Abstract
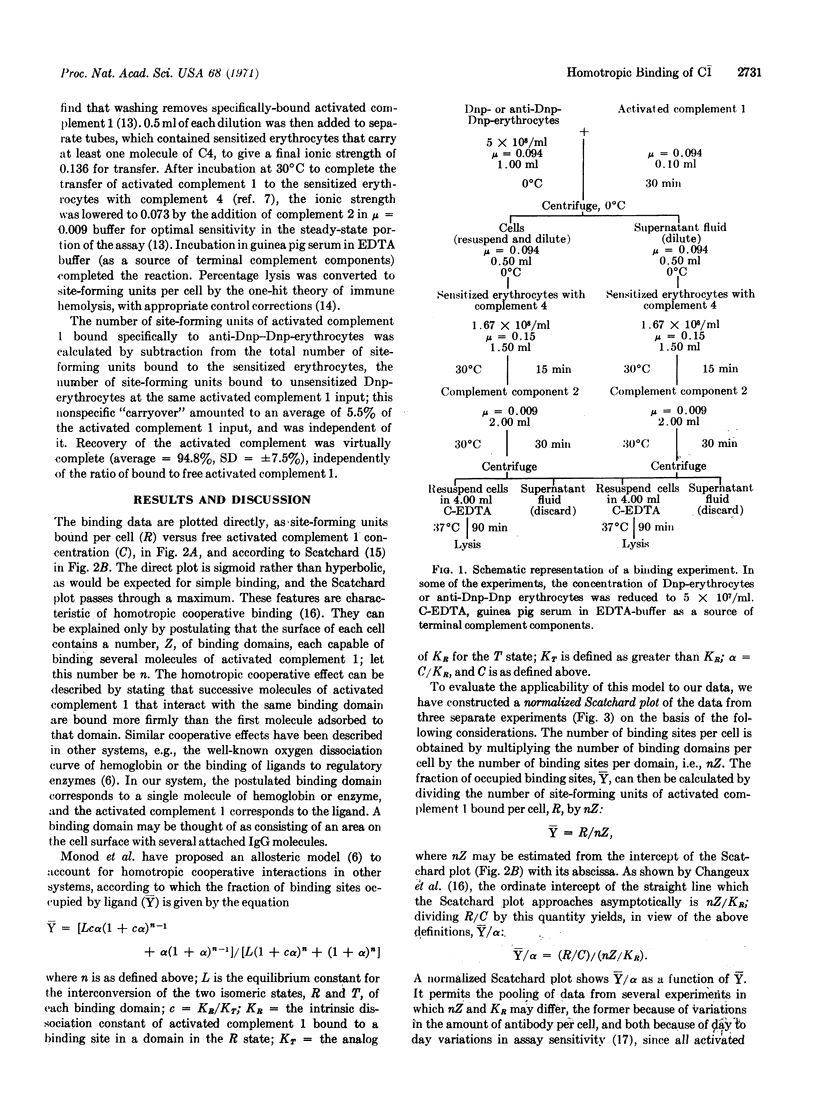
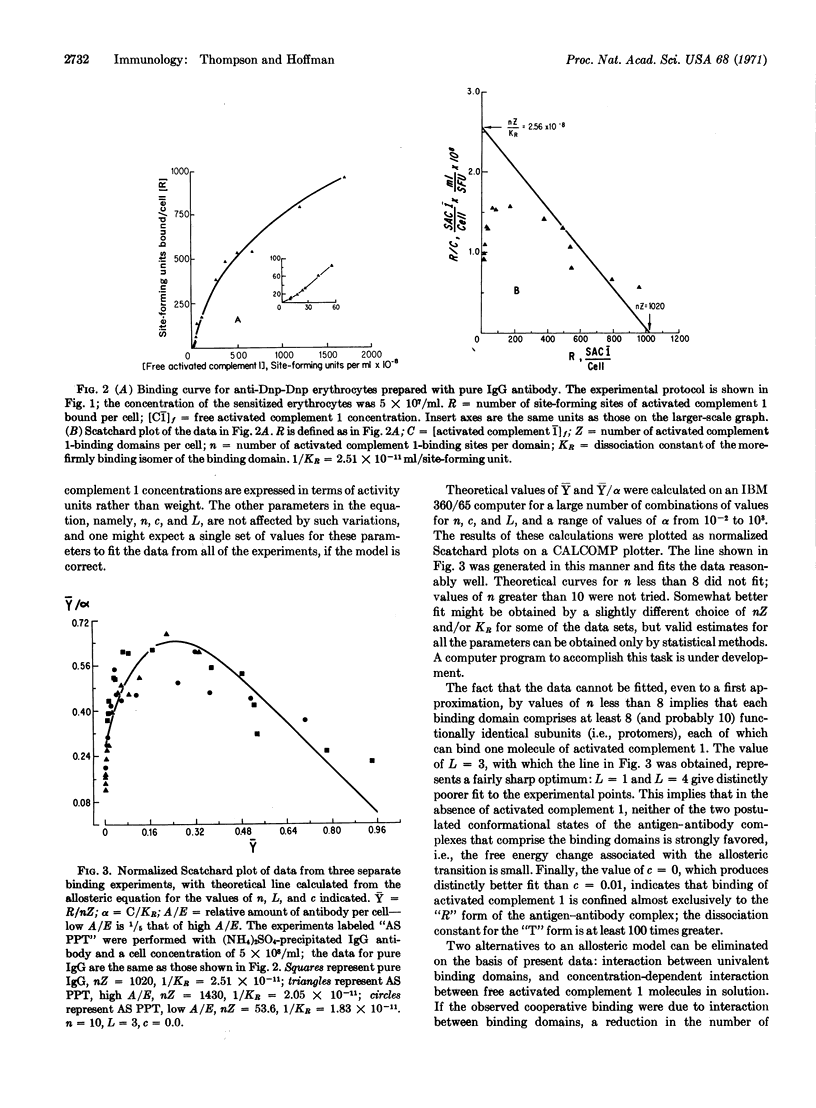
Binding of the activated first component of guinea pig complement to immune complexes formed between dinitrophenylated erythrocytes and rabbit IgG antibody to 2,4-dinitrophenylhapten has been studied quantitatively. Cooperative binding was observed; it in volves no interactions between the domains on the erythrocyte surface that bind the activated first component of complement, or between the activated complement molecules in solution. By curve-fitting methods, we find that the data are consistent with an allosteric model, which assumes 10 binding sites per domain, a low allosteric equilibrium constant, and virtually exclusive binding to one of the isomers.
Keywords: binding sites; 2,4-dinitrophenol; sensitized erythrocytes; binding domain
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borsos T., Rapp H. J. Hemolysin titration based on fixation of the activated first component of complement: evidence that one molecule of hemolysin suffices to sensitize an erythrocyte. J Immunol. 1965 Sep;95(3):559–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathou R. E., Kulczycki A., Jr, Haber E. Structural features of gamma-immunoglobulin, antibody, and their fragments. Circular dichroism studies. Biochemistry. 1968 Nov;7(11):3958–3964. doi: 10.1021/bi00851a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Rubin M. M. Allosteric interactions in aspartate transcarbamylase. 3. Interpretation of experimental data in terms of the model of Monod, Wyman, and Changeux. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):553–561. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colten H. R., Borsos T., Rapp H. J. Antigenic relationships between the first component (Cl) of human and guinea pig complement. J Immunol. 1970 May;104(5):1048–1051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M. Electron microscopy of the immunoglobulins. Adv Immunol. 1969;11:1–30. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60476-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann L. G. Solubility chromatography of serum proteins. I. Isolation of the first component of complement from guinea pig serum by solubility chromatography at low ionic strength. J Chromatogr. 1969 Mar 11;40(1):39–52. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)96616-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann L. G. Statistical evaluation of reaction mechanisms in immune hemolysis. II. The kinetics of release of 86rubidium and hemoglobin from erythrocytes damaged by antibody and complement. Immunochemistry. 1969 Mar;6(2):309–325. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90167-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Tada T., Ishizaka K. Fixation of C' and C'la by rabbit gamma-G- and gamma-M-antibodies with particulate and soluble antigens. J Immunol. 1968 Jun;100(6):1145–1153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONOD J., WYMAN J., CHANGEUX J. P. ON THE NATURE OF ALLOSTERIC TRANSITIONS: A PLAUSIBLE MODEL. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:88–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small P. A., Jr, Lamm M. E. Polypeptide chain structure of rabbit immunoglobulins. I. gamma-G-immunoglobulin. Biochemistry. 1966 Jan;5(1):259–267. doi: 10.1021/bi00865a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


