Abstract
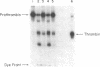
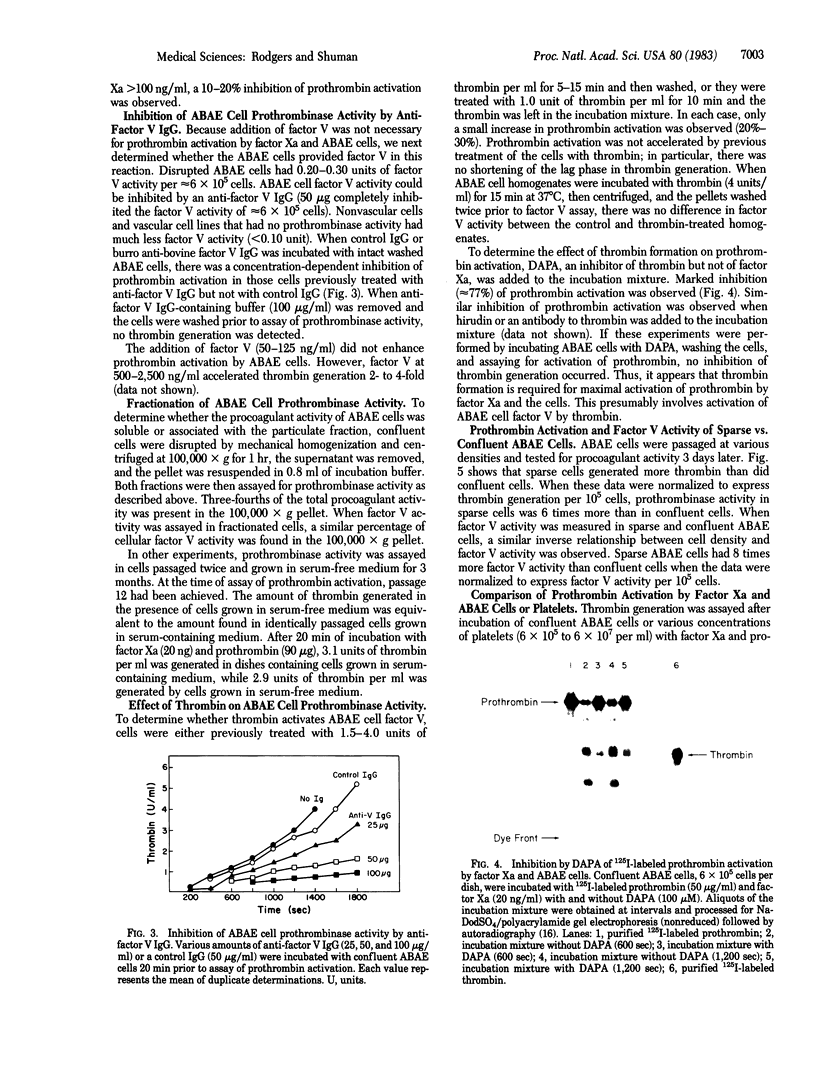
Vascular endothelial cells derived from adult bovine aorta (ABAE) treated with factor Xa and calcium were found to activate prothrombin. In contrast, nonvascular cells (human foreskin fibroblasts, bovine corneal endothelial cells, or human fetal lung cells) had either no or very little effect on prothrombin activation. In the presence of 6 X 10(5) ABAE cells, 20 ng of factor Xa converted 90 micrograms of prothrombin into 80 units of thrombin after 45 min at 37 degrees C. Exogenous factor V was not required for prothrombin activation, but thrombin generation was enhanced 2- to 4-fold by the addition of factor V (500-2,500 ng/ml). Treatment of ABAE cells with anti-bovine factor V IgG markedly inhibited prothrombin activation by factor Xa and calcium. In cells grown in serum-free medium for 3 months, the amount of factor V activity was equivalent to that found in cells grown with serum, which suggests that these cells probably synthesize factor V. Sparse ABAE cells increased prothrombin activation by factor Xa 6-fold compared to activation in confluent cells. Although previous thrombin treatment of ABAE cells did not enhance prothrombin activation, addition of dansyl arginine-4-ethyl piperidine amide markedly inhibited activation of 125I-labeled prothrombin by factor Xa, indicating that thrombin formation is necessary for optimal prothrombin activation. These data indicate that aortic endothelium may provide a physiologically important surface for activation of prothrombin as well as a mechanism for optimal formation of clots at sites of vascular injury.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breederveld K., Giddings J. C., ten Cate J. W., Bloom A. L. The localization of factor V within normal human platelets and the demonstration of a platelet-factor V antigen in congenital factor V deficiency. Br J Haematol. 1975 Mar;29(3):405–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb01838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesney C. M., Pifer D., Colman R. W. Subcellular localization and secretion of factor V from human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5180–5184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison P. M., Bensch K., Karasek M. A. Isolation and growth of endothelial cells from the microvessels of the newborn human foreskin in cell culture. J Invest Dermatol. 1980 Oct;75(4):316–321. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12530941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd, Fasco M. J. Polyethylene glycol 6,000 enhancement of the clotting of fibrinogen solutions in visual and mechanical assays. Thromb Res. 1974 Jun;4(6):809–817. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(74)90024-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frojmovic M. M., Panjwani R. Geometry of normal mammalian platelets by quantitative microscopic studies. Biophys J. 1976 Sep;16(9):1071–1089. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85756-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane W. H., Majerus P. W. Purification and characterization of human coagulation factor V. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):1002–1007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS M. L., WARE A. G. A one-stage method for the determination of accelerator globulin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Dec;84(3):640–643. doi: 10.3181/00379727-84-20738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March S. C., Parikh I., Cuatrecasas P. A simplified method for cyanogen bromide activation of agarose for affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miletich J. P., Broze G. J., Jr, Majerus P. W. The synthesis of sulfated dextran beads for isolation of human plasma coagulation factors II, IX, and X. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):304–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90462-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miletich J. P., Jackson C. M., Majerus P. W. Interaction of coagulation factor Xa with human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):4033–4036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.4033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miletich J. P., Jackson C. M., Majerus P. W. Properties of the factor Xa binding site on human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6908–6916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miletich J. P., Kane W. H., Hofmann S. L., Stanford N., Majerus P. W. Deficiency of factor Xa-factor Va binding sites on the platelets of a patient with a bleeding disorder. Blood. 1979 Nov;54(5):1015–1022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPAPORT S. I., SCHIFFMAN S., PATCH M. J., AMES S. B. The importance of activation of antihemophilic globulin and proaccelerin by traces of thrombin in the generation of intrinsic prothrombinase activity. Blood. 1963 Feb;21:221–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers G. M., Greenberg C. S., Shuman M. A. Characterization of the effects of cultured vascular cells on the activation of blood coagulation. Blood. 1983 Jun;61(6):1155–1162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savion N., Isaacs J. D., Gospodarowicz D., Shuman M. A. Internalization and degradation of thrombin and up regulation of thrombin-binding sites in corneal endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4514–4519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tangen O., Berman H. J., Marfey P. Gel filtration. A new technique for separation of blood platelets from plasma. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1971 Jun 30;25(2):268–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauber J. P., Cheng J., Gospodarowicz D. Effect of high and low density lipoproteins on proliferation of cultured bovine vascular endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1980 Oct;66(4):696–708. doi: 10.1172/JCI109907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauber J. P., Cheng J., Massoglia S., Gospodarowicz D. High density lipoproteins and the growth of vascular endothelial cells in serum-free medium. In Vitro. 1981 Jun;17(6):519–530. doi: 10.1007/BF02633513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy P. B., Nesheim M. E., Mann K. G. Coordinate binding of factor Va and factor Xa to the unstimulated platelet. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):743–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy P. B., Peterson J. M., Nesheim M. E., McDuffie F. C., Mann K. G. Interaction of coagulation factor V and factor Va with platelets. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10354–10361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall R. T., Harker L. A. The endothelium and thrombosis. Annu Rev Med. 1980;31:361–371. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.31.020180.002045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]