Abstract
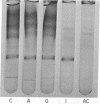
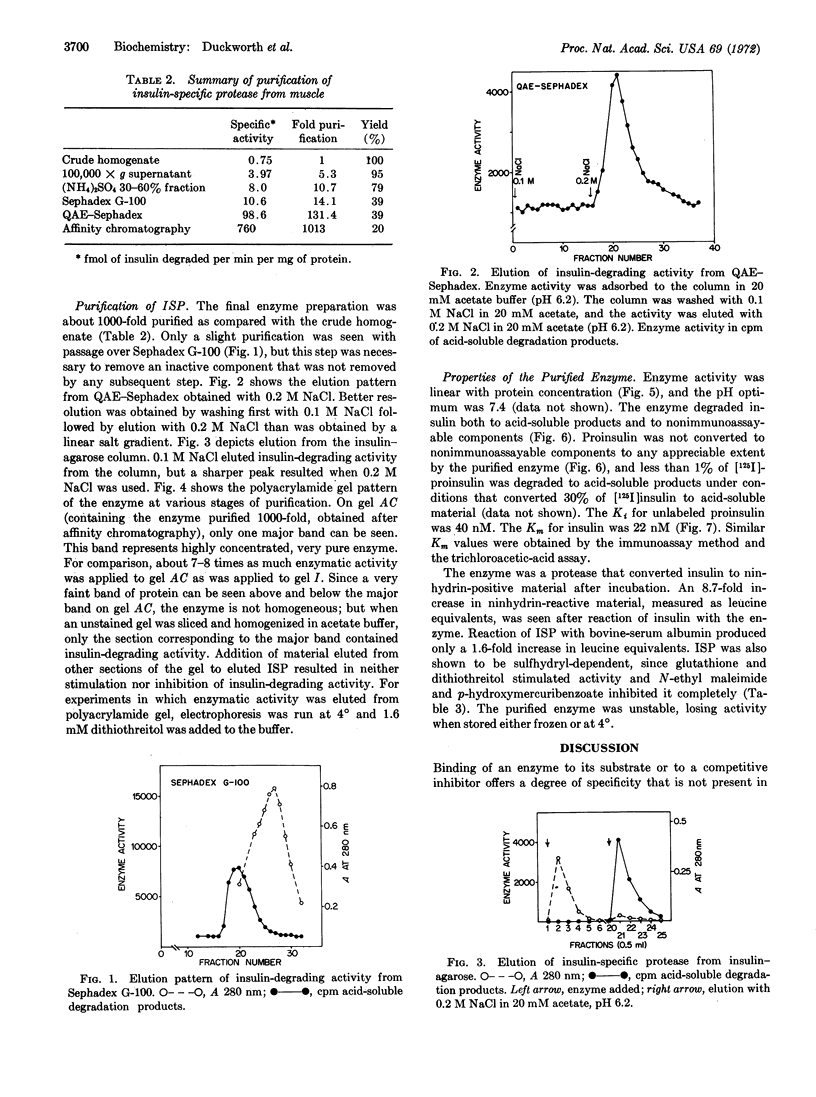
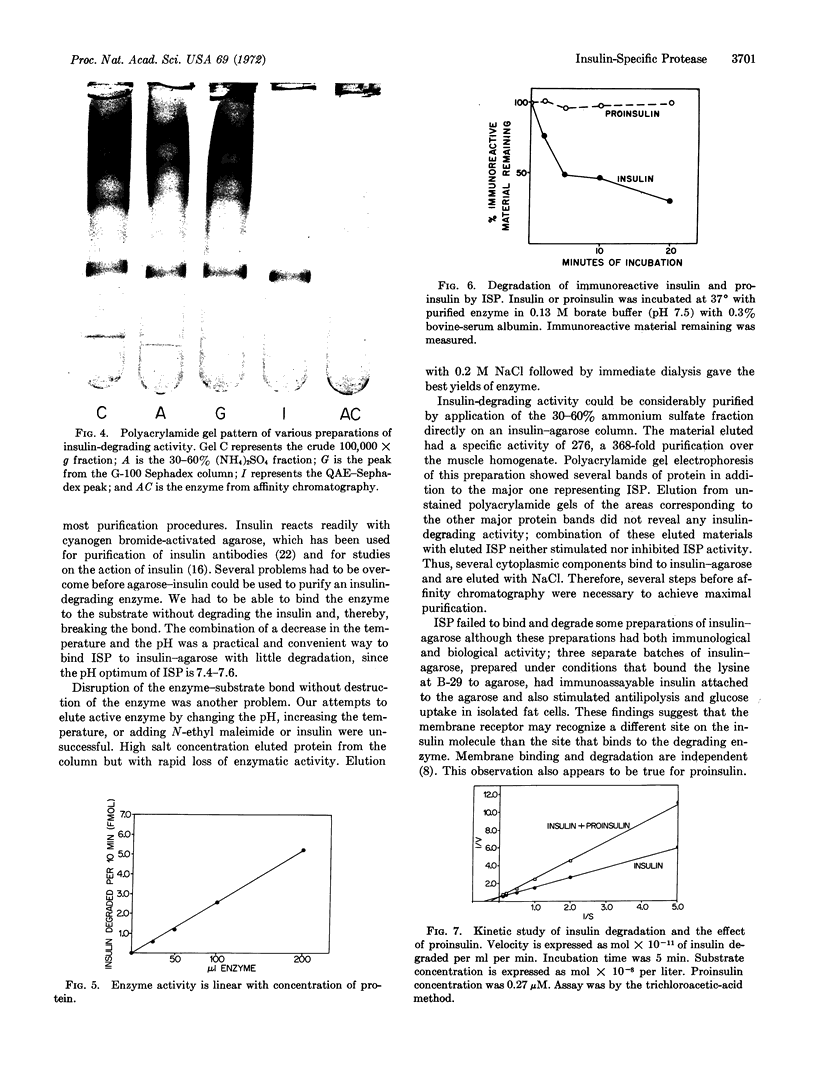
A single enzyme that proteolytically degrades insulin was isolated from rat skeletal muscle. This enzyme was purified 1000-fold by a series of steps, including affinity chromatography on insulin bound to agarose at the NH2-terminal phenylalanine of the B chain. Insulin linked to agarose at the B-29 lysine residue did not bind the enzyme and, therefore, was not suitable for purification procedures. Insulin linked at the phenylalanine residue was a substrate for the enzyme and was degraded by it; insulin attached to agarose at the lysine residue was not degraded by the enzyme. The purified enzyme preparation yielded one major band on polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and elution of this area of the gel yielded insulin-degrading activity. The purified enzyme degraded insulin but not proinsulin, with a Km for insulin of 22 nM and a Ki for proinsulin of 40 nM. The enzyme is sulfhydryl-dependent, with a physiological pH optimum.
Keywords: rat-skeletal muscle, sulfhydryl dependence, cytoplasm
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blundell T. L., Cutfield J. F., Cutfield S. M., Dodson E. J., Dodson G. G., Hodgkin D. C., Mercola D. A. Three-dimensional atomic structure of insulin and its relationship to activity. Diabetes. 1972;21(2 Suppl):492–505. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.2.s492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brush J. S., Kitabchi A. E. Metabolic disposition of [131I] iodoinsulin within the rat diaphragm. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jul 21;215(1):134–144. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90396-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brush J. S. Purification and characterizatoion of a protease with specificity for insulin from rat muscle. Diabetes. 1971 Mar;20(3):140–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burghen G. A., Kitabchi A. E., Brush J. S. Characterization of a rat liver protease with specificity for insulin. Endocrinology. 1972 Sep;91(3):633–642. doi: 10.1210/endo-91-3-633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Affinity chromatography. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:259–278. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.001355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Interaction of insulin with the cell membrane: the primary action of insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):450–457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Properties of the insulin receptor of isolated fat cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 10;246(23):7265–7274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Kahn R., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin interactions with liver plasma membranes. Independence of binding of the hormone and its degradation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3953–3961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izzo J. L., Roncone A., Izzo M. J., Foley R., Bartlett J. W. Degradation of 131 I-insulins by rat liver. Studies in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1219–1226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZEN H. M., STETTEN D., Jr Hepatic glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase. Diabetes. 1962 Jul-Aug;11:271–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabchi A. E., Duckworth W. C., Benson B. In vivo effects of insulin and proinsulin on diaphragm and epididymal fat pads in rats. Diabetes. 1972 Sep;21(9):935–938. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.9.935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabchi A. E., Duckworth W. C., Brush J. S., Heinemann M. Direct measurement of proinsulin in human plasma by the use of an insulin-degrading enzyme. J Clin Invest. 1971 Sep;50(9):1792–1799. doi: 10.1172/JCI106669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabchi A. E., Duckworth W. C., Stentz F. B., Yu S. Properties of proinsulin and related polypeptides. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1972 Feb;1(1):59–94. doi: 10.3109/10409237209102544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabchi A. E. The biological and immunological properties of pork and beef insulin, proinsulin, and connecting peptides. J Clin Invest. 1970 May;49(5):979–987. doi: 10.1172/JCI106317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIRSKY I. A. Insulinase, insulinase-inhibitors, and diabetes mellitus. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1957;13:429–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudman D., Garcia L. A., DiGirolamo M., Shank P. W. Cleavage of bovine insulin by rat adipose tissue. Endocrinology. 1966 Jan;78(1):169–185. doi: 10.1210/endo-78-1-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMIZAWA H. H. Mode of action of an insulin-degrading enzyme from beef liver. J Biol Chem. 1962 Feb;237:428–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMIZAWA H. H., NUTLEY M. L., NARAHARA H. T., WILLIAMS R. H. The mode of inactivation of insulin by rat liver extracts. J Biol Chem. 1955 May;214(1):285–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAUGHAN M. The inactivation of insulin by an enzyme from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Nov;15(3):432–433. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]