Abstract
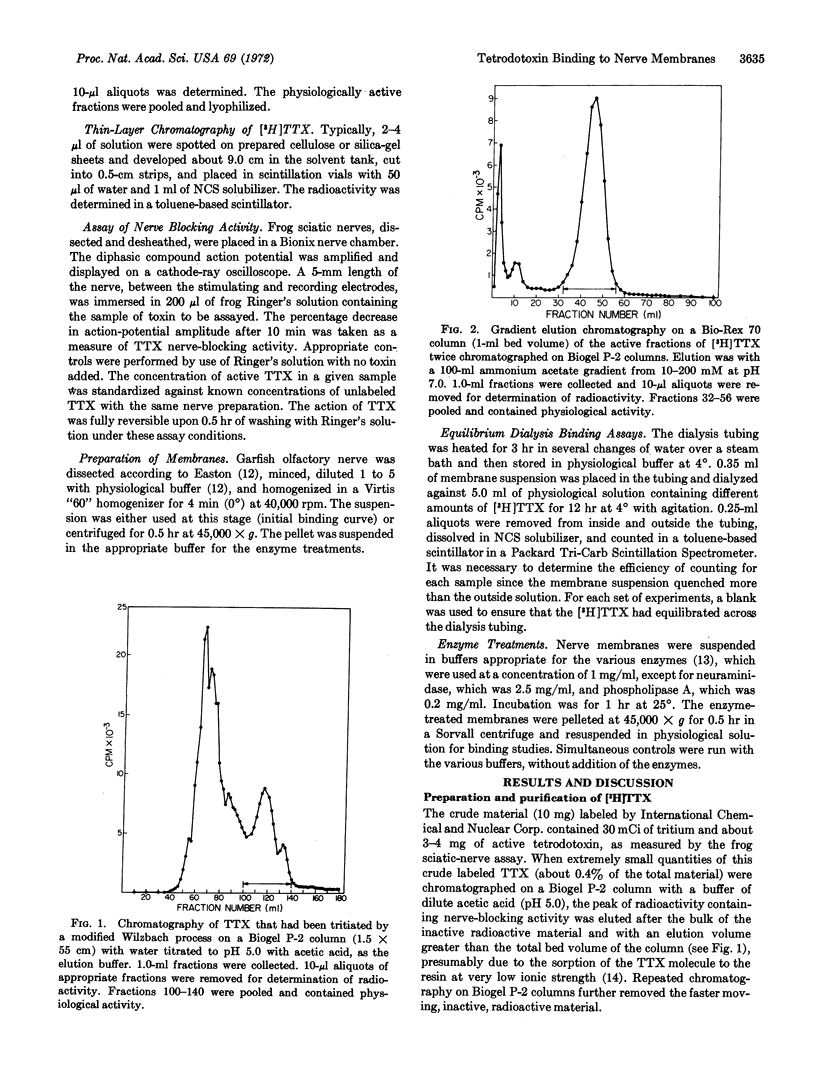
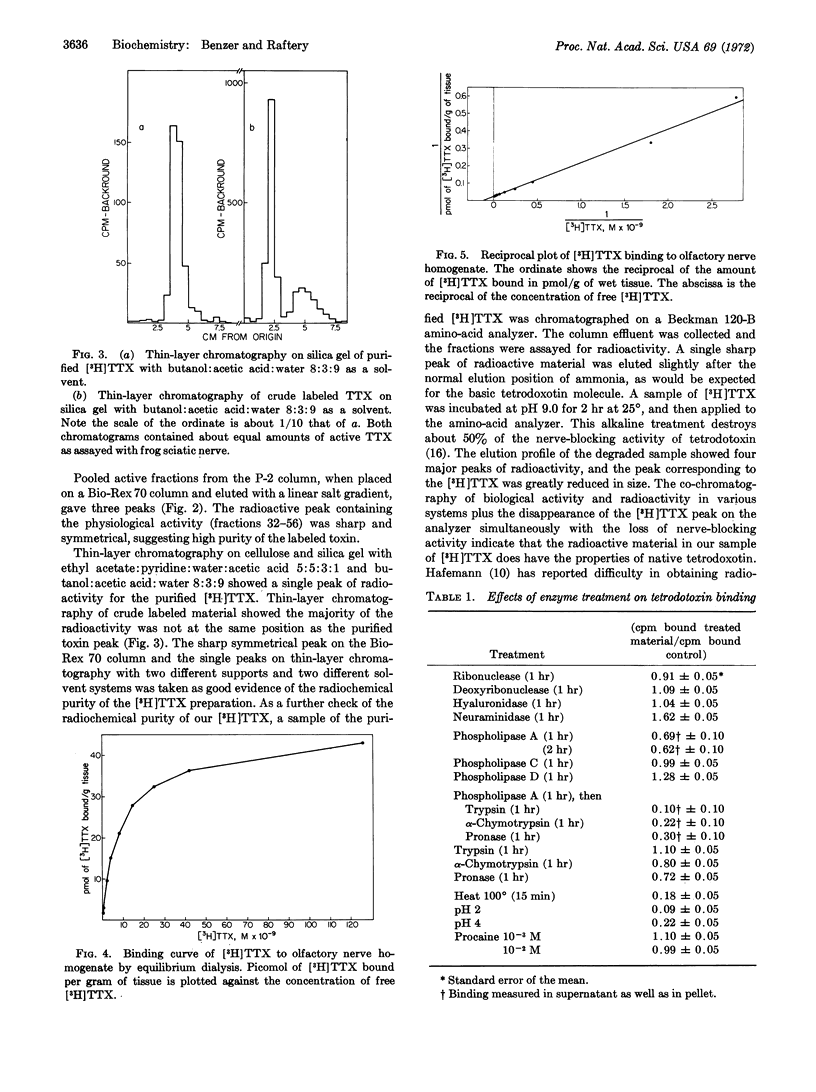
Tetrodotoxin from Japanese puffer fish has been labeled with tritium and purified from the crude mixture obtained. The interaction between the purified [3H]tetrodotoxin and membrane suspensions from the olfactory nerve of long-nosed garfish has been investigated by equilibrium dialysis. Tetrodotoxin binds to membrane suspensions with a dissociation constant KD = 8.3 nM. The nerve preparation binds 42 pmol of [3H]tetrodotoxin/g of wet tissue at saturating toxin concentrations. With various hydrolytic enzymes, the binding component is shown to be a protein embedded in a phospholipid environment. The binding is inhibited below pH 4.0 and is not stable towards heat. Tetrodotoxin binding is not inhibited by the local anesthetic, procaine.
Keywords: garfish olfactory nerve, membrane-bound protein, excitable ion channels
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clark D. G., Wolcott R. G., Raftery M. A. Partial characterization of an -bungarotoxin-binding component of electroplax membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 5;48(5):1061–1067. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90816-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuervo L. A., Adelman W. J., Jr Equilibrium and kinetic properties of the interaction between tetrodotoxin and the excitable membrane of the squid giant axon. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Mar;55(3):309–335. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.3.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easton D. M. Garfish olfactory nerve: easily accessible source of numerous long, homogeneous, nonmyelinated axons. Science. 1971 May 28;172(3986):952–955. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3986.952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURUKAWA T., SASAOKA T., HOSOYA Y. Effects of tetrodotoxin on the neuromuscular junction. Jpn J Physiol. 1959 Jun 25;9(2):143–152. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.9.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafemann D. R. Binding of radioactive tetrodotoxin to nerve membrane preparations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 9;266(2):548–556. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90110-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The permeability of the sodium channel to organic cations in myelinated nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Dec;58(6):599–619. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.6.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keynes R. D., Ritchie J. M., Rojas E. The binding of tetrodotoxin to nerve membranes. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):235–254. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marumo F., Yamada T., Asano Y., Sasaoka T., Yoshida A., Endou H. Role of the inhibitory effect of tetrodotoxin on the active sodium transport of the toad bladder. Pflugers Arch. 1968;303(1):49–54. doi: 10.1007/BF00586826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. W., Blaustein M. P., Anderson N. C., Narahashi T. Basis of tetrodotoxin's selectivity in blockage of squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1967 May;50(5):1401–1411. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.5.1401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. W., Narahashi T., Shaw T. I. An upper limit to the number of sodium channels in nerve membrane? J Physiol. 1967 Jan;188(1):99–105. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda K., Ikuma S., Kawamura M., Tachikawa R., Sakai K. Tetrodotoxin. VII. On the structure of tetrodotoxin and its derivatives. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1964 Nov;12(11):1357–1374. doi: 10.1248/cpb.12.1357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


