Abstract
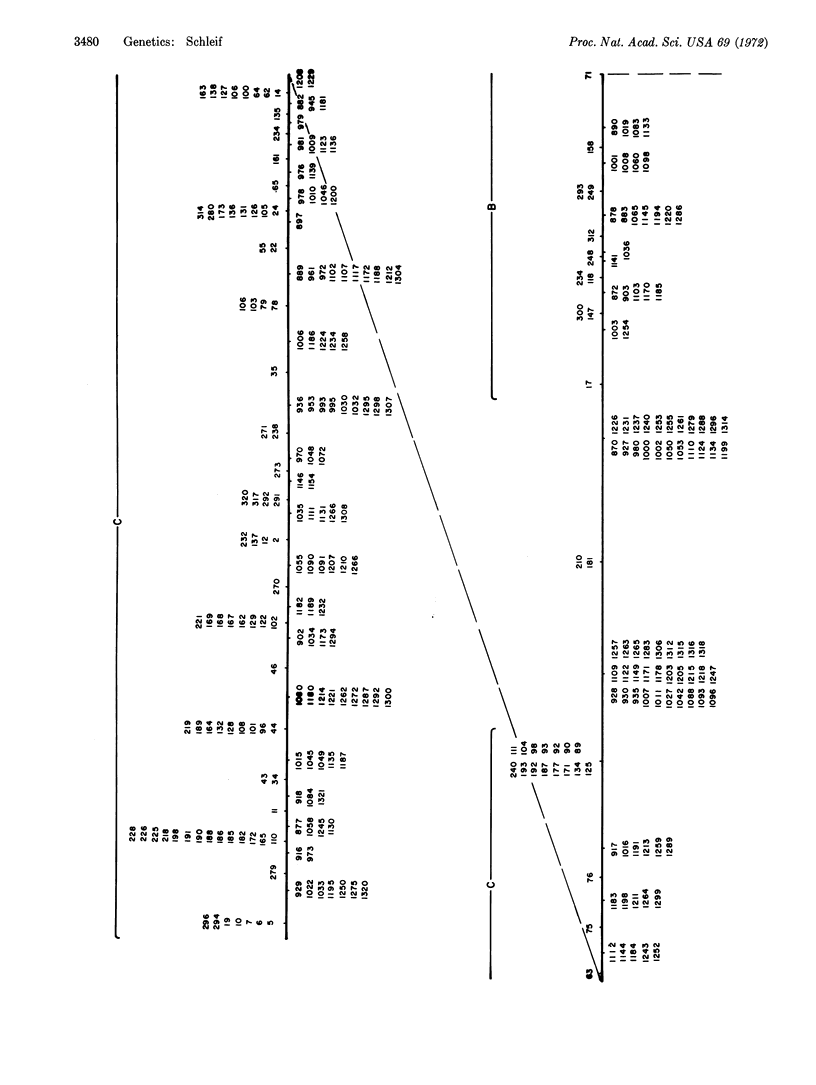
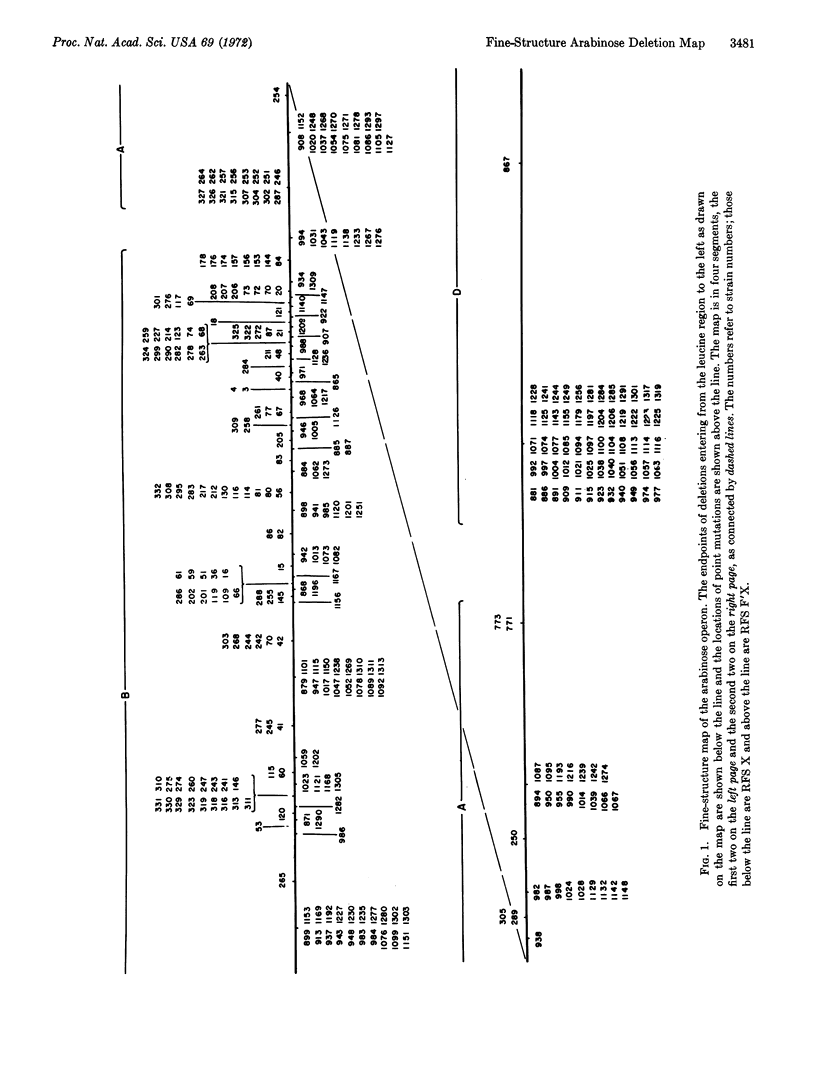
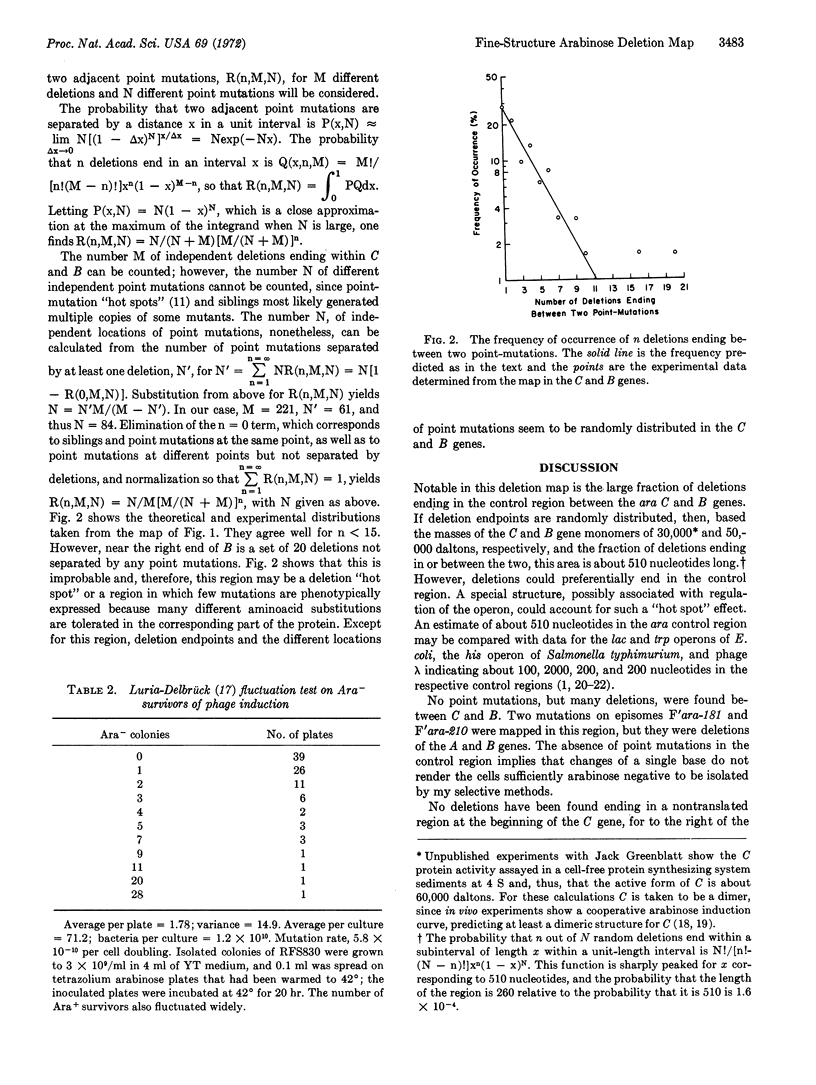
A fine-structure deletion map of the L-arabinose operon of E. coli was constructed by mapping deletion endpoints against point mutations. Of 350 independent deletions with average endpoint separation of ten nucleotides, 51 ended in the control region between the C and B genes, and the rest ended in the structural genes A, B, C, and D. If deletion endpoints are randomly distributed, the C and B genes are separated by about 510 nucleotides. Deletion endpoints and locations of point mutations in fact do appear randomly interspersed in the C and B genes, but no point mutations were found in the control region between them. Deletions were isolated with the aid of a heat-inducible λ phage inserted into leucine genes adjacent to the arabinose genes. A high-capacity mating technique was developed for rapidly generating fine structure maps from many deletions and point mutations.
Keywords: lambda phage, mating, regulation, suppression
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amati P, Meselson M. Localized Negative Interference in Bacteriophage. Genetics. 1965 Mar;51(3):369–379. doi: 10.1093/genetics/51.3.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benzer S. ON THE TOPOGRAPHY OF THE GENETIC FINE STRUCTURE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Mar;47(3):403–415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.3.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Dahlberg J. E., Boettiger J. K., Fiandt M., Szybalski W. Distance from a promoter mutation to an RNA synthesis startpoint on bacteriophage lambda DNA. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jun 21;237(77):232–236. doi: 10.1038/newbio237232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle M. E., Brown C., Hogg R. W., Helling R. B. Induction of the ara operon of Escherichia coli B-r. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):56–65. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.56-65.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englesberg E., Squires C., Meronk F., Jr The L-arabinose operon in Escherichia coli B-r: a genetic demonstration of two functional states of the product of a regulator gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1100–1107. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J., Schleif R. Arabinose C protein: regulation of the arabinose operon in vitro. Nat New Biol. 1971 Oct 6;233(40):166–170. doi: 10.1038/newbio233166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraga S. Operator mutants of the tryptophan operon in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jan 14;39(1):159–179. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90340-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz L. Selection of araB and araC mutants of Escherichia coli B-r by resistance to ribitol. J Bacteriol. 1970 May;102(2):593–595. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.2.593-595.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee N., Bendet I. Crystalline L-ribulokinase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 10;242(9):2043–2050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee N., Patrick J. W., Masson M. Crystalline L-ribulose 5-phosphate 4-epimerase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 25;243(18):4700–4705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low B. Formation of merodiploids in matings with a class of Rec- recipient strains of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 May;60(1):160–167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.1.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luria S. E., Delbrück M. Mutations of Bacteria from Virus Sensitivity to Virus Resistance. Genetics. 1943 Nov;28(6):491–511. doi: 10.1093/genetics/28.6.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. H., Ippen K., Scaife J. G., Beckwith J. R. The promoter-operator region of the lac operon of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 Dec;38(3):413–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90395-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick J. W., Lee N. Purification and properties of an L-arabinose isomerase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1968 Aug 25;243(16):4312–4318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T., Weber K., Ganem D., Miller J. H. Translational restarts: AUG reinitiation of a lac repressor fragment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):897–901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. L., Abelson J. N., Landy A., Gefter M. L., Brenner S., Smith J. D. Duplicate genes for tyrosine transfer RNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jan 14;47(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90397-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler J. R., Smith T. F. Mapping of the lactose operator. J Mol Biol. 1971 Nov 28;62(1):139–169. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleif R. An L-arabinose binding protein and arabinose permeation in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 Nov 28;46(1):185–196. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleif R., Greenblatt J., Davis R. W. Dual control of arabinose genes on transducing phage lambda-dara. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jul 14;59(1):127–150. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90417-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleif R. Induction of the L-arabinose operon. J Mol Biol. 1969 Nov 28;46(1):197–199. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard D. E., Englesberg E. Further evidence for positive control of the L-arabinose system by gene araC. J Mol Biol. 1967 May 14;25(3):443–454. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90197-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada K., Weisberg R. A., Gottesman M. E. Prophage lambda at unusual chromosomal locations. I. Location of the secondary attachment sites and the properties of the lysogens. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 14;63(3):483–503. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90443-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


