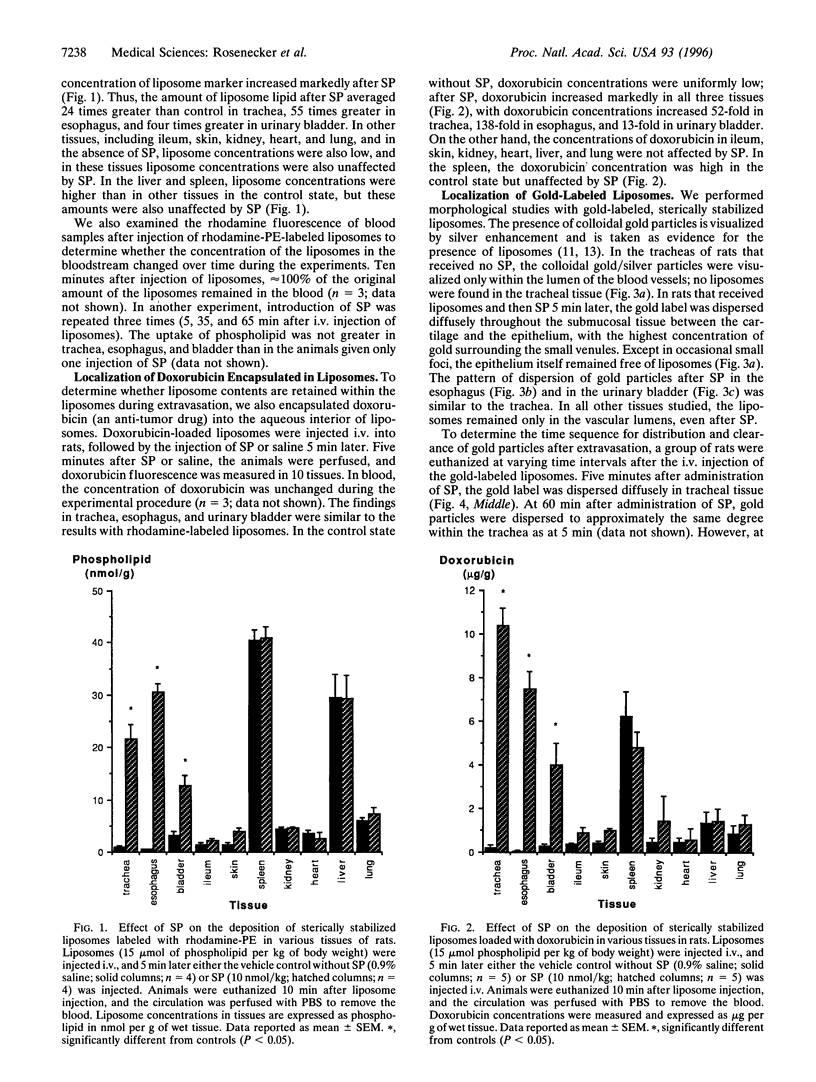
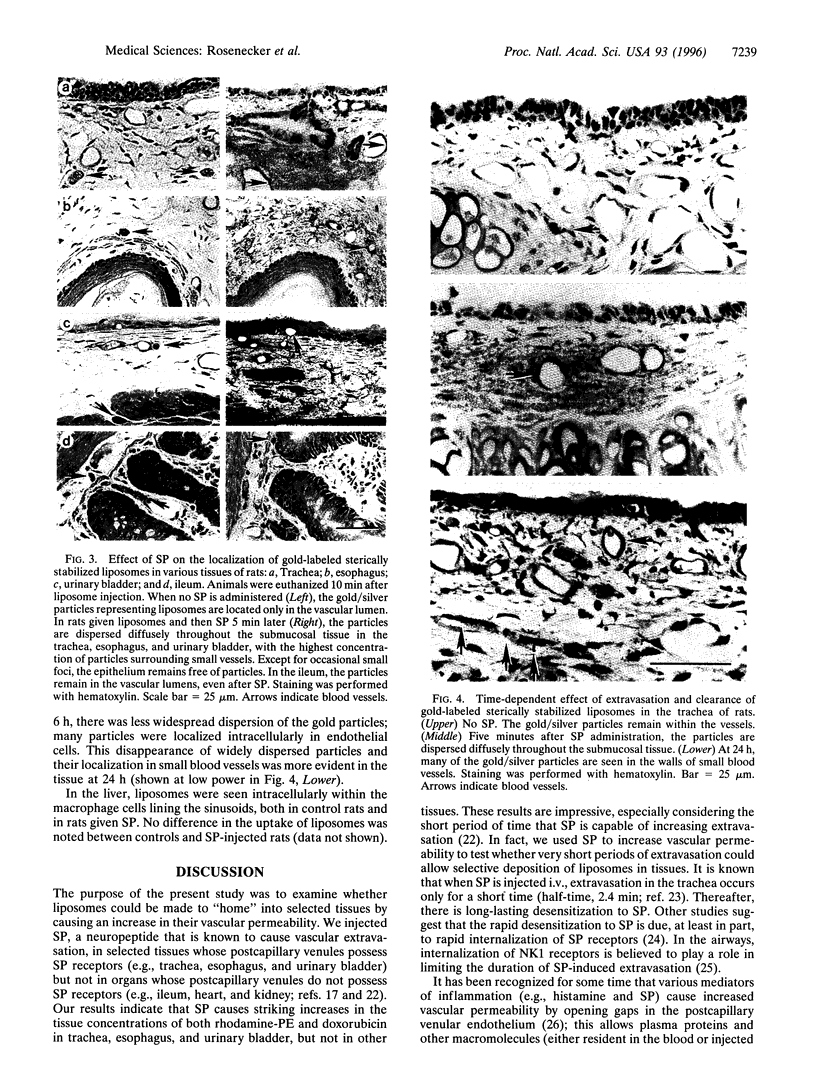
Abstract
We have used a pharmacologic mediator to open intercellular connections in selected vessels to allow liposomes to escape from the blood stream and to extravasate into tissues that have appropriate receptors. We have examined the effects of substance P (SP), a peptide known to increase vascular permeability in selected tissues, such as trachea, esophagus, and urinary bladder in rats. We used quantitative fluorescence analysis of tissues to measure two fluorescent markers, one attached to the lipid (rhodamine-phosphatidylethanolamine) and another, doxorubicin (an anti-tumor drug), encapsulated within the aqueous interior. We have also examined the deposition of liposomes microscopically by the use of encapsulated colloidal gold and silver enhancement. Analysis of the biochemical and morphological observations indicate the following: (i) Injection of SP produces a striking increase in both liposome labels, but only in tissues that possess receptors for SP in postcapillary venules; (ii) liposome material in these tissues has extravasated and is found extracellularly near a variety of cells beyond the endothelial layer over the first few hours; (iii) 24 h following injection of liposomes and SP, liposome material is found in these tissues, localized intracellularly in both endothelial cells and macrophages. We propose that appropriate application of tissue-specific mediators can result in liposome extravasation deep within tissues that normally do not take up significant amounts of liposomes from the blood. Such liposomes are able to carry a variety of pharmacological agents that can be released locally within selected target tissues for therapeutic purposes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abelli L., Maggi C. A., Rovero P., Del Bianco E., Regoli D., Drapeau G., Giachetti A. Effect of synthetic tachykinin analogues on airway microvascular leakage in rats and guinea-pigs: evidence for the involvement of NK-1 receptors. J Auton Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;11(4):267–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1991.tb00324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abra R. M., Hunt C. A. Liposome disposition in vivo. III. Dose and vesicle-size effects. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 23;666(3):493–503. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90311-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen T. M., Hansen C., Martin F., Redemann C., Yau-Young A. Liposomes containing synthetic lipid derivatives of poly(ethylene glycol) show prolonged circulation half-lives in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jul 1;1066(1):29–36. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90246-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker-Woudenberg I. A., Lokerse A. F., ten Kate M. T., Mouton J. W., Woodle M. C., Storm G. Liposomes with prolonged blood circulation and selective localization in Klebsiella pneumoniae-infected lung tissue. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jul;168(1):164–171. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.1.164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker-Woudenberg I. A., Lokerse A. F., ten Kate M. T., Storm G. Enhanced localization of liposomes with prolonged blood circulation time in infected lung tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Apr 14;1138(4):318–326. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(92)90010-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand C., Geppetti P., Baker J., Yamawaki I., Nadel J. A. Role of neurogenic inflammation in antigen-induced vascular extravasation in guinea pig trachea. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 15;150(4):1479–1485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowden J. J., Garland A. M., Baluk P., Lefevre P., Grady E. F., Vigna S. R., Bunnett N. W., McDonald D. M. Direct observation of substance P-induced internalization of neurokinin 1 (NK1) receptors at sites of inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 13;91(19):8964–8968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.19.8964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplen N. J., Alton E. W., Middleton P. G., Dorin J. R., Stevenson B. J., Gao X., Durham S. R., Jeffery P. K., Hodson M. E., Coutelle C. Liposome-mediated CFTR gene transfer to the nasal epithelium of patients with cystic fibrosis. Nat Med. 1995 Jan;1(1):39–46. doi: 10.1038/nm0195-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haran G., Cohen R., Bar L. K., Barenholz Y. Transmembrane ammonium sulfate gradients in liposomes produce efficient and stable entrapment of amphipathic weak bases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Sep 19;1151(2):201–215. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(93)90105-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong K., Friend D. S., Glabe C. G., Papahadjopoulos D. Liposomes containing colloidal gold are a useful probe of liposome-cell interactions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jul 13;732(1):320–323. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90220-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S. K., Lee K. D., Hong K., Friend D. S., Papahadjopoulos D. Microscopic localization of sterically stabilized liposomes in colon carcinoma-bearing mice. Cancer Res. 1992 Oct 1;52(19):5135–5143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S. K., Martin F. J., Jay G., Vogel J., Papahadjopoulos D., Friend D. S. Extravasation and transcytosis of liposomes in Kaposi's sarcoma-like dermal lesions of transgenic mice bearing the HIV tat gene. Am J Pathol. 1993 Jul;143(1):10–14. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S. K., Mayhew E., Gilani S., Lasic D. D., Martin F. J., Papahadjopoulos D. Pharmacokinetics and therapeutics of sterically stabilized liposomes in mice bearing C-26 colon carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1992 Dec 15;52(24):6774–6781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasic D. D., Papahadjopoulos D. Liposomes revisited. Science. 1995 Mar 3;267(5202):1275–1276. doi: 10.1126/science.7871422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Saria A. Capsaicin-induced desensitization of airway mucosa to cigarette smoke, mechanical and chemical irritants. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):251–253. doi: 10.1038/302251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAJNO G., PALADE G. E. Studies on inflammation. 1. The effect of histamine and serotonin on vascular permeability: an electron microscopic study. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Dec;11:571–605. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald D. M., Mitchell R. A., Gabella G., Haskell A. Neurogenic inflammation in the rat trachea. II. Identity and distribution of nerves mediating the increase in vascular permeability. J Neurocytol. 1988 Oct;17(5):605–628. doi: 10.1007/BF01260989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald D. M. Neurogenic inflammation in the respiratory tract: actions of sensory nerve mediators on blood vessels and epithelium of the airway mucosa. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Dec;136(6 Pt 2):S65–S72. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.6_Pt_2.S65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillian M. K., Soltoff S. P., Talamo B. R. Rapid desensitization of substance P- but not carbachol-induced increases in inositol trisphosphate and intracellular Ca++ in rat parotid acinar cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Nov 13;148(3):1017–1024. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80233-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson F., Hunt C. A., Szoka F. C., Vail W. J., Papahadjopoulos D. Preparation of liposomes of defined size distribution by extrusion through polycarbonate membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 19;557(1):9–23. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90085-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D., Allen T. M., Gabizon A., Mayhew E., Matthay K., Huang S. K., Lee K. D., Woodle M. C., Lasic D. D., Redemann C. Sterically stabilized liposomes: improvements in pharmacokinetics and antitumor therapeutic efficacy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11460–11464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saria A., Lundberg J. M., Skofitsch G., Lembeck F. Vascular protein linkage in various tissue induced by substance P, capsaicin, bradykinin, serotonin, histamine and by antigen challenge. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1983 Nov;324(3):212–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00503897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior J. H. Fate and behavior of liposomes in vivo: a review of controlling factors. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 1987;3(2):123–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan F., Leunig M., Huang S. K., Berk D. A., Papahadjopoulos D., Jain R. K. Microvascular permeability and interstitial penetration of sterically stabilized (stealth) liposomes in a human tumor xenograft. Cancer Res. 1994 Jul 1;54(13):3352–3356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu N., Liggitt D., Liu Y., Debs R. Systemic gene expression after intravenous DNA delivery into adult mice. Science. 1993 Jul 9;261(5118):209–211. doi: 10.1126/science.7687073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]