Abstract
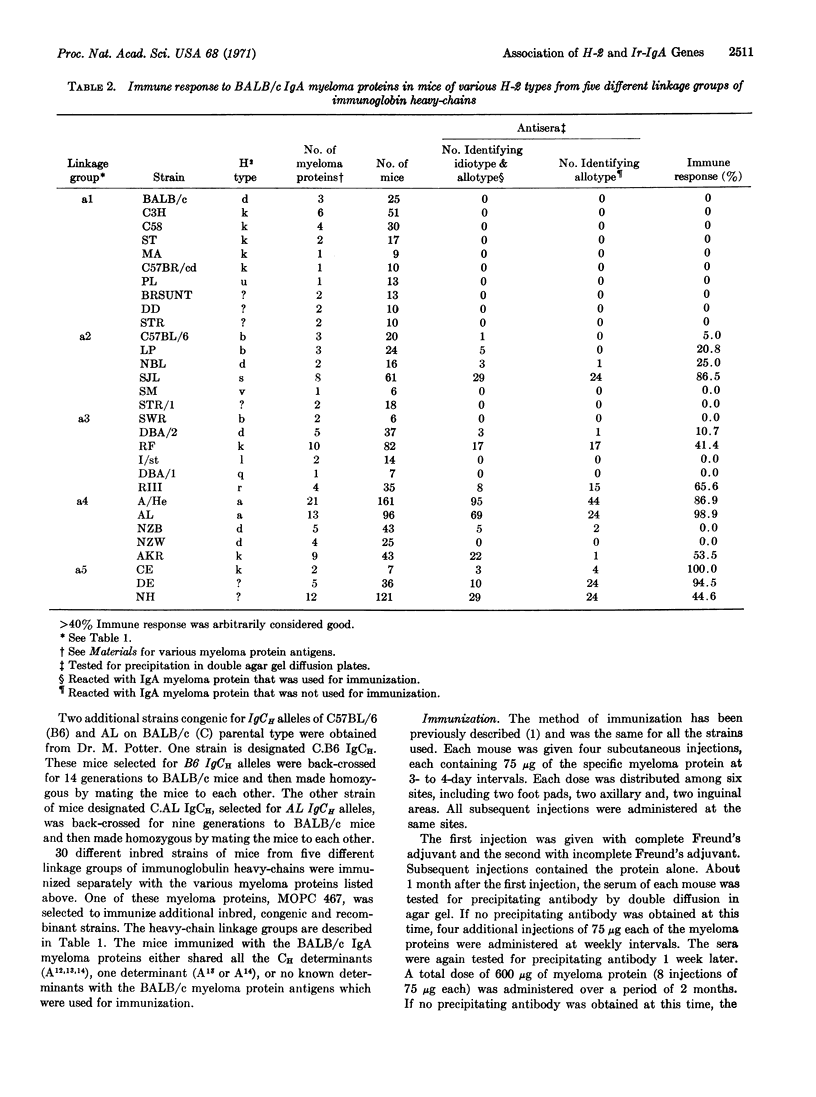
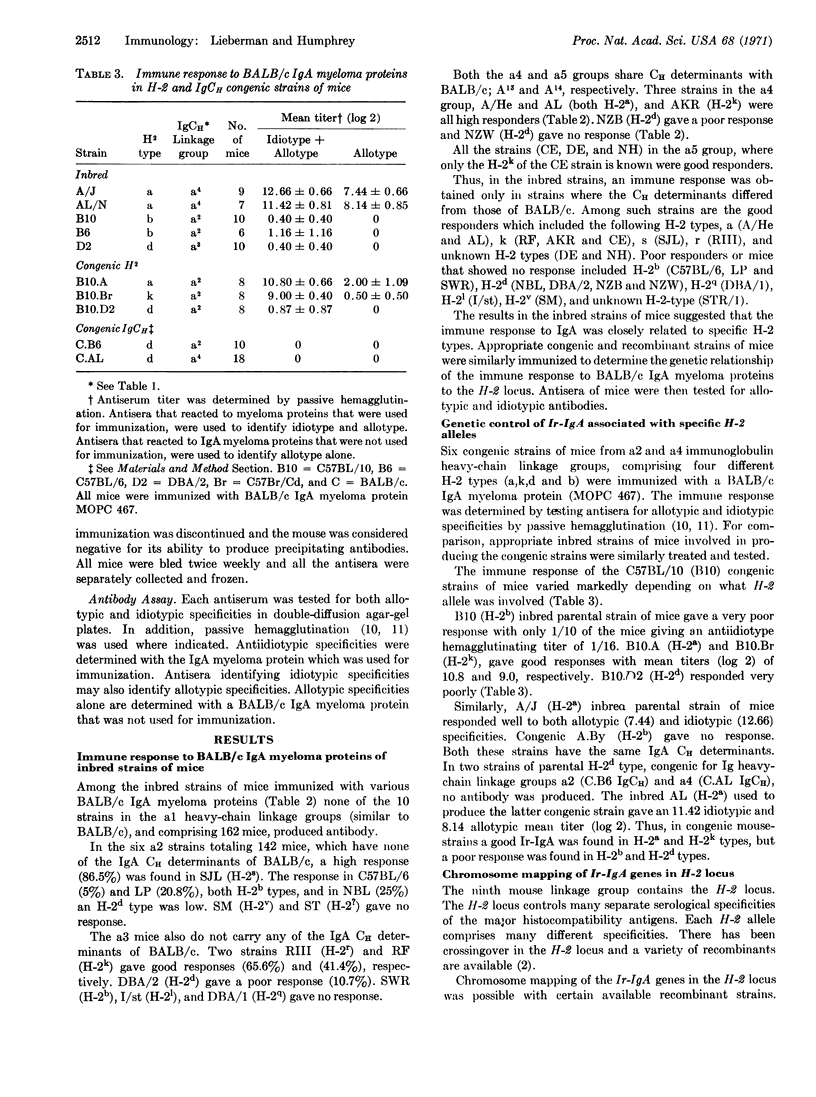
The immune response to BALB/c IgA myeloma proteins (Ir-IgA) was determined in mice of various H-2 types from five different linkage groups of immunoglobulin heavy chains (IgCH). Antisera were examined for antibodies to idiotypic (Fab) and allotypic (Fc) specificities. No immune response to IgA myeloma proteins was found in mice with the same linkage group as BALB/c but with different H-2 alleles. In mice with immunoglobulin heavy chains that are different than BALB/c, a high immune response to IgA myeloma proteins was found in H-2 types a, k, r, and s; a low response is associated with H-2b and H-2d types. Chromosome mapping of Ir-IgA genes in the H-2 locus indicate that they are on the right side of the chromosome, to the right of the Ss locus. Ir-IgA genes are controlled by dominant autosomal genes.
Keywords: heavy-chain linkage groups, idiotype, chromosome mapping, H-2 locus
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dubiski S. Immunochemistry and genetics of a "new" allotypic specificity Ae14 of rabbit gamma-G immunoglobulins: recombination in somatic cells. J Immunol. 1969 Jul;103(1):120–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman R., Potter M. Crossing over between genes in the immunoglobulin heavy chain linkage group of the mouse. J Exp Med. 1969 Sep 1;130(3):519–541. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.3.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt H. O., Benacerraf B. Genetic control of specific immune responses. Adv Immunol. 1969;11:31–74. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60477-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt H. O., Chinitz A. Genetic control of the antibody response: relationship between immune response and histocompatibility (H-2) type. Science. 1969 Mar 14;163(3872):1207–1208. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3872.1207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M., Lieberman R. Common individual antigenic determinants in five of eight BALB-c IgA myeloma proteins that bind phosphoryl choline. J Exp Med. 1970 Oct 1;132(4):737–751. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.4.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M., Lieberman R. Genetics of immunoglobulins in the mouse. Adv Immunol. 1967;7:91–145. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60127-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rathbun W. E., Hildemann W. H. Genetic control of the antibody response to simple haptens in congenic strains of mice. J Immunol. 1970 Jul;105(1):98–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAVITSKY A. B., ARQUILLA E. R. Micromethods for the study of proteins and antibodies. III. Procedures and applications of hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition reactions with bis-diazotized benzidine and protein-conjugated red blood cells. J Immunol. 1955 Apr;74(4):306–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaz N. M., Levine B. B. Immune responses of inbred mice to repeated low doses of antigen: relationship to histocompatibility (H-2) type. Science. 1970 May 15;168(3933):852–854. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3933.852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaz N. M., Vaz E. M., Levine B. B. Relationship between histocompatibility (H-2) genotype and immune responsiveness to low doses of ovalbumin in the mouse. J Immunol. 1970 Jun;104(6):1572–1574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


