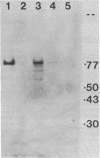
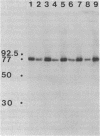
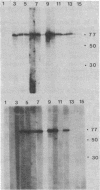
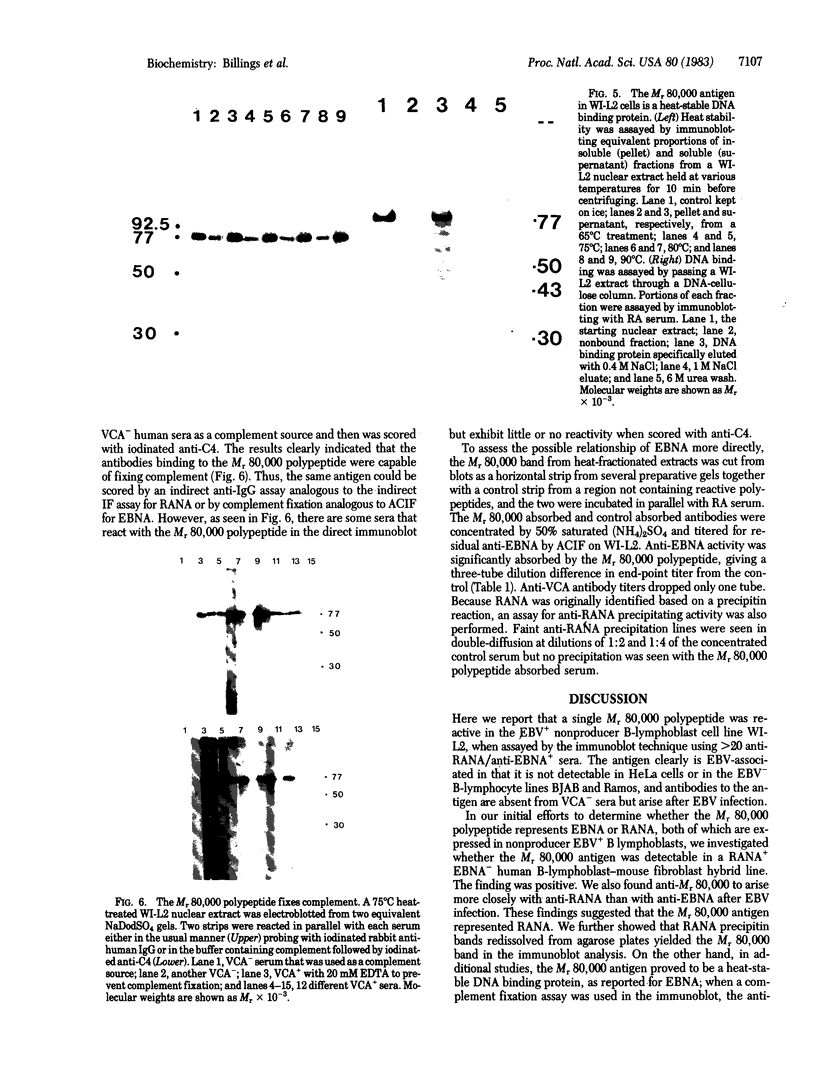
Abstract
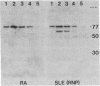
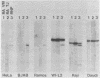
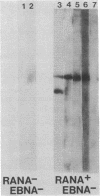
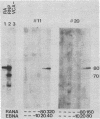
Patients with seropositive rheumatoid arthritis (RA) have elevated titers of precipitating antibody toward an antigen designated RA nuclear antigen (RANA). Anti-RANA reactivity has been associated with prior Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection. Using the protein blot technique, we have identified, in extracts of WI-L2, an EBV+ nonproducer B-lymphoblast line, a Mr 80,000 polypeptide that is reactive with anti-RANA-containing sera. This same polypeptide can be recovered from RANA precipitin bands. The Mr 80,000 polypeptide appears to be EBV-associated, as a homologous antigen was detected in two other EBV+ cell lines, Daudi and Raji, but was not present in three EBV- human cell lines tested, HeLa, BJAB, and Ramos. Anti-RANA antibodies and antibodies reactive with the Mr 80,000 polypeptide also appear coincidently in the sera of individuals exhibiting an EBV infection (infectious mononucleosis). Further analysis of the RANA-associated Mr 80,000 polypeptide suggested its identity with the previously recognized EBV-associated nuclear antigen designated EBNA. The Mr 80,000 antigen shares with EBNA the properties of being a heat-stable, DNA binding protein. EBNA is traditionally assayed by a complement fixation reaction and anti-Mr 80,000 antibodies were shown to be reactive when a complement fixation assay was used in the immunoblot. Finally, when the Mr 80,000 antigen was used to absorb an anti-RANA/anti-EBNA serum, both antibodies were reduced.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alspaugh M. A., Jensen F. C., Rabin H., Tan E. M. Lymphocytes transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. Induction of nuclear antigen reactive with antibody in rheumatoid arthritis. J Exp Med. 1978 Apr 1;147(4):1018–1027. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.4.1018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alspaugh M. A., Tan E. M. Antibodies to cellular antigens in Sjögren's syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):1067–1073. doi: 10.1172/JCI108007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aslpaugh M. A., Tan E. M. Serum antibody in rheumatoid arthritis reactive with a cell-associated antigen. Demonstration by precipitation and immunofluorescence. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 Jul-Aug;19(4):711–719. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(197607/08)19:4<711::aid-art1780190409>3.0.co;2-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron D., Strominger J. L. Partial purification and properties of the Epstein-Barr virus-associated nuclear antigen. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2875–2881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catalano M. A., Carson D. A., Niederman J. C., Feorino P., Vaughan J. H. Antibody to the rheumatoid arthritis nuclear antigen. Its relationship to in vivo Epstein-Barr virus infection. J Clin Invest. 1980 May;65(5):1238–1242. doi: 10.1172/JCI109779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catalano M. A., Carson D. A., Slovin S. F., Richman D. D., Vaughan J. H. Antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus-determined antigens in normal subjects and in patients with seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5825–5828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catalano M. A., Carson D. A., Stastny P., Freer S., Vaughan J. H. Correlation between anti-RANA and anti-EBNA titers in normal subjects with and without HLA-DRw4. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Sep;23(9):1049–1052. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. H., Lenoir G. M. Epstein-Barr virus and rheumatoid arthritis: are rheumatoid arthritis associated nuclear antigen and Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen different? Biomed Pharmacother. 1982;36(5):246–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller M., van Santen V., Kieff E. Simple repeat sequence in Epstein-Barr virus DNA is transcribed in latent and productive infections. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):311–320. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.311-320.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Heller M., van Santen V., Kieff E. Simple repeat array in Epstein-Barr virus DNA encodes part of the Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen. Science. 1983 Jun 24;220(4604):1396–1398. doi: 10.1126/science.6304878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Kieff E. One of two Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigens contains a glycine-alanine copolymer domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5665–5669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenoir G., Berthelon M. C., Favre M. C., de-Thé G. Characterization of Epstein-Barr virus antigens. I. Biochemical analysis of the complement-fixing soluble antigen and relationship with Epstein-Barr virus-associated nuclear antigen. J Virol. 1976 Feb;17(2):672–674. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.2.672-674.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Virolainen M., Defendi V. Human lymphoblastoid lines from lymph node and spleen. Cancer. 1968 Sep;22(3):517–524. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196809)22:3<517::aid-cncr2820220305>3.0.co;2-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luka J., Lindahl T., Klein G. Purification of the Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen from Epstein-Barr virus-transformed human lymphoid cell lines. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):604–611. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.604-611.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo T., Hibi N., Nishi S., Hirai H., Osato T. Studies on Epstein-Barr virus-related antigens. III. Purification of the virus-determined nuclear antigen (EBNA) from non-producer Raji cells. Int J Cancer. 1978 Dec;22(6):747–752. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910220618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedman B. M., Klein G. Cellular localization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated complement-fixing antigen in producer and non-producer lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1973 May;11(3):499–520. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sculley T. B., Kreofsky T., Pearson G. R., Spelsberg T. C. Partial purification of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen(s). J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3974–3982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slovin S. F., Glassy M. C., Dambaugh T., Catalano M. A., Curry R. A., Ferrone S., Kieff E., Vaughan J. H., Carson D. A. Discordant expression of 2 Epstein-Barr virus-associated antigens, EBNA and RANA, in man-rodent somatic cell hybrids. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):585–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slovin S. F., Vaughan J. H., Carson D. A. Changes in the expression of two Epstein-Barr virus-associated antigens, EBNA and RANA, during the cell cycle of transformed human B lymphoblasts. Int J Cancer. 1980 Jul 15;26(1):9–12. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910260103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spelsberg T. C., Sculley T. B., Pikler G. M., Gilbert J. A., Pearson G. R. Evidence for two classes of chromatin-associated Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):555–565. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.555-565.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strnad B. C., Schuster T. C., Hopkins R. F., 3rd, Neubauer R. H., Rabin H. Identification of an Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen by fluoroimmunoelectrophoresis and radioimmunoelectrophoresis. J Virol. 1981 Jun;38(3):996–1004. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.3.996-1004.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. P., Grogan E. A., Shedd D., Robert M., Liu C. R., Miller G. Stable expression in mouse cells of nuclear neoantigen after transfer of a 3.4-megadalton cloned fragment of Epstein-Barr virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5688–5692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venables P. J., Roffe L. M., Erhardt C. C., Maini R. N., Edwards J. M., Porter A. D. Titers of antibodies to RANA in rheumatoid arthritis and normal sera. Relationship to Epstein-Barr virus infection. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Dec;24(12):1459–1468. doi: 10.1002/art.1780241201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. J., Hoch S. O. Definition of the antigenic polypeptides in the Sm and RNP ribonucleoprotein complexes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Sep 16;102(1):365–371. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91530-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]