Abstract
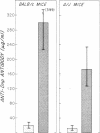
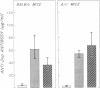
The effect of x-irradiation on the capacity of carrier-specific mouse T (thymus-derived) lymphocytes to exert a helper function for hapten-specific B (bone marrow-derived) lymphocytes in vivo has been investigated again. Helper function is abolished by exposure of such cells to x-irradiation before, or immediately after, transfer to adoptive hosts. On the other hand, when exposure to x-irradiation occurs under circumstances in which the carrier-primed cells are well-localized in the appropriate lymphoid organs, i.e., either in the carrier-primed animal or 24 hr after adoptive transfer to syngeneic recipients, the capacity of T lymphocytes to serve as specific helper cells is clearly radioresistant. Evidence indicates that x-irradiation results in undefined, and subtle, changes in the migratory capacity of mouse T lymphocytes, but not in abrogation of T-cell helper function.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. E., Sprent J., Miller J. F. Cell-to-cell interaction in the immune response. 8. Radiosensitivity of thymus-derived lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1972 Mar 1;135(3):711–717. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.3.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson B., Blomgren H. Evidence for a small pool of immunocompetent cells in the mouse thymus. Its role in the humoral antibody response against sheep erythrocytes, bovine serum albumin, ovalbumin and the NIP determinant. Cell Immunol. 1970 Oct;1(4):362–371. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asherson G. L., Loewi G. The effect of irradiation on the passive transfer of delayed hypersensitivity. Immunology. 1967 Nov;13(5):509–512. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENACERRAF B., LEVINE B. B. Immunological specificity of delayed and immediate hypersensitivity reactions. J Exp Med. 1962 May 1;115:1023–1036. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.5.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomgren H., Andersson B. Evidence for a small pool of immunocompetent cells in the mouse thymus. Exp Cell Res. 1969 Oct;57(2):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90140-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claman H. N., Chaperon E. A. Immunologic complementation between thymus and marrow cells--a model for the two-cell theory of immunocompetence. Transplant Rev. 1969;1:92–113. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1969.tb00137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claman H. N., Chaperon E. A., Triplett R. F. Immunocompetence of transferred thymus-marrow cell combinations. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):828–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claman H. N., Chaperon E. A., Triplett R. F. Thymus-marrow cell combinations. Synergism in antibody production. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Aug-Sep;122(4):1167–1171. doi: 10.3181/00379727-122-31353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. J., Claman H. N. Thymus-marrow immunocompetence. V. Hydrocortisone-resistant cells and processes in the hemolytic antibody response of mice. J Exp Med. 1971 May 1;133(5):1026–1034. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.5.1026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. J., Fschbach M., Claman H. N. Hydrocortisne resistance of graft vs host activity in mouse thymus, spleen and bone marrow. J Immunol. 1970 Nov;105(5):1146–1150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. J. Hydrocortisone resistance of activated initiator cells in graft versus host reactions. Nature. 1971 Jan 22;229(5282):274–275. doi: 10.1038/229274a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman J. D. The role of proliferation in delayed hypersensitivity. J Immunol. 1968 Sep;101(3):563–571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green I., Benacerraf B., Stone S. H. The effect of the amount of mycobacterial adjuvants on the immune response of strain 2, strain 13 and Hartley strain guinea pigs to DNP-PLL and DNP-GL. J Immunol. 1969 Sep;103(3):403–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst J. A., Dutton R. W. Cell components in the immune response. 3. Neonatal thymectomy: restoration in culture. Cell Immunol. 1970 Jul;1(2):190–195. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. H., Benacerraf B. The regulatory influence of activated T cells on B cell responses to antigen. Adv Immunol. 1972;15:1–94. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60683-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. H., Paul W. E., Goidl E. A., Benacerraf B. Carrier function in anti-hapten immune responses. I. Enhancement of primary and secondary anti-hapten antibody responses by carrier preimmunization. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):261–282. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. H., Paul W. E., Goidl E. A., Benacerraf B. Radioresistance of cooperative function of carrier-specific lymphocytes in antihapten antibody responses. Science. 1970 Oct 23;170(3956):462–464. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3956.462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettman J., Dutton R. W. Radioresistance of the enhancing effect of cells from carrier-immunized mice in an in vitro primary immune response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):699–703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. A., Claman H. N. Bone marrow and spleen: dissociation of immunologic properties by cortisone. Science. 1970 Mar 13;167(3924):1515–1517. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3924.1515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Mitchell G. F. Cell to cell interaction in the immune response. I. Hemolysin-forming cells in neonatally thymectomized mice reconstituted with thymus or thoracic duct lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1968 Oct 1;128(4):801–820. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.4.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Mitchell G. F. Thymus and antigen-reactive cells. Transplant Rev. 1969;1:3–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1969.tb00135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller G., Möller E. Plaque-formation by non-immune and x-irradiated lymphoid cells on monolayers of mouse embryo cells. Nature. 1965 Oct 16;208(5007):260–263. doi: 10.1038/208260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearer G. M., Cudkowicz G. Distinct events in the immune response elicited by transferred marrow and thymus cells. I. Antigen requirements and priferation of thymic antigen-reactive cells. J Exp Med. 1969 Dec 1;130(6):1243–1261. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.6.1243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]