Abstract
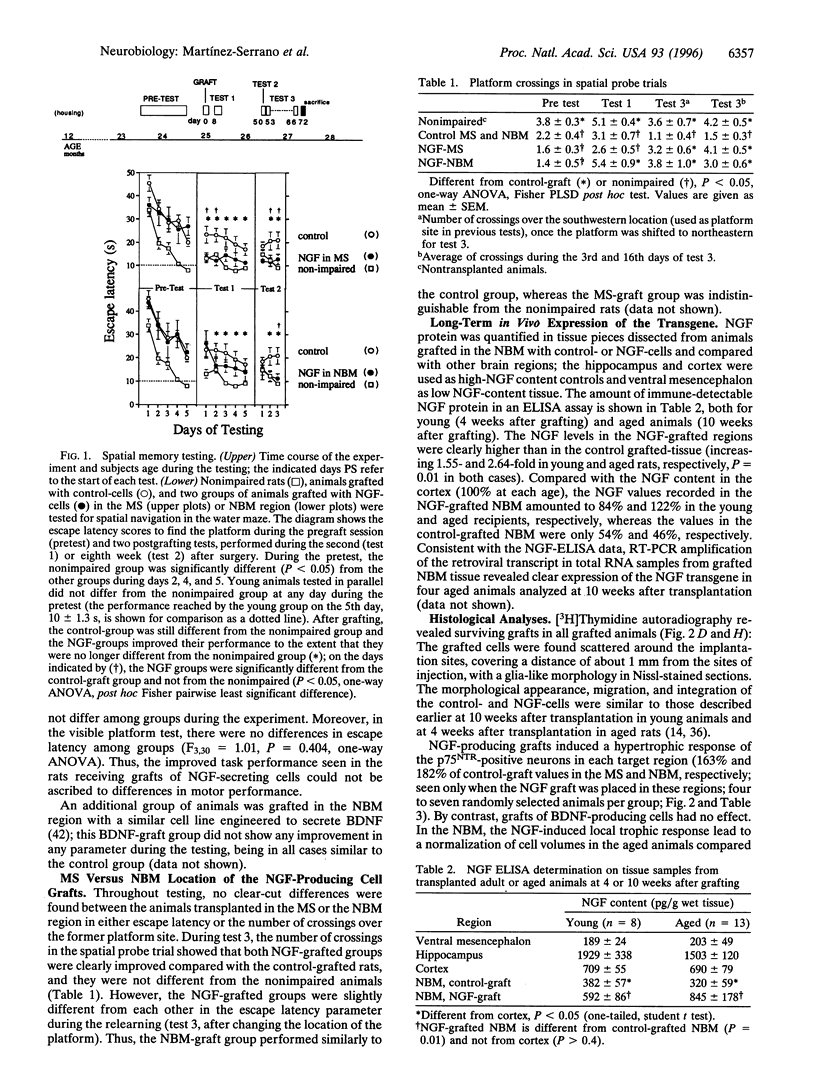
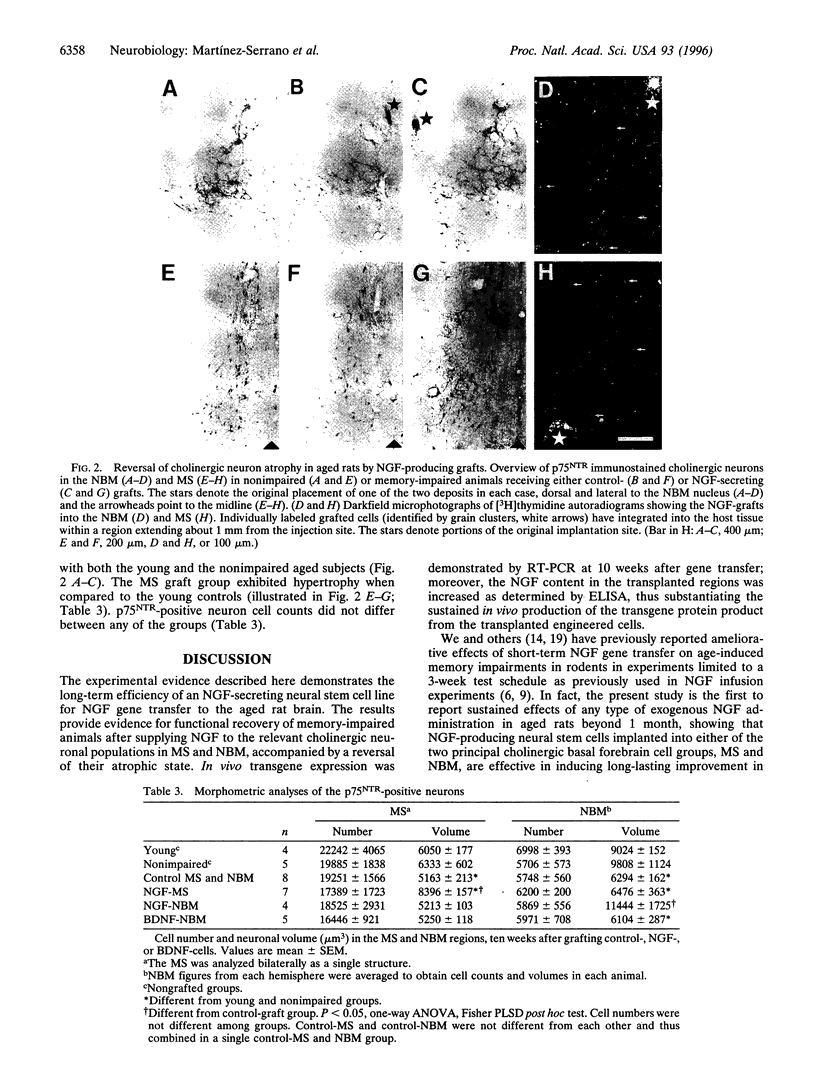
Nerve growth factor (NGF) stimulates functional recovery from cognitive impairments associated with aging, either when administered as a purified protein or by means of gene transfer to the basal forebrain. Because gene transfer procedures need to be tested in long-term experimental paradigms to assess their in vivo efficiency, we have used ex vivo experimental gene therapy to provide local delivery of NGF to the aged rat brain over a period of 2.5 months by transplanting immortalized central nervous system-derived neural stem cells genetically engineered to secrete NGF. By grafting them at two independent locations in the basal forebrain, medial septum and nucleus basalis magnocellularis, we show that functional recovery as assessed in the Morris water maze can be achieved by neurotrophic stimulation of any of these cholinergic cell groups. Moreover, the cholinergic neurons in the grafted regions showed a hypertrophic response resulting in a reversal of the age-associated atrophy seen in the learning-impaired aged control rats. Long-term expression of the transgene lead to an increased NGF tissue content (as determined by NGF-ELISA) in the transplanted regions up to at least 10 weeks after grafting. We conclude that the gene transfer procedure used here is efficient to provide the brain with a long-lasting local supply of exogenous NGF, induces long-term functional recovery of cognitive functions, and that independent trophic stimulation of the medial septum or nucleus basalis magnocellularis has similar consequences at the behavioral level.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altavista M. C., Bentivoglio A. R., Crociani P., Rossi P., Albanese A. Age-dependent loss of cholinergic neurones in basal ganglia of rats. Brain Res. 1988 Jul 5;455(1):177–181. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90130-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. D., Alderson R. F., Altar C. A., DiStefano P. S., Corcoran T. L., Lindsay R. M., Wiegand S. J. Differential distribution of exogenous BDNF, NGF, and NT-3 in the brain corresponds to the relative abundance and distribution of high-affinity and low-affinity neurotrophin receptors. J Comp Neurol. 1995 Jun 26;357(2):296–317. doi: 10.1002/cne.903570209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartus R. T., Dean R. L., 3rd, Beer B., Lippa A. S. The cholinergic hypothesis of geriatric memory dysfunction. Science. 1982 Jul 30;217(4558):408–414. doi: 10.1126/science.7046051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger-Sweeney J., Heckers S., Mesulam M. M., Wiley R. G., Lappi D. A., Sharma M. Differential effects on spatial navigation of immunotoxin-induced cholinergic lesions of the medial septal area and nucleus basalis magnocellularis. J Neurosci. 1994 Jul;14(7):4507–4519. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-07-04507.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biegon A., Greenberger V., Segal M. Quantitative histochemistry of brain acetylcholinesterase and learning rate in the aged rat. Neurobiol Aging. 1986 May-Jun;7(3):215–217. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(86)90046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen K. S., Gage F. H. Somatic gene transfer of NGF to the aged brain: behavioral and morphological amelioration. J Neurosci. 1995 Apr;15(4):2819–2825. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-04-02819.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle J. T., Price D. L., DeLong M. R. Alzheimer's disease: a disorder of cortical cholinergic innervation. Science. 1983 Mar 11;219(4589):1184–1190. doi: 10.1126/science.6338589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekker A. J., Fagan A. M., Gage F. H., Thal L. J. Effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor on remaining neurons in the lesioned nucleus basalis magnocellularis. Brain Res. 1994 Mar 7;639(1):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)91775-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnett S. B., Fibiger H. C. Role of forebrain cholinergic systems in learning and memory: relevance to the cognitive deficits of aging and Alzheimer's dementia. Prog Brain Res. 1993;98:413–420. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)62425-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerich D. F., Hammang J. P., Baetge E. E., Winn S. R. Implantation of polymer-encapsulated human nerve growth factor-secreting fibroblasts attenuates the behavioral and neuropathological consequences of quinolinic acid injections into rodent striatum. Exp Neurol. 1994 Nov;130(1):141–150. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1994.1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fibiger H. C. Cholinergic mechanisms in learning, memory and dementia: a review of recent evidence. Trends Neurosci. 1991 Jun;14(6):220–223. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90117-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch C. E. Neuron atrophy during aging: programmed or sporadic? Trends Neurosci. 1993 Mar;16(3):104–110. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90134-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer W., Björklund A., Chen K., Gage F. H. NGF improves spatial memory in aged rodents as a function of age. J Neurosci. 1991 Jul;11(7):1889–1906. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-07-01889.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer W., Chen K. S., Gage F. H., Björklund A. Progressive decline in spatial learning and integrity of forebrain cholinergic neurons in rats during aging. Neurobiol Aging. 1992 Jan-Feb;13(1):9–23. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(92)90003-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer W. Nerve growth factor reverses spatial memory impairments in aged rats. Neurochem Int. 1994 Jul;25(1):47–52. doi: 10.1016/0197-0186(94)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer W., Sirevaag A., Wiegand S. J., Lindsay R. M., Björklund A. Reversal of spatial memory impairments in aged rats by nerve growth factor and neurotrophins 3 and 4/5 but not by brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 30;91(18):8607–8611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.18.8607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer W., Wictorin K., Björklund A., Williams L. R., Varon S., Gage F. H. Amelioration of cholinergic neuron atrophy and spatial memory impairment in aged rats by nerve growth factor. Nature. 1987 Sep 3;329(6134):65–68. doi: 10.1038/329065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer Walter, Gage Fred H., Björklund Anders. Degenerative Changes in Forebrain Cholinergic Nuclei Correlate with Cognitive Impairments in Aged Rats. Eur J Neurosci. 1989 Jan;1(1):34–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1989.tb00772.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friden P. M., Walus L. R., Watson P., Doctrow S. R., Kozarich J. W., Bäckman C., Bergman H., Hoffer B., Bloom F., Granholm A. C. Blood-brain barrier penetration and in vivo activity of an NGF conjugate. Science. 1993 Jan 15;259(5093):373–377. doi: 10.1126/science.8420006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage F. H., Kelly P. A., Björklund A. Regional changes in brain glucose metabolism reflect cognitive impairments in aged rats. J Neurosci. 1984 Nov;4(11):2856–2865. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-11-02856.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher M., Burwell R. D., Kodsi M. H., McKinney M., Southerland S., Vella-Rountree L., Lewis M. H. Markers for biogenic amines in the aged rat brain: relationship to decline in spatial learning ability. Neurobiol Aging. 1990 Sep-Oct;11(5):507–514. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(90)90111-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher M., Colombo P. J. Ageing: the cholinergic hypothesis of cognitive decline. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1995 Apr;5(2):161–168. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(95)80022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen H. J., Bendtsen T. F., Korbo L., Marcussen N., Møller A., Nielsen K., Nyengaard J. R., Pakkenberg B., Sørensen F. B., Vesterby A. Some new, simple and efficient stereological methods and their use in pathological research and diagnosis. APMIS. 1988 May;96(5):379–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1988.tb05320.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelsma T. N., Aguayo A. J. Trophic factors. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1994 Oct;4(5):717–725. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(94)90015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaja M. D., Rosenberg M. B., Yoshida K., Gage F. H. Somatic gene transfer of nerve growth factor promotes the survival of axotomized septal neurons and the regeneration of their axons in adult rats. J Neurosci. 1992 Jul;12(7):2849–2864. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-07-02849.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koh S., Chang P., Collier T. J., Loy R. Loss of NGF receptor immunoreactivity in basal forebrain neurons of aged rats: correlation with spatial memory impairment. Brain Res. 1989 Oct 2;498(2):397–404. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordower J. H., Charles V., Bayer R., Bartus R. T., Putney S., Walus L. R., Friden P. M. Intravenous administration of a transferrin receptor antibody-nerve growth factor conjugate prevents the degeneration of cholinergic striatal neurons in a model of Huntington disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 13;91(19):9077–9080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.19.9077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay R. M., Wiegand S. J., Altar C. A., DiStefano P. S. Neurotrophic factors: from molecule to man. Trends Neurosci. 1994 May;17(5):182–190. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(94)90099-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowska A. L., Koliatsos V. E., Breckler S. J., Price D. L., Olton D. S. Human nerve growth factor improves spatial memory in aged but not in young rats. J Neurosci. 1994 Aug;14(8):4815–4824. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-08-04815.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Serrano A., Hantzopoulos P. A., Björklund A. Ex vivo gene transfer of brain-derived neurotrophic factor to the intact rat forebrain: neurotrophic effects on cholinergic neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 1996 Apr;8(4):727–735. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1996.tb01258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Serrano A., Fischer W., Björklund A. Reversal of age-dependent cognitive impairments and cholinergic neuron atrophy by NGF-secreting neural progenitors grafted to the basal forebrain. Neuron. 1995 Aug;15(2):473–484. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Serrano A., Lundberg C., Horellou P., Fischer W., Bentlage C., Campbell K., McKay R. D., Mallet J., Björklund A. CNS-derived neural progenitor cells for gene transfer of nerve growth factor to the adult rat brain: complete rescue of axotomized cholinergic neurons after transplantation into the septum. J Neurosci. 1995 Aug;15(8):5668–5680. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-08-05668.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mufson E. J., Bothwell M., Kordower J. H. Loss of nerve growth factor receptor-containing neurons in Alzheimer's disease: a quantitative analysis across subregions of the basal forebrain. Exp Neurol. 1989 Sep;105(3):221–232. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(89)90124-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson O. G., Leanza G., Rosenblad C., Lappi D. A., Wiley R. G., Björklund A. Spatial learning impairments in rats with selective immunolesion of the forebrain cholinergic system. Neuroreport. 1992 Nov;3(11):1005–1008. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199211000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitta A., Murase K., Furukawa Y., Hayashi K., Hasegawa T., Nabeshima T. Memory impairment and neural dysfunction after continuous infusion of anti-nerve growth factor antibody into the septum in adult rats. Neuroscience. 1993 Dec;57(3):495–499. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90001-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renfranz P. J., Cunningham M. G., McKay R. D. Region-specific differentiation of the hippocampal stem cell line HiB5 upon implantation into the developing mammalian brain. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):713–729. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90116-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M. B., Friedmann T., Robertson R. C., Tuszynski M., Wolff J. A., Breakefield X. O., Gage F. H. Grafting genetically modified cells to the damaged brain: restorative effects of NGF expression. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1575–1578. doi: 10.1126/science.3201248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rylett R. J., Goddard S., Schmidt B. M., Williams L. R. Acetylcholine synthesis and release following continuous intracerebral administration of NGF in adult and aged Fischer-344 rats. J Neurosci. 1993 Sep;13(9):3956–3963. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-09-03956.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rylett R. J., Williams L. R. Role of neurotrophins in cholinergic-neurone function in the adult and aged CNS. Trends Neurosci. 1994 Nov;17(11):486–490. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(94)90138-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. L., Booze R. M. Cholinergic and GABAergic neurons in the nucleus basalis region of young and aged rats. Neuroscience. 1995 Aug;67(3):679–688. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(95)00076-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strada O., Vyas S., Hirsch E. C., Ruberg M., Brice A., Agid Y., Javoy-Agid F. Decreased choline acetyltransferase mRNA expression in the nucleus basalis of Meynert in Alzheimer disease: an in situ hybridization study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9549–9553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strömberg I., Wetmore C. J., Ebendal T., Ernfors P., Persson H., Olson L. Rescue of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons after implantation of genetically modified cells producing recombinant NGF. J Neurosci Res. 1990 Mar;25(3):405–411. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490250318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderström S., Hallbök F., Ibáez C. F., Persson H., Ebendal T. Recombinant human beta-nerve growth factor (NGF): biological activity and properties in an enzyme immunoassay. J Neurosci Res. 1990 Dec;27(4):665–677. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490270427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres E. M., Perry T. A., Blockland A., Wilkinson L. S., Wiley R. G., Lappi D. A., Dunnet S. B. Behavioural, histochemical and biochemical consequences of selective immunolesions in discrete regions of the basal forebrain cholinergic system. Neuroscience. 1994 Nov;63(1):95–122. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)90010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Zee C. E., Lourenssen S., Stanisz J., Diamond J. NGF deprivation of adult rat brain results in cholinergic hypofunction and selective impairments in spatial learning. Eur J Neurosci. 1995 Jan 1;7(1):160–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1995.tb01030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse P. J., Price D. L., Struble R. G., Clark A. W., Coyle J. T., Delon M. R. Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia: loss of neurons in the basal forebrain. Science. 1982 Mar 5;215(4537):1237–1239. doi: 10.1126/science.7058341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcock G. K., Esiri M. M., Bowen D. M., Smith C. C. Alzheimer's disease. Correlation of cortical choline acetyltransferase activity with the severity of dementia and histological abnormalities. J Neurol Sci. 1982 Dec;57(2-3):407–417. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(82)90045-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan Q., Matheson C., Sun J., Radeke M. J., Feinstein S. C., Miller J. A. Distribution of intracerebral ventricularly administered neurotrophins in rat brain and its correlation with trk receptor expression. Exp Neurol. 1994 May;127(1):23–36. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1994.1076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]