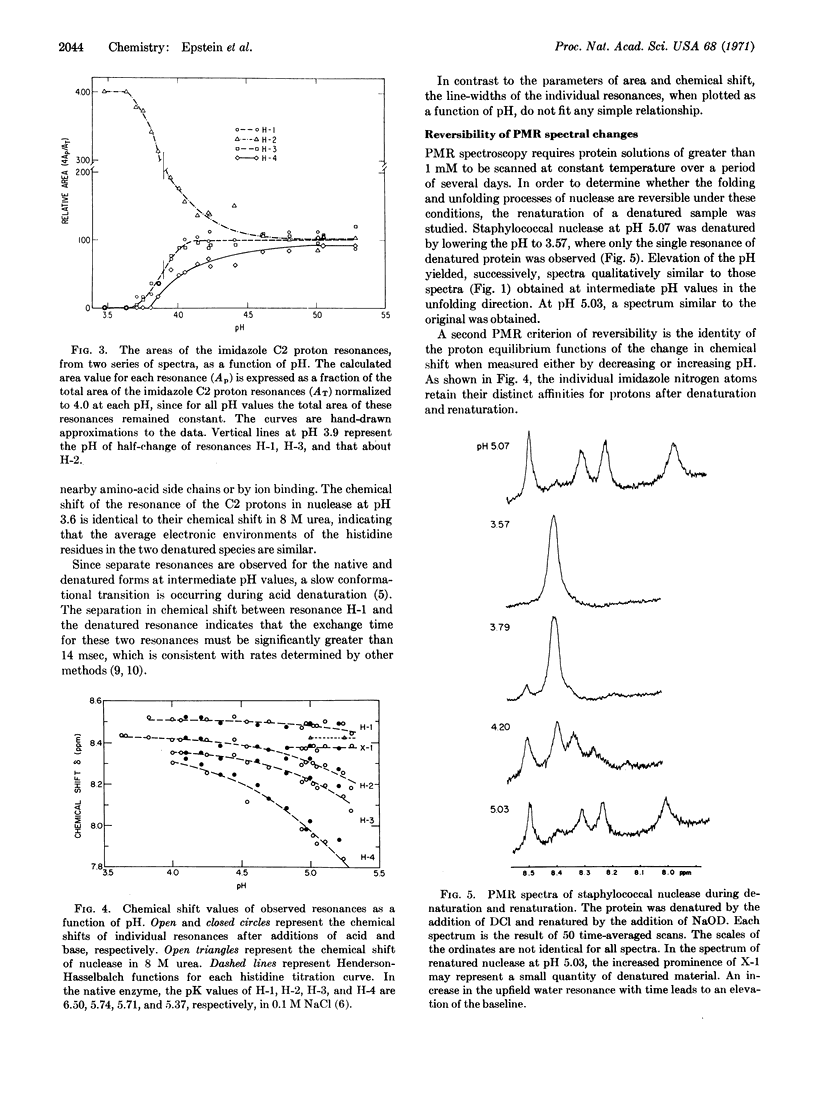
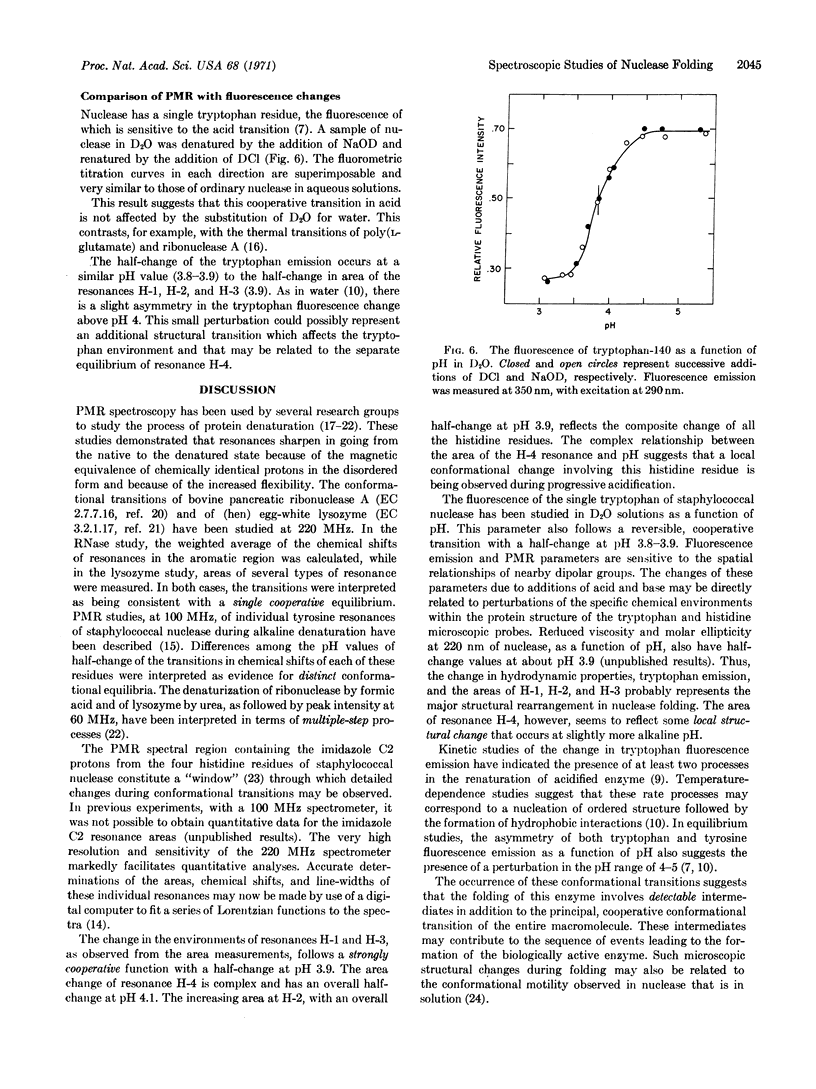

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addad J. P. Conformational changes of ribonuclease A as seen by nuclear magnetic resonance line shifts. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 28;50(3):595–603. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90087-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anfinsen C. B. The formation of the tertiary structure of proteins. Harvey Lect. 1967;61:95–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnone A., Bier C. J., Cotton F. A., Day V. W., Hazen E. E., Jr, Richardson D. C., Yonath A., Richardson J. S. A high resolution structure of an inhibitor complex of the extracellular nuclease of Staphylococcus aureus. I. Experimental procedures and chain tracing. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):2302–2316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury J. H., King N. L. Denaturation of proteins: single or multiple step process? Nature. 1969 Sep 13;223(5211):1154–1156. doi: 10.1038/2231154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. S., Jardetzky O. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the structure and binding sites of enzymes. II. Spectral assignments and inhibitor binding in hen egg-white lysozyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 May;60(1):92–99. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.1.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. S., Shrager R. I., McNeel M., Schechter A. N. Proton magnetic resonance studies at 220 MHz of the histidine residues of staphylococcal nuclease. Nature. 1970 Nov 14;228(5272):642–644. doi: 10.1038/228642a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. S., Shrager R. I., McNeel M., Schnechter A. N. On-line computer-assisted analysis of 220 MHz NMR data of protin imidazole resonances. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jul 13;40(1):144–151. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone J. L., Cusumano C. L., Taniuchi H., Anfinsen C. B. Staphylococcal nuclease (Foggi strain). II. The amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3103–3110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Taniuchi H., Anfinsen C. B. The structural basis of the catalytic function of staphylococcal nuclease. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1968 Jun;21(1):172–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H., Perlman R. L., Wilchek M. Tyrosine fluorescence in proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 May 16;158(1):391–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb56233.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDEL M. PROTON MAGNETIC RESONANCE SPECTRA OF SOME PROTEINS. I. RIBONUCLEASE, OXIDIZED RIBONUCLEASE, LYSOZYME, AND CYTOCHROME C. J Biol Chem. 1965 Apr;240:1586–1592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald C. C., Phillips W. D., Glickson J. D. Nuclear magnetic resonance study of the mechanism of reversible denaturation of lysozyme. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 Jan 13;93(1):235–246. doi: 10.1021/ja00730a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morávek L., Anfinsen C. B., Cone J. L., Taniuchi H. The large scale preparation of an extracellular nuclease of Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 25;244(2):497–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. C., Jardetzky O. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of amino acids, peptides, and proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1970;24:447–545. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHERAGA H. A. Deuterium exchange studies and protein structure. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1960 Nov;13:71–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter A. N., Chen R. F., Anfinsen C. B. Kinetics of folding of staphylococcal nuclease. Science. 1970 Feb 6;167(3919):886–887. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3919.886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C. Protein denaturation. C. Theoretical models for the mechanism of denaturation. Adv Protein Chem. 1970;24:1–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C. Protein denaturation. Adv Protein Chem. 1968;23:121–282. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60401-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


