Abstract
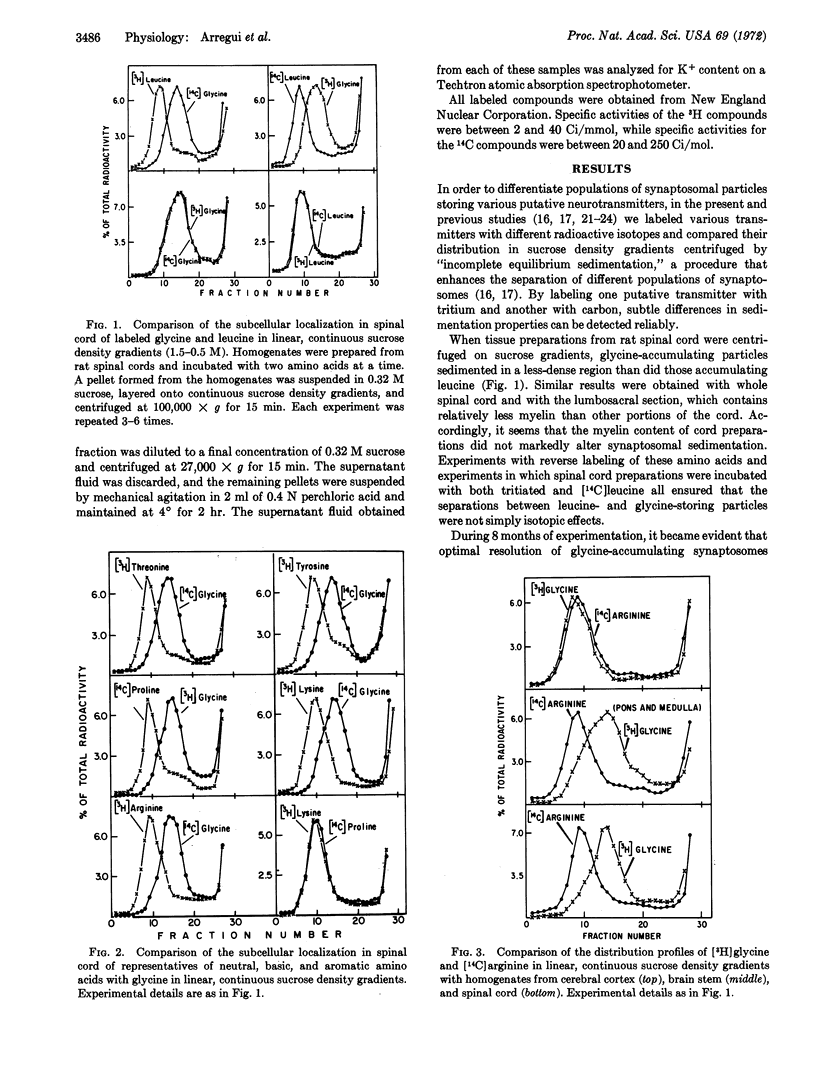
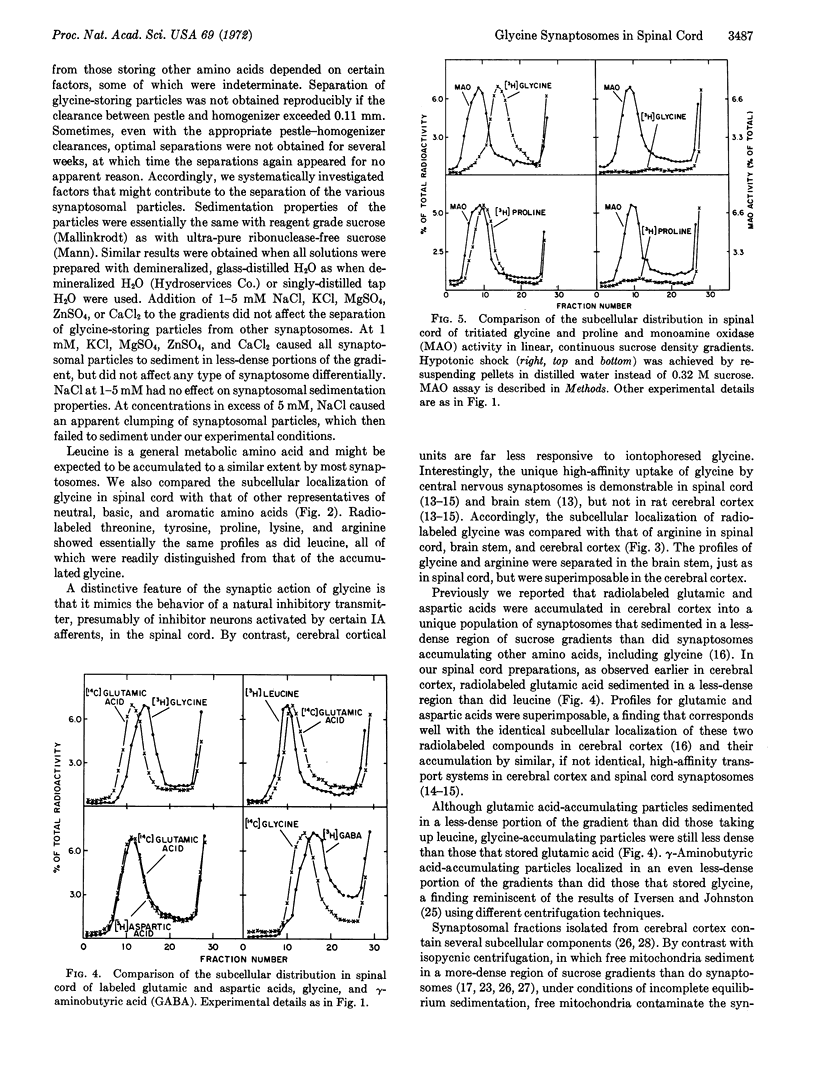
Subcellular fractionation of rat spinal cord on continuous sucrose density gradients provides evidence for the existence of a specific synaptosomal fraction (enriched in pinched-off nerve endings) that accumulates glycine selectively by way of a high-affinity transport system. The particles in this fraction sediment to a less-dense portion of sucrose gradients than do particles that accumulate neutral, basic, aromatic, and acidic amino acids. Particles accumulating γ-aminobutyric acid are even less-dense than those storing exogenous glycine. The glycine-specific synaptosomal fraction also exists in the brain stem but not in the cerebral cortex. These findings provide neurochemical support for the suggestion that glycine has a specialized synaptic function, perhaps as neurotransmitter, in mammalian spinal cord.
Keywords: neurotransmitters, glutamate, neutral inhibition, γ-aminobutyric acid
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aprison M. H., Werman R. A combined neurochemical and neurophysiological approach to identification of central nervous system transmitters. Neurosci Res (N Y) 1968;1(0):143–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aprison M. H., Werman R. The distribution of glycine in cat spinal cord and roots. Life Sci. 1965 Nov;4(21):2075–2083. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(65)90325-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasberg R., Levi G., Lajtha A. A comparison of inhibition of steady state, new transport, and exchange fluxes of amino acids in brain slices. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jun 2;203(3):464–483. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90186-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Hösli L., Johnston G. A. A pharmacological study of the depression of spinal neurones by glycine and related amino acids. Exp Brain Res. 1968;6(1):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00235443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Hösli L., Johnston G. A. Inhibition of spinal neurons by glycine. Nature. 1967 Sep 30;215(5109):1502–1503. doi: 10.1038/2151502a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Hösli L., Johnston G. A., Johnston I. H. The hyperpolarization of spinal motoneurones by glycine and related amino acids. Exp Brain Res. 1968;5(3):235–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00238666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff R. A., Shank R. P., Graham L. T., Jr, Aprison M. H., Werman R. Association of glycine with spinal interneurones. Nature. 1967 May 13;214(5089):680–681. doi: 10.1038/214680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham L. T., Jr, Shank R. P., Werman R., Aprison M. H. Distribution of some synaptic transmitter suspects in cat spinal cord: glutamic acid, aspartic acid, gamma-aminobutyric acid, glycine and glutamine. J Neurochem. 1967 Apr;14(4):465–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1967.tb09545.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A. I., Snyder S. H., Iversen L. L. Separation of catecholamine-storing synaptosomes in different regions of rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Aug;168(2):264–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerstad J. P., Murray J. E., Cutler R. W. Efflux of amino acid neurotransmitters from rat spinal cord slices. II. Factors influencing the electrically induced efflux of ( 14 C)glycine and 3 H-GABA. Brain Res. 1971 Dec 24;35(2):357–367. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90480-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkin J., Neal M. J. Effect of electrical stimulation and high potassium concentrations on the effux of (14C) glycine from slices of spinal cord. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Jun;42(2):215–223. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb07102.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Ljungdahl A. Light and electron microscopic autoradiography on spinal cord slices after incubation with labeled glycine. Brain Res. 1971 Sep 10;32(1):189–194. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90163-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen L. L., Johnston G. A. GABA uptake in rat central nervous system: comparison of uptake in slices and homogenates and the effects of some inhibitors. J Neurochem. 1971 Oct;18(10):1939–1950. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb09600.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen L. L., Snyder S. H. Synaptosomes: different populations storing catecholamines and gamma-aminobutyric acid in homogenates of rat brain. Nature. 1968 Nov 23;220(5169):796–798. doi: 10.1038/220796a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston G. A., Iversen L. L. Glycine uptake in rat central nervous system slices and homogenates: evidence for different uptake systems in spinal cord and cerebral cortex. J Neurochem. 1971 Oct;18(10):1951–1961. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb09601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston G. A. The intraspinal distribution of some depressant amino acids. J Neurochem. 1968 Sep;15(9):1013–1017. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1968.tb11644.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhar M. J., Green A. I., Snyder S. H., Gfeller E. Separation of synaptosomes storing catecholamines and gamma-aminobutyric acid in rat corpus striatum. Brain Res. 1970 Jul 29;21(3):405–417. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90420-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhar M. J., Shaskan E. G., Snyder S. H. The subcellular distribution of endogenous and exogenous serotonin in brain tissue: comparison of synaptosomes storing serotonin, norepinephrine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid. J Neurochem. 1971 Mar;18(3):333–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb11962.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhar M. J., Snyder S. H. The subcellular distribution of free H3-glutamic acid in rat cerebral cortical slices. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1970 Jan;171(1):141–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemkey-Johnston N., Dekirmenjian H. The identification of fractions enriched in nonmyelinated axons from rat whole brain. Exp Brain Res. 1970 Nov 26;11(4):392–410. doi: 10.1007/BF00237913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan W. J., Snyder S. H. High affinity uptake systems for glycine, glutamic and aspaspartic acids in synaptosomes of rat central nervous tissues. Brain Res. 1972 Jul 20;42(2):413–431. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90540-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan W. J., Snyder S. H. Unique high affinity uptake systems for glycine, glutamic and aspartic acids in central nervous tissue of the rat. Nature. 1971 Dec 3;234(5327):297–299. doi: 10.1038/234297b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matus A. I., Dennison M. E. Autoradiographic localisation of tritiated glycine at 'flat-vesicle' synapses in spinal cord. Brain Res. 1971 Sep 10;32(1):195–197. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal M. J., Pickles H. G. Uptake of 14C glycine by spinal cord. Nature. 1969 May 17;222(5194):679–680. doi: 10.1038/222679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WURTMAN R. J., AXELROD J. A SENSITIVE AND SPECIFIC ASSAY FOR THE ESTIMATION OF MONOAMINE OXIDASE. Biochem Pharmacol. 1963 Dec;12:1439–1441. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(63)90215-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werman R., Davidoff R. A., Aprison M. H. Inhibitory of glycine on spinal neurons in the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1968 Jan;31(1):81–95. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker V. P. The application of subcellular fractionation techniques to the study of brain function. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1965;15:39–96. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(65)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker V. P. The morphology of fractions of rat forebrain synaptosomes separated on continuous sucrose density gradients. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(2):412–417. doi: 10.1042/bj1060412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wofsey A. R., Kuhar M. J., Snyder S. H. A unique synaptosomal fraction, which accumulates glutamic and aspartic acids, in brain tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1102–1106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


