Abstract
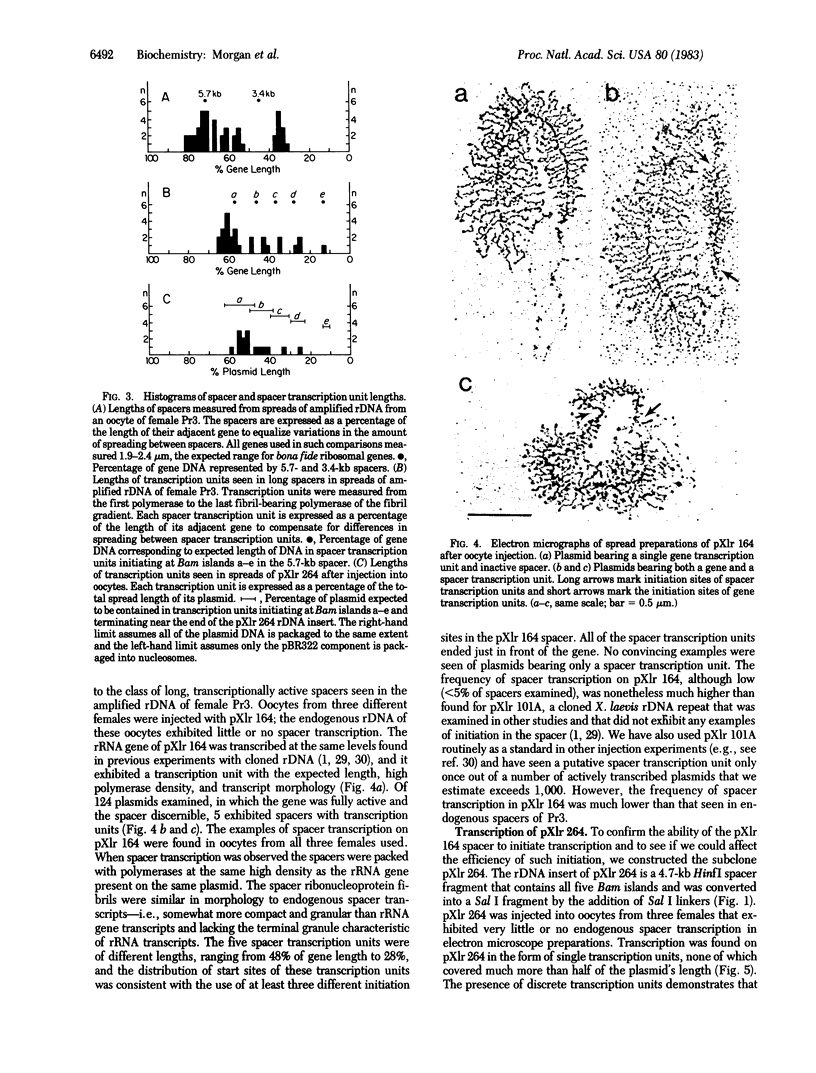
Rare individuals of Xenopus laevis exhibit frequent initiation of transcription in the spacers of oocyte ribosomal DNA (rDNA). Using electron microscopy we have characterized spacer transcription in such an individual and have confirmed that the sites of transcription initiation correspond to the imperfectly duplicated promoters ("Bam islands") present in the X. laevis rDNA spacer. We have cloned a repeat unit containing a gene and a spacer from this individual and have injected the recombinant plasmid, pXlr 164, into oocytes of other X. laevis individuals. In electron microscope preparations the spacers of some of the cloned repeats were transcribed by RNA polymerase I. This demonstrates that the ability to initiate transcription at the Bam islands is a property of the spacer DNA. On pXlr 164, initiation in the spacer occurred about 5% as frequently as transcription from the gene promoter. However, transcribed spacers were as closely packed with RNA polymerase as was the gene. We conclude that polymerase I promoters may vary over a wide range in the frequency with which they "activate" but that once activated all can load polymerases to maximal density. The presence or absence of spacer transcription had no observable effect on either the frequency of activation or the density of polymerase loading of the gene immediately downstream. A subclone, pXlr 264, containing only spacer DNA also showed regular initiation and termination, providing further evidence that there is an effective "fail-safe" termination signal 225 base pairs upstream from the rRNA gene initiation site.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach R., Allet B., Crippa M. Sequence organization of the spacer in the ribosomal genes of Xenopus clivii and Xenopus borealis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5311–5330. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakken A., Morgan G., Sollner-Webb B., Roan J., Busby S., Reeder R. H. Mapping of transcription initiation and termination signals on Xenopus laevis ribosomal DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):56–60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boseley P., Moss T., Mächler M., Portmann R., Birnstiel M. Sequence organization of the spacer DNA in a ribosomal gene unit of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):19–31. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90291-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bünemann H., Müller W. Base specific fractionation of double stranded DNA: affinity chromatography on a novel type of adsorbant. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Mar;5(3):1059–1074. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen E. S., Dover G. A. Multiple Pol I initiation sequences in rDNA spacers of Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):7017–7026. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.7017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont J. N. Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals. J Morphol. 1972 Feb;136(2):153–179. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Scheer U., Spring H., Trendelenburg M. F., Krohne G. Morphology of transcriptional units of rDNA. Evidence for transcription in apparent spacer intercepts and cleavages in the elongating nascent RNA. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Jul;100(2):233–244. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90143-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hipskind R. A., Reeder R. H. Initiation of ribosomal RNA chains in homogenates of oocyte nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7896–7906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohorn B. D., Rae P. M. Accurate transcription of truncated ribosomal DNA templates in a Drosophila cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1501–1505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohorn B. D., Rae P. M. Nontranscribed spacer sequences promote in vitro transcription of Drosophila ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6879–6886. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. R., Hayward D. C., Glover D. M. Transcription of the 'non-transcribed' spacer of Drosophila melanogaster rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 11;11(1):11–19. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller O. L., Jr, Bakken A. H. Morphological studies of transcription. Acta Endocrinol Suppl (Copenh) 1972;168:155–177. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.071s155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan G. T., Bakken A. H., Reeder R. H. Transcription of Xenopus borealis rRNA genes in nuclei of Xenopus laevis oocytes. Dev Biol. 1982 Oct;93(2):471–477. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90135-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T. A transcriptional function for the repetitive ribosomal spacer in Xenopus laevis. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):223–228. doi: 10.1038/302223a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T., Birnstiel M. L. The putative promoter of a Xenopus laevis ribosomal gene is reduplicated. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 24;6(12):3733–3743. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.12.3733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T., Boseley P. G., Birnstiel M. L. More ribosomal spacer sequences from Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Feb 11;8(3):467–485. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.3.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T. Transcription of cloned Xenopus laevis ribosomal DNA microinjected into Xenopus oocytes, and the identification of an RNA polymerase I promoter. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):835–842. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90288-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruitt S. C., Grainger R. M. A mosaicism in the higher order structure of Xenopus oocyte nucleolar chromatin prior to and during ribosomal gene transcription. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):711–720. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90434-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H., Wilkinson J., Bakken A., Morgan G., Busby S. J., Roan J., Sollner-Webb B. Evidence for two functional regions in the Xenopus laevis RNA polymerase I promoter. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):867–871. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rungger D., Achermann H., Crippa M. Transcription of spacer sequences in genes coding for ribosomal RNA in Xenopus cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3957–3961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheer U., Trendelenburg M. F., Krohne G., Franke W. W. Lengths and patterns of transcriptional units in the amplified nucleoli of oocytes of Xenopus laevis. Chromosoma. 1977 Mar 16;60(2):147–167. doi: 10.1007/BF00288462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simeone A., de Falco A., Macino G., Boncinelli E. Sequence organization of the ribosomal spacer of D.melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):8263–8272. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.8263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trendelenburg M. F., Gurdon J. B. Transcription of cloned Xenopus ribosomal genes visualised after injection into oocyte nuclei. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):292–294. doi: 10.1038/276292a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]