Abstract
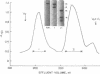
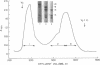
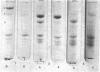
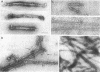
Platelet myosin (thrombosthenin M) and two additional proteins corresponding to the head and rod portion of the myosin molecule have been prepared from human blood platelets. Characterization of these proteins by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, actin binding studies, assay of enzymic ATPase activity, and electron microscopy has shown that the platelet contractile proteins closely resemble the corresponding muscle proteins. Platelet myosin and platelet myosin-head bind to both muscle and platelet actin and have an EDTA + K-stimulated ATPase activity, which is suppressed by Mg2+ in high salt concentration, whereas platelet rod does not possess either of these properties; platelet myosin and platelet myosin rod aggregate to form thick filaments at low ionic strength. Both intact platelet myosin and myosin head form typical arrowhead-shaped complexes with either platelet or muscle F-actin.
Keywords: agarose filtration, SDS-acrylamide gel electrophoresis, actin binding, electron micrographs
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelstein R. S., Kuehl W. M. Structural studies on rabbit skeletal actin. I. Isolation and characterization of the peptides produced by cyanogen bromide cleavage. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 17;9(6):1355–1364. doi: 10.1021/bi00808a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baenziger N. L., Brodie G. N., Majerus P. W. A thrombin-sensitive protein of human platelet membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):240–243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booyse F. M., Hoveke T. P., Zschocke D., Rafelson M. E., Jr Human platelet myosin. Isolation and properties. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4291–4297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAVEN G. R., STEERS E., Jr, ANFINSEN C. B. PURIFICATION, COMPOSITION, AND MOLECULAR WEIGHT OF THE BETA-GALACTOSIDASE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI K12. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2468–2477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I., Bohak Z., De VriesA, Katchalski E. Thrombosthenin M. Purification and interaction with thrombin. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Sep;10(2):388–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00702.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIELLEY W. W., BRADLEY L. B. The relationship between sulfhydryl groups and the activation of myosin adenosinetriphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1956 Feb;218(2):653–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. B., Huxley H. E., DeRosier D. J. Three-dimensional reconstruction of F-actin, thin filaments and decorated thin filaments. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 14;50(2):279–295. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEKINE T., BARNETT L. M., KIELLEY W. W. The active site of myosin adenosine triphosphatase. I. Localization of one of the sulfhydryl groups. J Biol Chem. 1962 Sep;237:2769–2772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]