Abstract
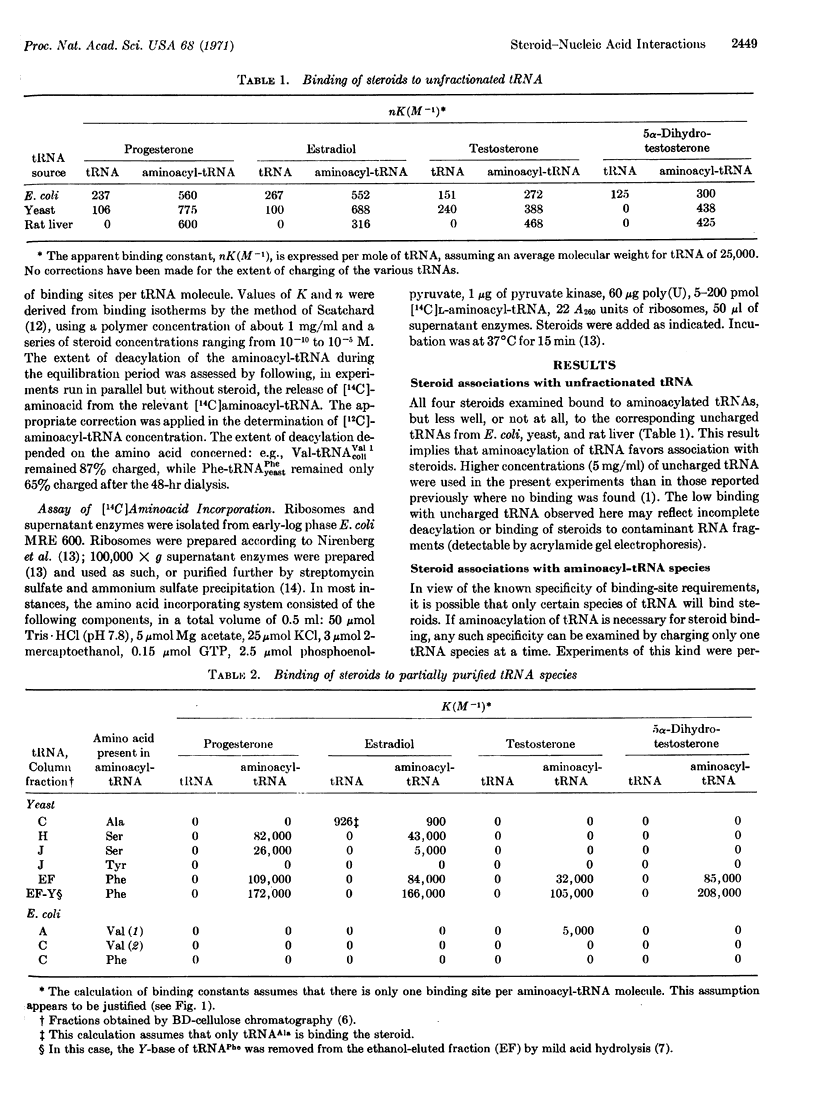
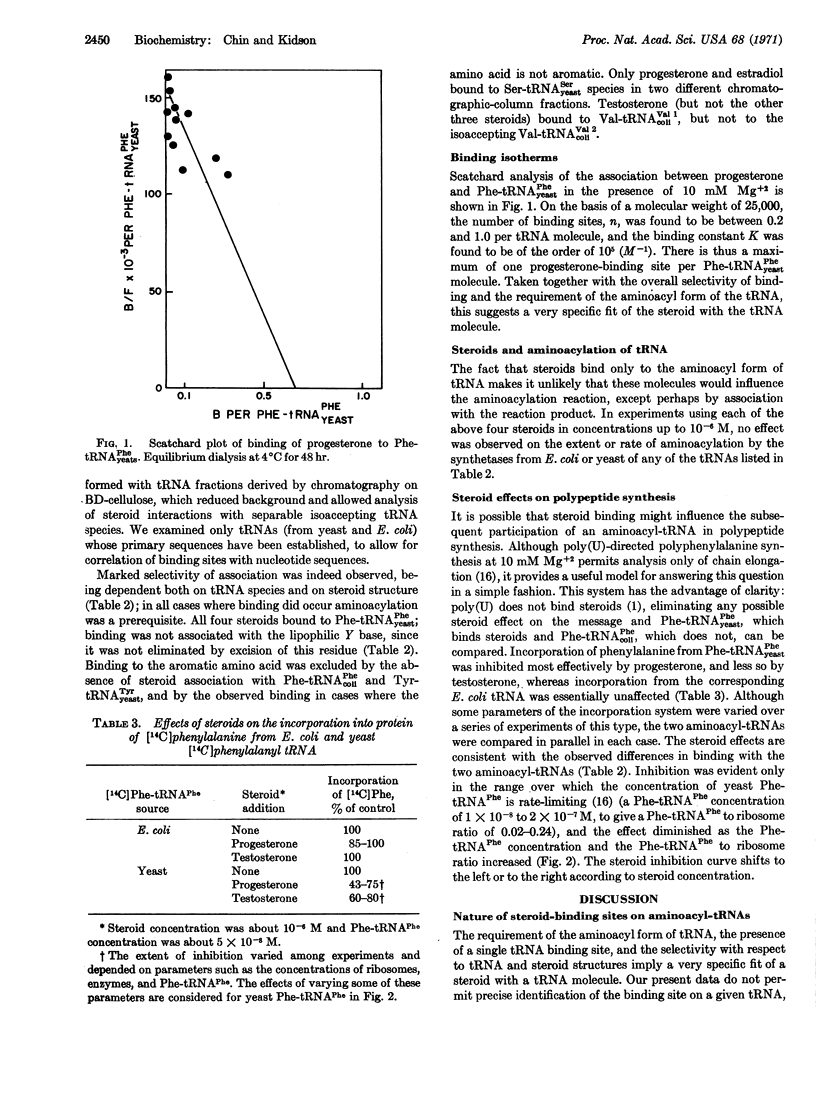
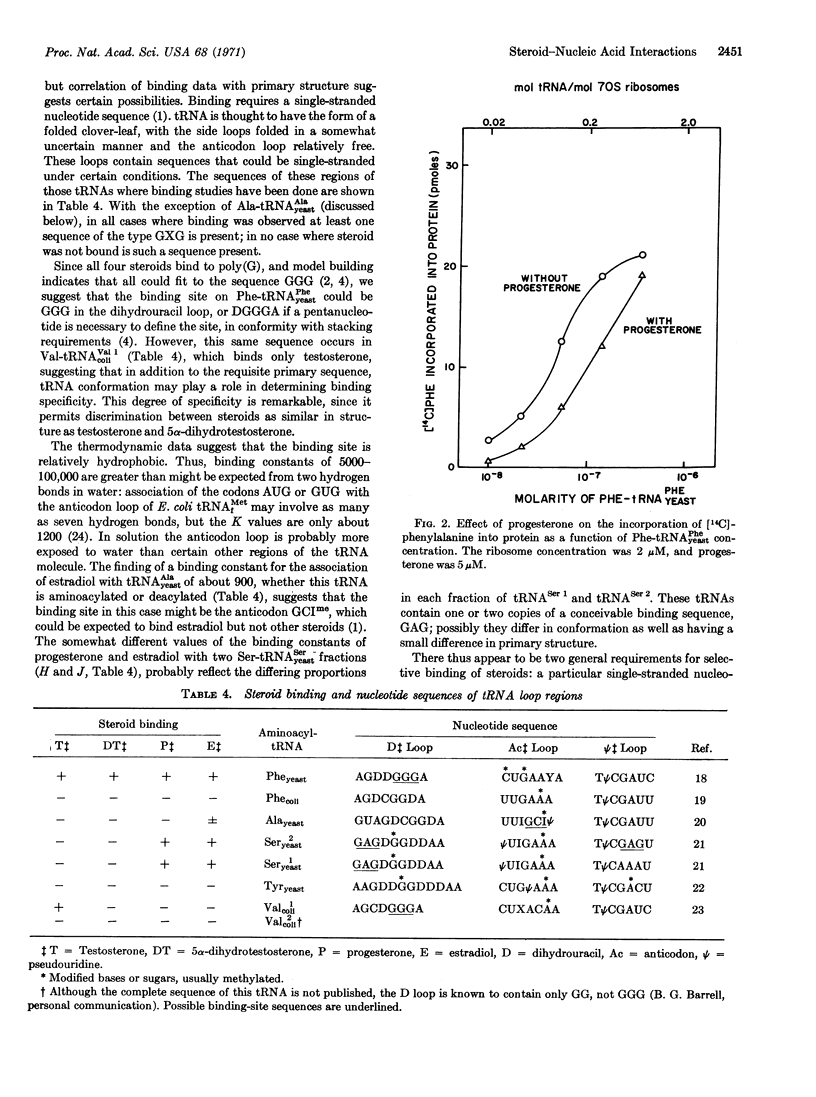
The hormonal steroids progesterone, estradiol, testosterone, and 5α-dihydrotestosterone bind to aminoacyl-tRNA, but not to deacylated tRNA, implying that a change in conformation of tRNA occurs on aminoacylation. Binding is restricted to a few tRNA species and depends on the structure of both tRNA and steroid. There is one binding site per aminoacyl-tRNA molecule, the specificity of which appears to depend on a restricted, single-stranded loop sequence and on the tRNA conformation. By binding to an aminoacyl-tRNA, a steroid can control polypeptide synthesis in a model in vitro system by inhibiting chain elongation under conditions where aminoacyl-tRNA concentration is rate-limiting.
Keywords: testosterone, progesterone, estradiol, yeast tRNA, E. coli tRNA
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler A. J., Fasman G. D. Circular dichroism of valine and formylmethionine transfer RNA from Escherichia coli: effect of aminoacylation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 19;204(1):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90501-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson W. F. The effect of tRNA concentration on the rate of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Feb;62(2):566–573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.2.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong D. J., Burrows W. J., Skoog F., Roy K. L., Söll D. Cytokinins: distribution in transfer RNA species of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jul;63(3):834–841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.3.834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrell B. G., Sanger F. The sequence of phenylalanine tRNA from E. coli. FEBS Lett. 1969 Jun;3(4):275–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80157-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Chin R. C., Kidson C. Interactions of hormonal steroids with nucleic acids. II. Structural and thermodynamic aspects of binding. Biochemistry. 1969 Sep;8(9):3603–3609. doi: 10.1021/bi00837a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Kidson C. Interactions of hormonal steroids with nucelic acids. I. A specific requirement for guanine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):458–464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gantt R. R., Englander S. W., Simpson M. V. Hydrogen-exchange measurements on Escherichia coli transfer ribonucleic acid before, after, and during its aminoacylation. Biochemistry. 1969 Feb;8(2):475–482. doi: 10.1021/bi00830a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillam I., Millward S., Blew D., von Tigerstrom M., Wimmer E., Tener G. M. The separation of soluble ribonucleic acids on benzoylated diethylaminoethylcellulose. Biochemistry. 1967 Oct;6(10):3043–3056. doi: 10.1021/bi00862a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLEY R. W., APGAR J., EVERETT G. A., MADISON J. T., MARQUISEE M., MERRILL S. H., PENSWICK J. R., ZAMIR A. STRUCTURE OF A RIBONUCLEIC ACID. Science. 1965 Mar 19;147(3664):1462–1465. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3664.1462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOSKINSON R. M., KHORANA H. G. STUDIES ON POLYNUCLEOTIDES. XLI. PURIFICATION OF PHENYLALANINE-SPECIFIC TRANSFER RIBONUCLEIC ACID FROM YEAST BY COUNTERCURRENT DISTRIBUTION. J Biol Chem. 1965 May;240:2129–2134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashizume H., Imahori K. Circular dichroism and conformation of natural and synthetic polynucleotides. J Biochem. 1967 Jun;61(6):738–749. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipmann F. Polypeptide chain elongation in protein biosynthesis. Science. 1969 May 30;164(3883):1024–1031. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3883.1024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litt M. Structural studies on transfer ribonucleic acid. I. Labeling of exposed guanine sites in yeast phenylalanine transfer ribonucleic acid with kethoxal. Biochemistry. 1969 Aug;8(8):3249–3253. doi: 10.1021/bi00836a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison J. T., Everett G. A., Kung H. Nucleotide sequence of a yeast tyrosine transfer RNA. Science. 1966 Jul 29;153(3735):531–534. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3735.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NATHANS D., LIPMANN F. Amino acid transfer from aminoacyl-ribonucleic acids to protein on ribosomes of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Apr 15;47:497–504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.4.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIRENBERG M. W., MATTHAEI J. H., JONES O. W. An intermediate in the biosynthesis of polyphenylalanine directed by synthetic template RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jan 15;48:104–109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.1.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajbhandary U. L., Chang S. H., Stuart A., Faulkner R. D., Hoskinson R. M., Khorana H. G. Studies on polynucleotides, lxviii the primary structure of yeast phenylalanine transfer RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Mar;57(3):751–758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.3.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoultchi A., Ono Y., Moon H. M., Lengyel P. On three complementary amino acid polymerization factors from Bacillus stearothermophilus: separation of a complex containing two of the factors, guanosine-5'-triphosphate and aminoacyl-transfer RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jun;60(2):675–682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.2.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TISSIERES A., BOURGEOIS S., GROS F. Inhibition of RNA polymerase by RNA. J Mol Biol. 1963 Jul;7:100–103. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemura S., Mizutani T., Miyazaki M. The primary structure of valine-I transfer ribonucleic acid from Torulopsis utilis. J Biochem. 1968 Feb;63(2):277–278. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiebe R., Zachau H. G. A specific modification next to the anticodon of phenylalanine transfer ribonucleic acid. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Sep 24;5(4):546–555. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00404.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlenbeck O. C., Baller J., Doty P. Complementary oligonucleotide binding to the anticodon loop of fMet-transfer RNA. Nature. 1970 Feb 7;225(5232):508–510. doi: 10.1038/225508a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON EHRENSTEIN G., DAIS D. A leucine acceptor sRNA with ambiguous coding properties in polynuletide-stimulated polypeptide synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jul;50:81–86. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaniv M., Barrell B. G. Nucleotide sequence of E. coli B tRNA1-Val. Nature. 1969 Apr 19;222(5190):278–279. doi: 10.1038/222278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachau H. G., Dütting D., Feldmann H. Nucleotide sequences of two serine-specific transfer ribonucleic acids. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1966 Apr;5(4):422–422. doi: 10.1002/anie.196604221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


