Abstract
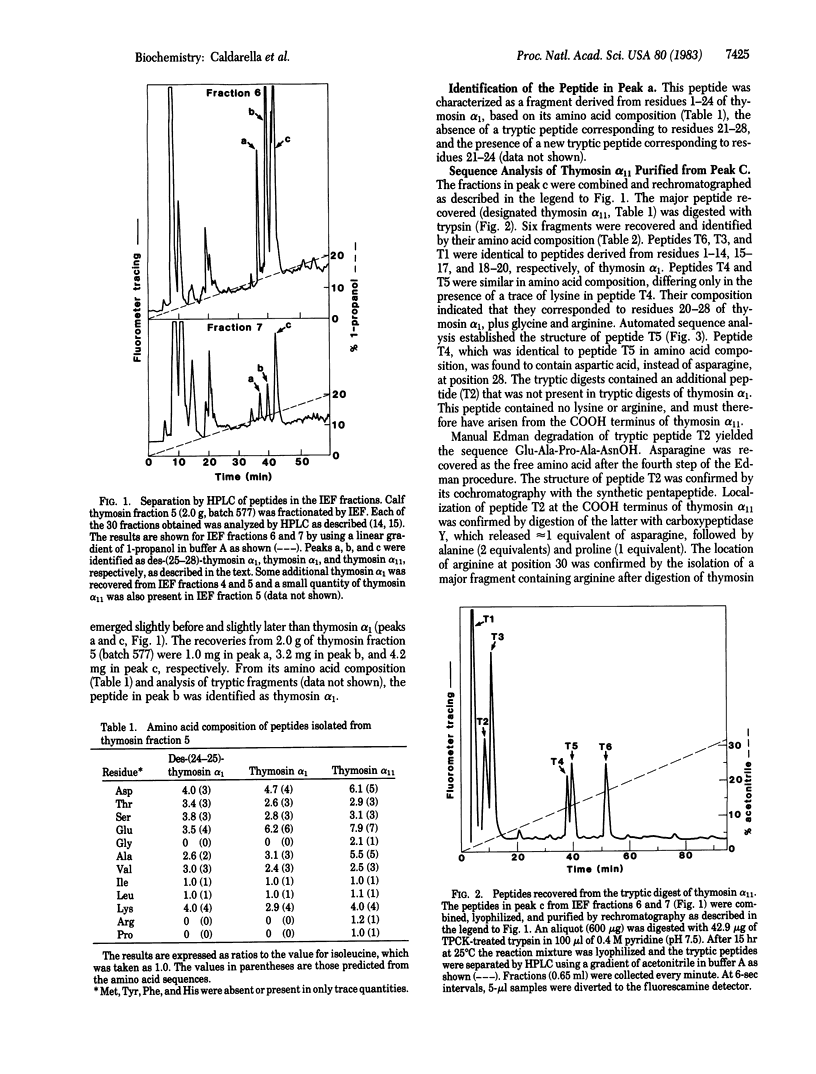
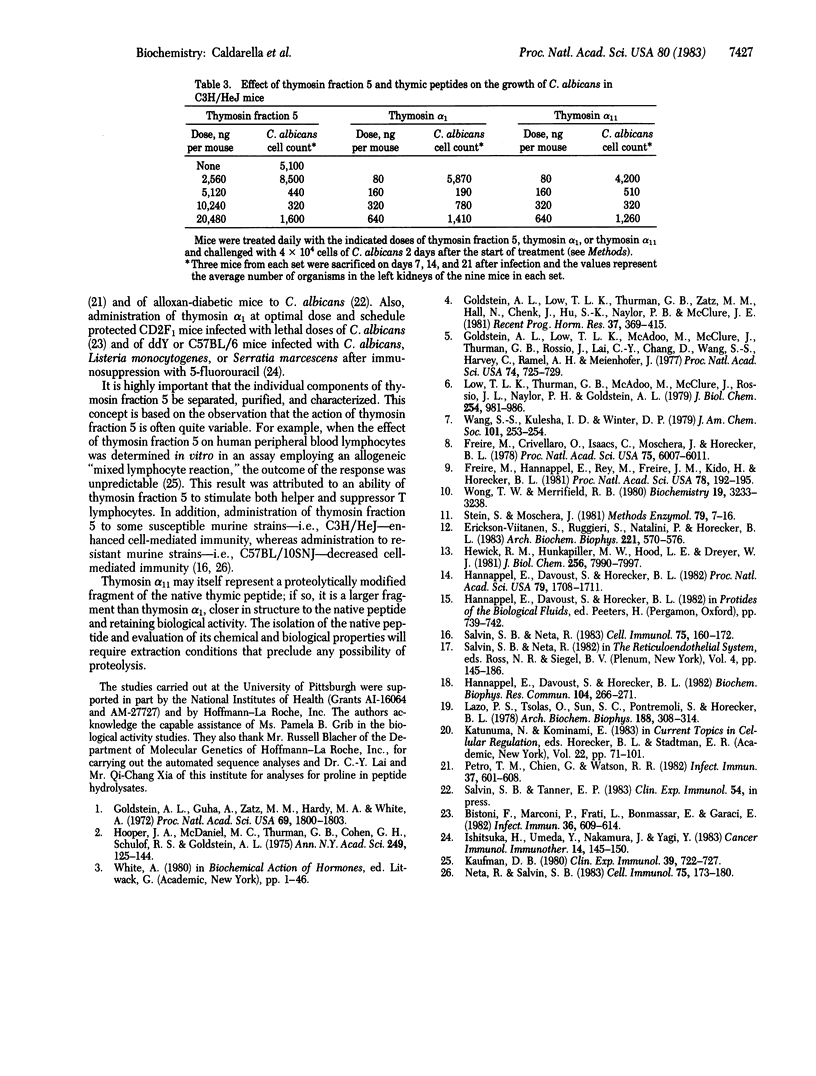
Two peptides related to thymosin alpha 1 have been isolated from preparations of calf thymosin fraction 5. One, lacking four amino acid residues at the COOH terminus, is designated des-(25-28)-thymosin alpha 1. The other, named thymosin alpha 11, contains seven additional amino acid residues at the COOH terminus. The sequence of this peptide is: AcSer-Asp-Ala-Ala-Val-Asp-Thr-Ser-Ser-Glu-Ile-Thr-Thr-Lys-Asp-Leu- Lys-Glu-Lys- Lys-Glu-Val-Val-Glu-Glu-Ala-Glu-Asn-Gly-Arg-Glu-Ala-Pro-Ala-AsnOH. Thymosin alpha 11, in doses of less than 300 ng per mouse, protects susceptible inbred murine strains against opportunistic infections with Candida albicans. It is approximately equal to 30 times as potent as thymosin fraction 5 and approximately equal in potency to thymosin alpha 1.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bistoni F., Marconi P., Frati L., Bonmassar E., Garaci E. Increase of mouse resistance to Candida albicans infection by thymosin alpha 1. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):609–614. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.609-614.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson-Viitanen S., Ruggieri S., Natalini P., Horecker B. L. Distribution of thymosin beta 4 in vertebrate classes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Mar;221(2):570–576. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90177-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freire M., Crivellaro O., Isaacs C., Moschera J., Horecker B. L. Translation of mRNA from calf thymus in the wheat germ system: evidence for a precursor of thymosin alpha1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6007–6011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freire M., Hannappel E., Rey M., Freire J. M., Kido H., Horecker B. L. Purification of thymus mRNA coding for a 16,000-dalton polypeptide containing the thymosin alpha 1 sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):192–195. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A. L., Guha A., Zatz M. M., Hardy M. A., White A. Purification and biological activity of thymosin, a hormone of the thymus gland. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1800–1803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A. L., Low T. L., McAdoo M., McClure J., Thurman G. B., Rossio J., Lai C. Y., Chang D., Wang S. S., Harvey C. Thymosin alpha1: isolation and sequence analysis of an immunologically active thymic polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):725–729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A. L., Low T. L., Thurman G. B., Zatz M. M., Hall N., Chen J., Hu S. K., Naylor P. B., McClure J. E. Current status of thymosin and other hormones of the thymus gland. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1981;37:369–415. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571137-1.50012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannappel E., Davoust S., Horecker B. L. Isolation of peptides from calf thymus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jan 15;104(1):266–271. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91969-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannappel E., Davoust S., Horecker B. L. Thymosins beta 8 and beta 9: two new peptides isolated from calf thymus homologous to thymosin beta 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1708–1711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Dreyer W. J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7990–7997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper J. A., McDaniel M. C., Thurman G. B., Cohen G. H., Schulof R. S., Goldstein A. L. Purification and properties of bovine thymosin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Feb 28;249:125–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29063.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishitsuka H., Umeda Y., Nakamura J., Yagi Y. Protective activity of thymosin against opportunistic infections in animal models. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1983;14(3):145–150. doi: 10.1007/BF00205352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman D. B. Maturational effects of thymic hormones on human helper and suppressor T cells: effects of FTS ('Facteur Thymique Sérique') and thymosin. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Mar;39(3):722–727. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazo P. S., Tsolas O., Sun S. C., Pontremoli S., Horecker B. L. Modification of fructose bisphosphatase by a proteolytic enzyme from rat liver lysosomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Jun;188(2):308–314. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(78)80014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low T. L., Thurman G. B., McAdoo M., McClure J., Rossio J. L., Naylor P. H., Goldstein A. L. The chemistry and biology of thymosin. I. Isolation, characterization, and biological activities of thymosin alpha1 and polypeptide beta1 from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):981–986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neta R., Salvin S. B. Resistance and susceptibility to infection in inbred murine strains. II. Variations in the effect of treatment with thymosin fraction 5 on the release of lymphokines in vivo. Cell Immunol. 1983 Jan;75(1):173–180. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90316-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petro T. M., Chien G., Watson R. R. Alteration of cell-mediated immunity to Listeria monocytogenes in protein-malnourished mice treated with thymosin fraction V. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):601–608. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.601-608.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvin S. B., Neta R. Resistance and susceptibility to infection in inbred murine strains. I. Variations in the response to thymic hormones in mice infected with Candida albicans. Cell Immunol. 1983 Jan;75(1):160–172. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90315-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein S., Moschera J. High-performance liquid chromatography and picomole-level detection of peptides and proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1981;79(Pt B):7–16. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)79006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong T. W., Merrifield R. B. Solid-phase synthesis of thymosin alpha 1 using tert-butyloxycarbonylaminoacyl-4-(oxymethyl)phenylacetamidomethyl-resin. Biochemistry. 1980 Jul 8;19(14):3233–3238. doi: 10.1021/bi00555a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


