Abstract
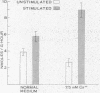
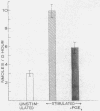
Dopamine-β-hydroxylase (EC 1.14.2.1), an enzyme localized in sympathetic synaptic vesicles, was released together with norepinephrine during in vitro stimulation of the hypogastric nerve that innervates the vas deferens of the guinea pig. Stimulation of the nerve in the presence of high concentrations of calcium (7.5 mM) or phenoxybenzamine caused a marked increase in the amounts of the enzyme and norepinephrine released into the bath. The augmentation of release of dopamine-β-hydroxylase by 7.5 mM calcium or phenoxybenzamine was reversed by prostaglandin E2. These findings suggest that the release of the sympathetic neurotransmitter, norepinephrine, occurs by a process of exocytosis in which the vesicular content of soluble dopamine-β-hydroxylase is also released. The depolarization-induced exocytosis, which is stimulated by calcium, may be affected by prostaglandin E2 or phenoxybenzamine through inhibition or enhancement of the actions of calcium in the release process.
Keywords: norepinephrine, hypogastric nerves, vas deferens, guinea pigs
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROWN G. L., GILLESPIE J. S. The output of sympathetic transmitter from the spleen of the cat. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):81–102. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boullin D. J. The action of extracellular cations on the release of the sympathetic transmitter from peripheral nerves. J Physiol. 1967 Mar;189(1):85–99. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE ROBERTIS E., VAZ FERREIRA A. Electron microscope study of the excretion of cathecol-containing droplets in the adrenal medulla. Exp Cell Res. 1957 Jun;12(3):568–574. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(57)90172-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS W. W., RUBIN R. P. The role of calcium in the secretory response of the adrenal medulla to acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1961 Nov;159:40–57. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies B. N., Horton E. W., Withrington P. G. The occurrence of prostaglandin E2 in splenic venous blood of the dog following splenic nerve stimulation. J Physiol. 1967 Jan;188(2):38P–39P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W., Poisner A. M. Evidence that the secreting adrenal chromaffin cell releases catecholamines directly from ATP-rich granules. J Physiol. 1966 Mar;183(1):236–248. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gewirtz G. P., Kopin I. J. Release of dopamine-beta-hydroxylase with norepinephrine during cat splenic nerve stimulation. Nature. 1970 Jul 25;227(5256):406–407. doi: 10.1038/227406a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERTING G., AXELROD J., WHITBY L. G. Effect of drugs on the uptake and metabolism of H3-norepinephrine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1961 Nov;134:146–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedqvist P. Antagonism between prostaglandin E2 and phenoxybenzamine on noradrenaline release from the cat spleen. Acta Physiol Scand. 1969 Jul;76(3):383–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1969.tb04482.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedqvist P. Antagonism by calcium of the inhibitory action of prostaglandin E2 on sympathetic neurotransmission in the cat spleen. Acta Physiol Scand. 1970 Oct;80(2):269–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1970.tb04790.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRPEKAR S. M., CERVONI P. EFFECT OF COCAINE, PHENOXYBENZAMINE AND PHENTOLAMINE ON THE CATECHOLAMINE OUTPUT FROM SPLEEN AND ADRENAL MEDULLA. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 Oct;142:59–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRSHNER N. Pathway of noradrenaline formation from DOPA. J Biol Chem. 1957 Jun;226(2):821–825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpekar S. M., Misu Y. Release of noradrenaline by splenic nerve stimulation and its dependence on calcium. J Physiol. 1967 Jan;188(2):219–234. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirshner N., Sage H. J., Smith W. J. Mechanism of secretion from the adrenal medulla. II. Release of catecholamines and storage vesicle protein in response to chemical stimulation. Mol Pharmacol. 1967 May;3(3):254–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molinoff P. B., Brimijoin S., Weinshilboum R., Axelrod J. Neurally mediated increase in dopamine-beta-hydroxylase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):453–458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POTTER L. T., AXELROD J. PROPERTIES OF NOREPINEPHRINE STORAGE PARTICLES OF THE RAT HEART. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 Dec;142:299–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSELL S., KOPIN I. J., AXELROD J. FATE OF H3-NORADRENALINE IN SKELETAL MUSCLE BEFORE AND FOLLOWING SYMPATHETIC STIMULATION. Am J Physiol. 1963 Aug;205:317–321. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.205.2.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. P. The role of calcium in the release of neurotransmitter substances and hormones. Pharmacol Rev. 1970 Sep;22(3):389–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Potter W. P., de Schaepdryver A. F., Moerman E. J., Smith A. D. Evidence for the release of vesicle-proteins together with noradrenaline upon stimulation of the splenic nerve. J Physiol. 1969 Oct;204(2):102P+–102P+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von EULER U., LISHAJKO F. Improved technique for the fluorimetric estimation of catecholamines. Acta Physiol Scand. 1961 Apr;51:348–355. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1961.tb02128.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]