Abstract
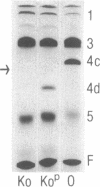
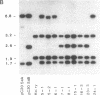
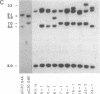
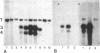
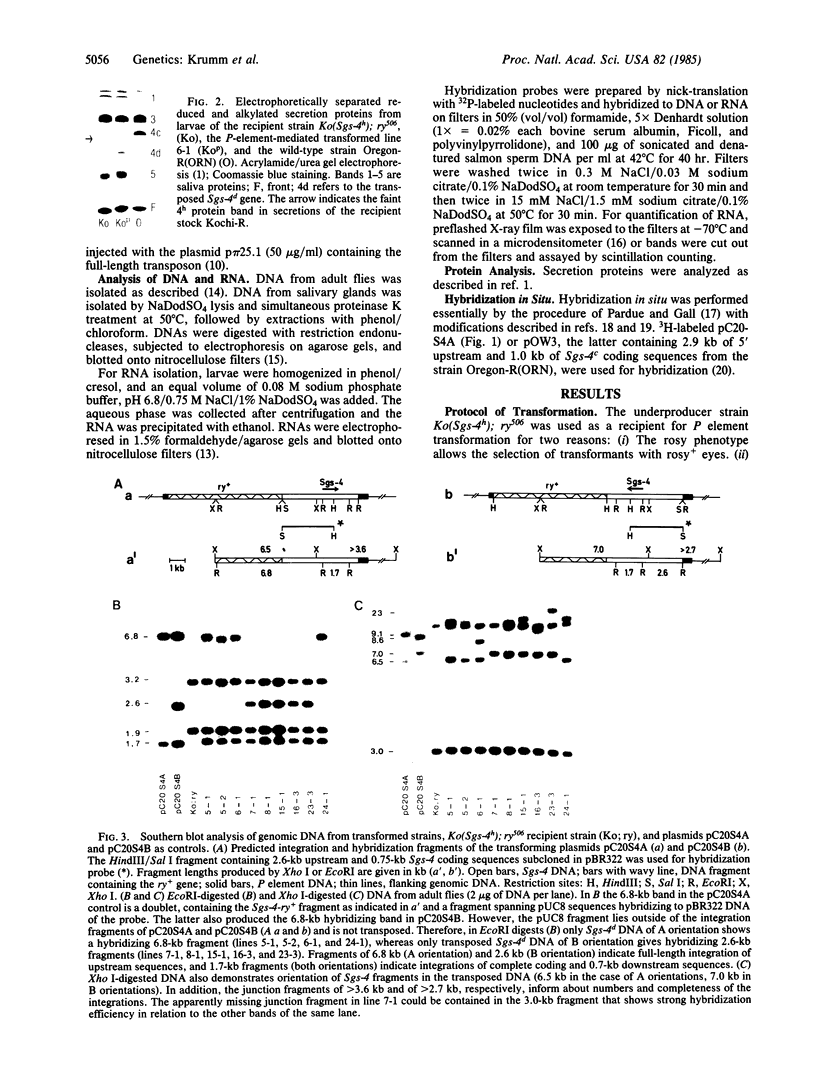
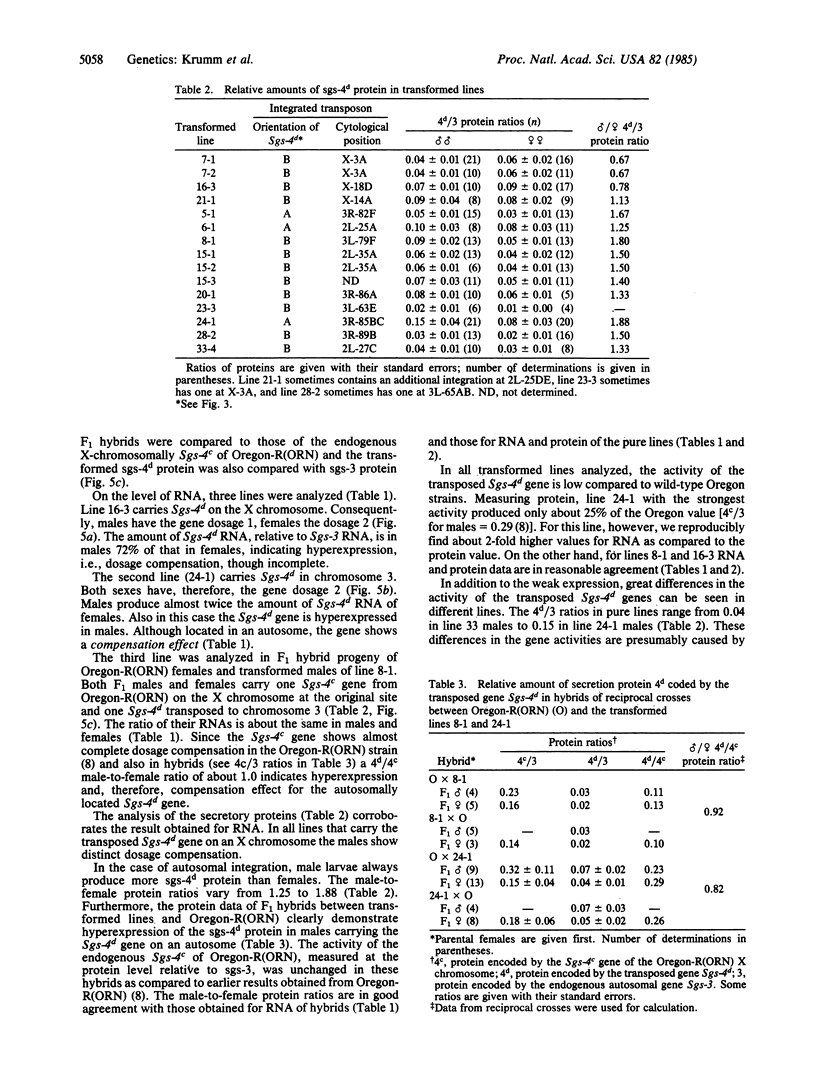
The Sgs-4 gene of Drosophila melanogaster encodes one of the larval secretion proteins and is active only in salivary glands at the end of larval development. This gene lies in the X chromosome and is controlled by dosage compensation--i.e., the gene is hyperexpressed in males. Therefore, males with one X chromosome produce nearly as much Sgs-4 products as females with two X chromosomes. We used a 4.9-kilobase-pair (kb) DNA fragment containing the Sgs-4d coding region embedded in 2.6 kb of upstream sequences and 1.3 kb of downstream sequences for P-element-mediated transformation of the Sgs-4h underproducer strain Kochi-R. Sgs-4d gene expression was found in all 15 transformed lines analyzed, varying with the site of chromosomal integration. The transposed gene was subject to tissue- and stage-specific regulation. At X-chromosomal sites, the levels of gene expression were similar in both sexes, signifying dosage compensation. At autosomal sites, it was on average 1.5 times higher in males than in females. The results indicate that the transforming DNA fragment contains all sequences necessary for tissue- and stage-specific regulation and for hyperexpression in males.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashburner M. Patterns of puffing activity in the salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophila. I. Autosomal puffing patterns in a laboratory stock of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma. 1967;21(4):398–428. doi: 10.1007/BF00336950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECKER H. J. [The puffs of salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophilia melanogaster. Part 1. Observations on the behavior of a typical puff in the normal strain and in two mutants, giant and lethal giant larvae]. Chromosoma. 1959;10:654–678. doi: 10.1007/BF00396591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckendorf S. K., Kafatos F. C. Differentiation in the salivary glands of Drosophila melanogaster: characterization of the glue proteins and their developmental appearance. Cell. 1976 Nov;9(3):365–373. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen E. H., Bowman S. C. Detection and location of three simple sequence DNAs in polytene chromosomes from virilis group species of Drosophila. Chromosoma. 1979 Aug;73(3):327–355. doi: 10.1007/BF00288696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring W. J., Klemenz R., Weber U., Kloter U. Functional analysis of the white gene of Drosophila by P-factor-mediated transformation. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2077–2085. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02094.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. A., Posakony J. W., Maniatis T. Correct developmental expression of a cloned alcohol dehydrogenase gene transduced into the Drosophila germ line. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):59–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Gillam I. C., Delaney A. D., Tener G. M. Acetylation of chromosome squashes of Drosophila melanogaster decreases the background in autoradiographs from hybridization with [125I]-labeled RNA. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Aug;26(8):677–679. doi: 10.1177/26.8.99471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelrigg T., Levis R., Rubin G. M. Transformation of white locus DNA in drosophila: dosage compensation, zeste interaction, and position effects. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):469–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90240-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korge G. Chromosome puff activity and protein synthesis in larval salivary glands of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4550–4554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korge G. Direct correlation between a chromosome puff and the synthesis of a larval saliva protein in Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma. 1977 Jul 5;62(2):155–174. doi: 10.1007/BF00292637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korge G. Genetic analysis of the larval secretion gene Sgs-4 and its regulatory chromosome sites in Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma. 1981;84(3):373–390. doi: 10.1007/BF00286027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korge G. Larval saliva in Drosophila melanogaster: production, composition, and relationship to chromosome puffs. Dev Biol. 1977 Jul 15;58(2):339–355. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird C. D. Structural paradox of polytene chromosomes. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):869–874. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90563-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A. The use of intensifying screens or organic scintillators for visualizing radioactive molecules resolved by gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):363–371. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Shermoen A. W., Heemskerk J., Beckendorf S. K. DNA sequence changes in an upstream DNase I-hypersensitive region are correlated with reduced gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1063–1067. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muskavitch M. A., Hogness D. S. An expandable gene that encodes a Drosophila glue protein is not expressed in variants lacking remote upstream sequences. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):1041–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90467-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muskavitch M. A., Hogness D. S. Molecular analysis of a gene in a developmentally regulated puff of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7362–7366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardue M. L., Gall J. G. Nucleic acid hybridization to the DNA of cytological preparations. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;10:1–16. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60727-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards G., Cassab A., Bourouis M., Jarry B., Dissous C. The normal developmental regulation of a cloned sgs3 'glue' gene chromosomally integrated in Drosophila melanogaster by P element transformation. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2137–2142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01714.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Genetic transformation of Drosophila with transposable element vectors. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):348–353. doi: 10.1126/science.6289436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Vectors for P element-mediated gene transfer in Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6341–6351. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholnick S. B., Morgan B. A., Hirsh J. The cloned dopa decarboxylase gene is developmentally regulated when reintegrated into the Drosophila genome. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):37–45. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90134-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Rubin G. M. The effect of chromosomal position on the expression of the Drosophila xanthine dehydrogenase gene. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):47–57. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90135-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Rubin G. M. Transposition of cloned P elements into Drosophila germ line chromosomes. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):341–347. doi: 10.1126/science.6289435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]