Abstract
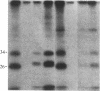
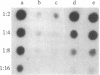
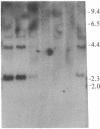
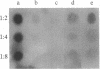
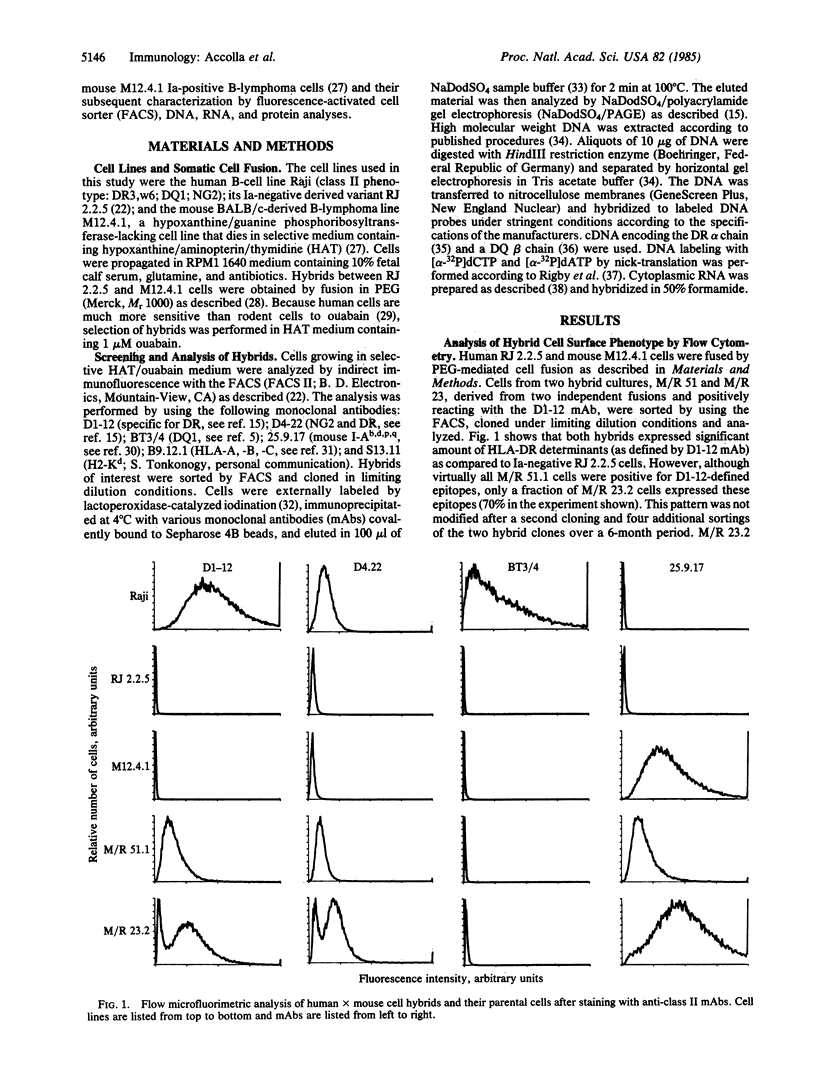
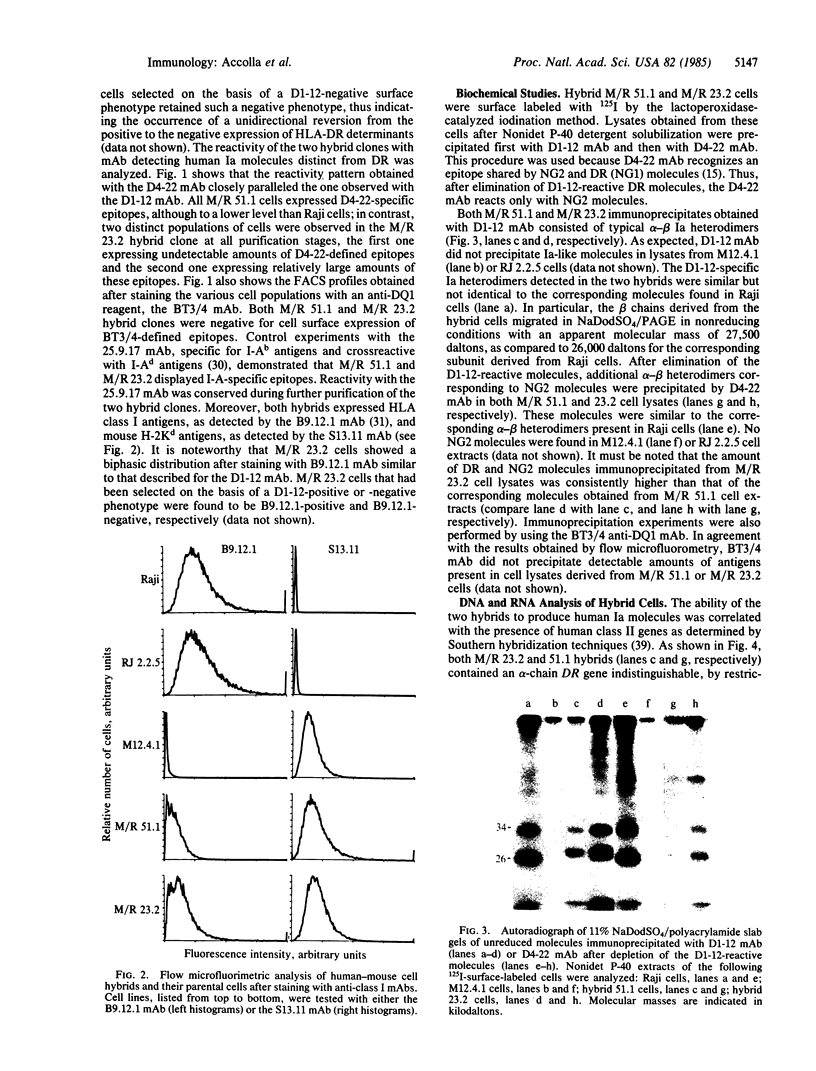
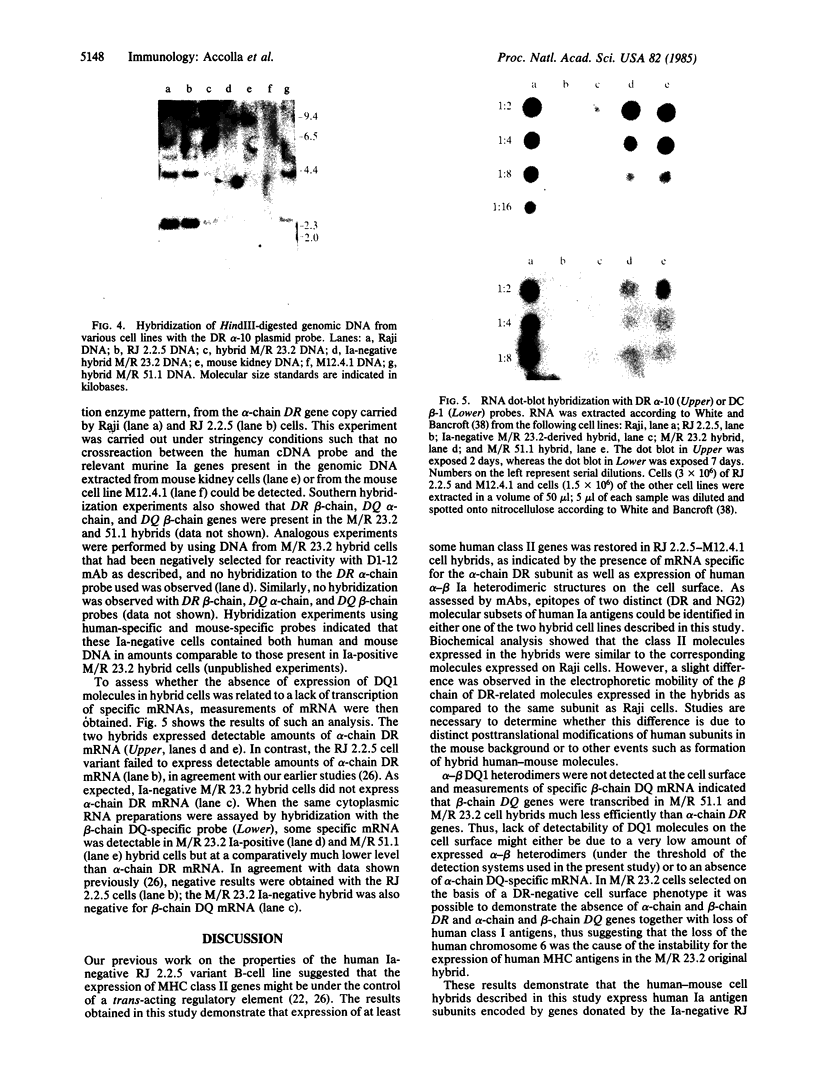
Raji, a human B-lymphoma cell line, expresses high levels of class II (Ia) antigens. The expression of Ia antigens is totally abolished at the level of specific mRNA accumulation in RJ 2.2.5, a variant cell line derived from Raji after mutagenesis and immunoselection. We report here that the human Ia antigen expression can be restored in interspecies somatic cell hybrids between RJ 2.2.5 cells and BALB/c-derived M12.4.1 (I-A+, I-E+) B-lymphoma cells. Two hybrid clones were studied in detail. In both clones Ia molecules of the DR and NG2 type were easily detected by cell surface immunofluorescence and specific immunoprecipitation. In contrast, the DQ1 molecules were not detected with the above technique. DNA hybridization experiments using specific probes indicated that alpha-chain DR and beta-chain DQ genes were present in the hybrids. However, RNA hybridization experiments revealed that beta-chain DQ mRNA was present in the hybrids at very low amount compared to alpha-chain DR-specific mRNA. These results indicate that at least several genes of the class II gene cluster are coordinately regulated by trans-acting factor(s) that operate across species barriers. The basis of the mechanisms controlling the expression of class II antigens in these human-mouse hybrids might be related to the extinction (lack of expression) or activation of tissue-specific traits that take place when genomes of cells of dissimilar developmental potentials are brought together.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Accolla R. S. Analysis of the structural heterogeneity and polymorphism of human Ia antigens. Four distinct subsets of molecules are coexpressed in the Ia pool of both DR1,1 homozygous and DR3,W6 heterozygous B cell lines. J Exp Med. 1984 Feb 1;159(2):378–393. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.2.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Accolla R. S., Carrel S., Mach J. P. Monoclonal antibodies specific for carcinoembryonic antigen and produced by two hybrid cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):563–566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Accolla R. S., Gross N., Carrel S., Corte G. Distinct forms of both alpha and beta subunits are present in the human Ia molecular pool. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4549–4551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Accolla R. S. Human B cell variants immunoselected against a single Ia antigen subset have lost expression of several Ia antigen subsets. J Exp Med. 1983 Mar 1;157(3):1053–1058. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.3.1053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Accolla R. S., Moretta A., Carrel S. The human Ia system: an overview. Semin Hematol. 1984 Oct;21(4):287–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Kuo J., DeMars R., Strominger J. L. A minimum of four human class II alpha-chain genes are encoded in the HLA region of chromosome 6. Nature. 1983 Jul 14;304(5922):174–177. doi: 10.1038/304174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker E., Pearson P. L., Meera Khan P., Schreuder G. M., Madan K. Orientation of major histocompatibility (MHC) genes relative to the centromere of human chromosome 6. Clin Genet. 1979 Feb;15(2):198–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1979.tb01762.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham F. J., Quintero M. A., Goodfellow P. N. Human-mouse hybrids with an embryonal carcinoma phenotype continue to transcribe HLA-A,B,C. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):1963–1968. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01685.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corte G., Calabi F., Damiani G., Bargellesi A., Tosi R., Sorrentino R. Human Ia molecules carrying DC1 determinants differ in both alpha- and beta-subunits from Ia molecules carrying DR determinants. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):357–360. doi: 10.1038/292357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBerardino M. A., Hoffner N. J., Etkin L. D. Activation of dormant genes in specialized cells. Science. 1984 Jun 1;224(4652):946–952. doi: 10.1126/science.6719127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladstone P., Pious D. Identification of a trans-acting function regulation HLA-DR expression in a DR-negative B cell variant. Somatic Cell Genet. 1980 Mar;6(2):285–298. doi: 10.1007/BF01538802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladstone, Pious D. Stable variants affecting B cell alloantigens in human lymphoid cells. Nature. 1978 Feb 2;271(5644):459–461. doi: 10.1038/271459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyert S. M., Shively J. E., Silver J. Biochemical characterization of a second family of human Ia molecules, HLA-DS, equivalent to murine I-A subregion molecules. J Exp Med. 1982 Aug 1;156(2):550–566. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.2.550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamano T., Kim K. J., Leiserson W. M., Asofsky R. Establishment of B cell hybridomas with B cell surface antigens. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1403–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard A. L., Cohn Z. A. Externally disposed plasma membrane proteins. I. Enzymatic iodination of mouse L cells. J Cell Biol. 1975 Feb;64(2):438–460. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.2.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley C. K., Shaw S., Nadler L., Schlossman S., Capra J. D. Alpha and beta chains of SB and DR antigens are structurally distinct. J Exp Med. 1982 Nov 1;156(5):1557–1562. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.5.1557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killary A. M., Fournier R. E. A genetic analysis of extinction: trans-dominant loci regulate expression of liver-specific traits in hepatoma hybrid cells. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):523–534. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90507-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratzin H., Yang C. Y., Götz H., Pauly E., Kölbel S., Egert G., Thinnes F. P., Wernet P., Altevogt P., Hilschmann N. Primärstruktur menschlicher Histokompatibilitätsantigene der Klasse II. 1. Mitteilung: Aminosäuresequenz der N-terminalen 198 Reste der beta-Kette des HLA-Dw2,2;DR2,2-Alloantigens. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1981 Dec;362(12):1665–1669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemonnier F. A., Rebai N., Le Bouteiller P. P., Malissen B., Caillol D. H., Kourilsky F. M. Epitopic analysis of detergent-solubilized HLA molecules by solid-phase radioimmunoassay. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Oct 15;54(1):9–22. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90108-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. O., Gorski J., Rollini P., Wake C. T., Strubin M., Rabourdin-Combe C., Mach B. Molecular analysis of the genes for human class II antigens of the major histocompatibility complex. Hum Immunol. 1983 Sep;8(1):113–121. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(83)90089-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. O., Mach B., Accolla R. S. Ia-negative B-cell variants reveal a coordinate regulation in the transcription of the HLA class II gene family. Immunogenetics. 1984;19(4):349–353. doi: 10.1007/BF00345408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. O., Wake C. T., Strubin M., Gross N., Accolla R. S., Carrel S., Mach B. Isolation of distinct cDNA clones encoding HLA-DR beta chains by use of an expression assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7465–7469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loosmore S., Gladstone P., Pious D., Jerry L. M., Tamaoki T. Control of HLA-DR antigen gene expression at the pretranslational level: comparison of an HLA-DR-positive B lymphoblastoid cell line and its HLA-DR-negative variant. Immunogenetics. 1982;15(2):139–150. doi: 10.1007/BF00621947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Sachs D. H. Monoclonal antibodies to mouse MHC antigens. III. Hybridoma antibodies reacting to antigens of the H-2b haplotype reveal genetic control of isotype expression. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):317–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. A., Weiss M. C. Expression of differentiated functions in hepatoma cell hybrids. I. Tyrosine aminotransferase in hepatoma-fibroblast hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):127–131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackelford D. A., Kaufman J. F., Korman A. J., Strominger J. L. HLA-DR antigens: structure, separation of subpopulations, gene cloning and function. Immunol Rev. 1982;66:133–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackelford D. A., Mann D. L., van Rood J. J., Ferrara G. B., Strominger J. L. Human B-cell alloantigens DC1, MT1, and LB12 are identical to each other but distinct from the HLA-DR antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4566–4570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanigaki N., Tosi R., Duquesnoy R. J., Ferrara G. B. Three Ia species with different structures and alloantigenic determinants in an HLA-homozygous cell line. J Exp Med. 1983 Jan 1;157(1):231–247. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.1.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowsdale J., Lee J., Carey J., Grosveld F., Bodmer J., Bodmer W. Sequences related to HLA-DR alpha chain on human chromosome 6: restriction enzyme polymorphism detected with DC alpha chain probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1972–1976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake C. T., Long E. O., Strubin M., Gross N., Accolla R., Carrel S., Mach B. Isolation of cDNA clones encoding HLA-DR alpha chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6979–6983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Bancroft F. C. Cytoplasmic dot hybridization. Simple analysis of relative mRNA levels in multiple small cell or tissue samples. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8569–8572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willing M. C., Nienhuis A. W., Anderson W. F. Selective activation of human beta-but not gamma-globin gene in human fibroblast x mouse erythroleukaemia cell hybrids. Nature. 1979 Feb 15;277(5697):534–538. doi: 10.1038/277534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]