Abstract
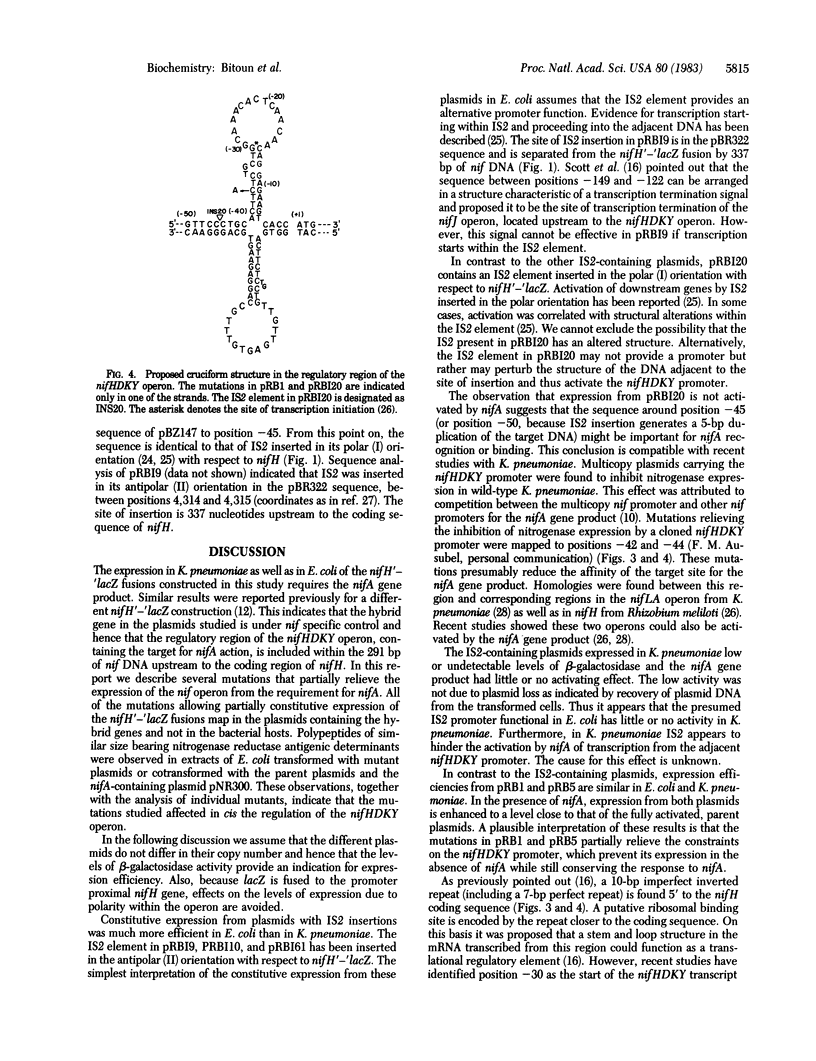
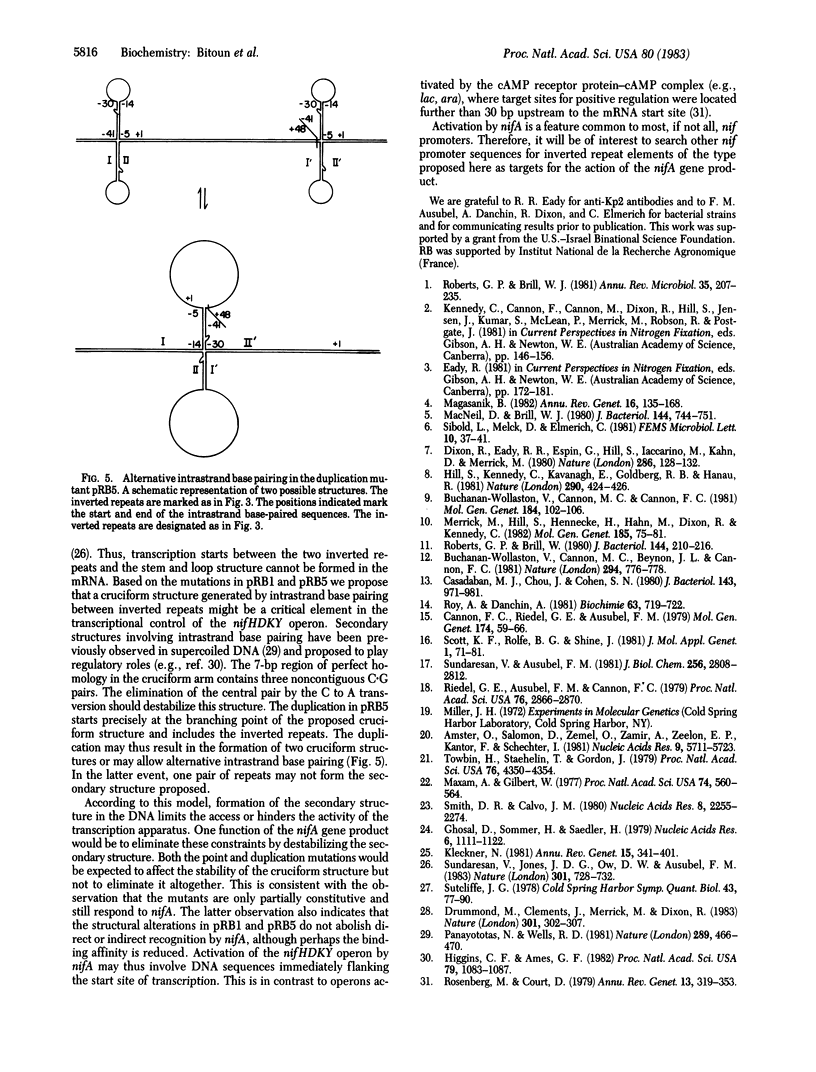
The nifHDKY operon of Klebsiella pneumoniae encodes for structural polypeptides of nitrogenase and requires the nifA gene product for transcription. Mutations that allow transcription of the nifHDKY operon in absence of the nifA gene product were characterized in plasmids containing the regulatory region of nifHDKY and nifH fused in phase to lacZ. beta-Galactosidase activity served as a measure for nifH expression. Most mutations were located in the nif regulatory region and included insertion sequence 2 (IS2) insertions, a sequence duplication, and a base substitution. In Escherichia coli, beta-galactosidase activity expressed from the mutant plasmids in the absence of nifA was 6-30% of the nifA-activated, parental level. Expression from most mutant plasmids was further increased by nifA. In K. pneumoniae, IS2-containing plasmids expressed low levels of beta-galactosidase and responded poorly, if at all, to activation by nifA, whereas expression from other mutant types was similar to that observed in E. coli. Nucleotide sequence analysis of two mutants indicated that sequences within 41 base pairs upstream to the nifH coding sequence were involved in nif-specific regulation. The results suggest that an inverted repeat element in this region, which could theoretically form a cruciform structure in the DNA, is involved in the transcriptional control of the nifHDKY operon.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buchanan-Wollaston V., Cannon M. C., Beynon J. L., Cannon F. C. Role of the nifA gene product in the regulation of nif expression in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):776–778. doi: 10.1038/294776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan-Wollaston V., Cannon M. C., Cannon F. C. The use of cloned nif (nitrogen fixation) DNA to investigate transcriptional regulation of nif expression in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(1):102–106. doi: 10.1007/BF00271203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon F. C., Riedel G. E., Ausubel F. M. Overlapping sequences of Klebsiella pneumoniae nifDNA cloned and characterized. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jul 2;174(1):59–66. doi: 10.1007/BF00433306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Chou J., Cohen S. N. In vitro gene fusions that join an enzymatically active beta-galactosidase segment to amino-terminal fragments of exogenous proteins: Escherichia coli plasmid vectors for the detection and cloning of translational initiation signals. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):971–980. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.971-980.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R., Eady R. R., Espin G., Hill S., Iaccarino M., Kahn D., Merrick M. Analysis of regulation of Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogen fixation (nif) gene cluster with gene fusions. Nature. 1980 Jul 10;286(5769):128–132. doi: 10.1038/286128a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond M., Clements J., Merrick M., Dixon R. Positive control and autogenous regulation of the nifLA promoter in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Nature. 1983 Jan 27;301(5898):302–307. doi: 10.1038/301302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosal D., Sommer H., Saedler H. Nucleotide sequence of the transposable DNA-element IS2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Mar;6(3):1111–1122. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.3.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Ames G. F. Regulatory regions of two transport operons under nitrogen control: nucleotide sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1083–1087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill S., Kennedy C., Kavanagh E., Goldberg R. B., Hanau R. Nitrogen fixation gene (nifL) involved in oxygen regulation of nitrogenase synthesis in K. pneumoniae. Nature. 1981 Apr 2;290(5805):424–426. doi: 10.1038/290424a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N. Transposable elements in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:341–404. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacNeil D., Brill W. J. Mutations in nif genes that cause Klebsiella pneumoniae to be derepressed for nitrogenase synthesis in the presence of ammonium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):744–751. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.744-751.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magasanik B. Genetic control of nitrogen assimilation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1982;16:135–168. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.001031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotatos N., Wells R. D. Cruciform structures in supercoiled DNA. Nature. 1981 Feb 5;289(5797):466–470. doi: 10.1038/289466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel G. E., Ausubel F. M., Cannon F. C. Physical map of chromosomal nitrogen fixation (nif) genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2866–2870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. P., Brill W. J. Gene-product relationships of the nif regulon of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):210–216. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.210-216.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. P., Brill W. J. Genetics and regulation of nitrogen fixation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:207–235. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.001231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A., Danchin A. Restriction map of the cya region of the Escherichia coli K12 chromosome. Biochimie. 1981 Aug-Sep;63(8-9):719–722. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(81)80220-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott K. F., Rolfe B. G., Shine J. Biological nitrogen fixation: primary structure of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifH and nifD genes. J Mol Appl Genet. 1981;1(1):71–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R., Calvo J. M. Nucleotide sequence of the E coli gene coding for dihydrofolate reductase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2255–2274. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundaresan V., Ausubel F. M. Nucleotide sequence of the gene coding for the nitrogenase iron protein from Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2808–2812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundaresan V., Jones J. D., Ow D. W., Ausubel F. M. Klebsiella pneumoniae nifA product activates the Rhizobium meliloti nitrogenase promoter. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):728–732. doi: 10.1038/301728a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Török I., Kondorosi A. Nucleotide sequence of the R.meliloti nitrogenase reductase (nifH) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5711–5723. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



