Abstract
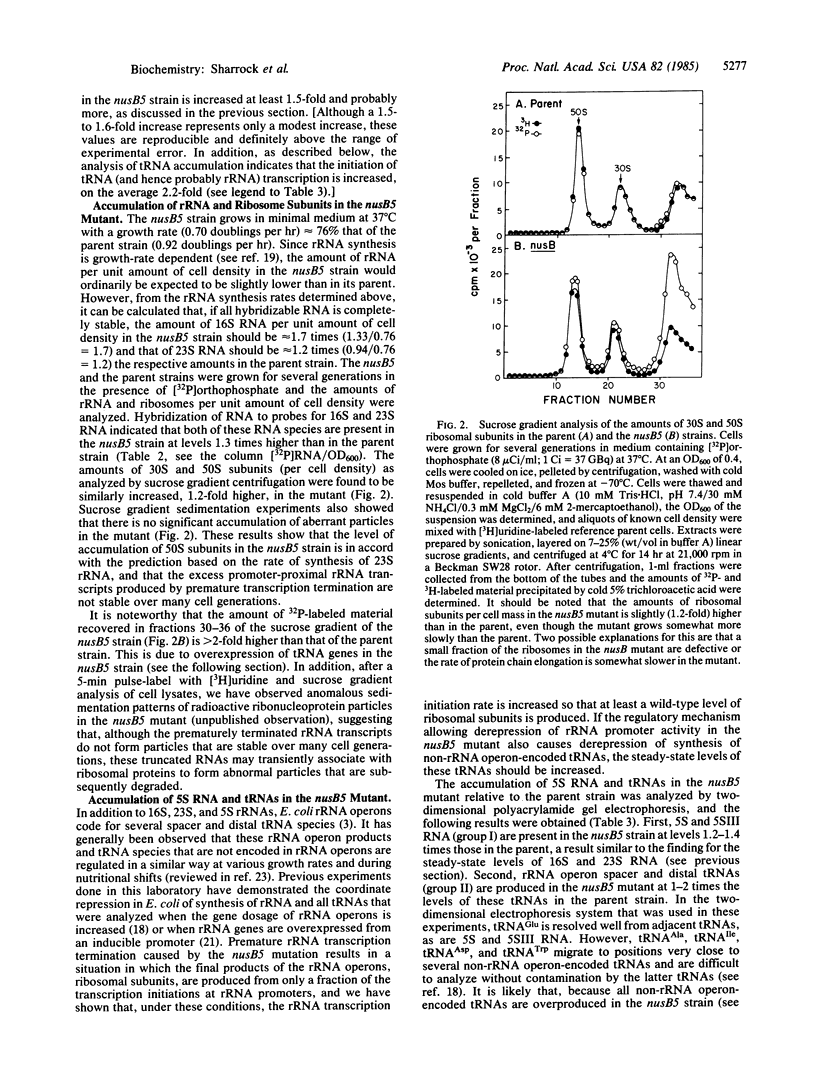
The nusB5 mutant of Escherichia coli was originally selected for reduced ability to support the antitermination of transcription that is mediated by the gene N product of bacteriophage lambda. By analyzing pulse-labeled RNA with an RNA.DNA filter hybridization technique, we have shown that, in the nusB5 mutant, the ratio of promoter-proximal rRNA transcripts to promoter-distal transcripts is increased at least by a factor of 1.6; that is, in the absence of the functional nusB gene product, premature transcription termination takes place within rRNA operons. These results demonstrate that rRNA transcription in E. coli utilizes an antitermination mechanism that has at least one factor in common with the phage lambda system, the nusB gene product. We have also observed that the transcription initiation frequency at rRNA promoters is increased in the nusB5 strain and that this strain accumulates 30S and 50S ribosomal subunits at approximately the same rate as the parent. Thus, it appears that E. coli compensates for premature termination of rRNA transcription by derepressing rRNA operon expression. The increase in rRNA promoter activity in the nusB5 mutant is accompanied by a parallel derepression of synthesis of tRNAs that are not encoded by rRNA operons. These results are consistent with a model for negative feedback regulation of rRNA and tRNA synthesis by products of rRNA operons.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Gottesman M. Control of transcription termination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:967–996. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.004535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aksoy S., Squires C. L., Squires C. Evidence for antitermination in Escherichia coli RRNA transcription. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):260–264. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.260-264.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewster J. M., Morgan E. A. Tn9 and IS1 inserts in a ribosomal ribonucleic acid operon of Escherichia coli are incompletely polar. J Bacteriol. 1981 Dec;148(3):897–903. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.3.897-903.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Dull T. J., Sleeter D. D., Noller H. F. Gene organization and primary structure of a ribosomal RNA operon from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 15;148(2):107–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90508-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das A., Gottesman M. E., Wardwell J., Trisler P., Gottesman S. lambda mutation in the Escherichia coli rho gene that inhibits the N protein activity of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5530–5534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood M., Nomura M. Chromosomal locations of the genes for rRNA in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):458–468. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.458-468.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood M., Nomura M. Deletion of a ribosomal ribonucleic acid operon in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):1077–1080. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.1077-1080.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnham P. J., Greenblatt J., Platt T. Effects of NusA protein on transcription termination in the tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):945–951. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90457-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I., Baron L. S. Genetic characterization of a bacterial locus involved in the activity of the N function of phage lambda. Virology. 1974 Mar;58(1):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90149-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I., Baumann M., Baron L. S. Cooperative effects of bacterial mutations affecting lambda N gene expression. I. Isolation and characterization of a nusB mutant. Virology. 1976 Aug;73(1):119–127. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90066-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I., Olson E. R. Evidence that a nucleotide sequence, "boxA," is involved in the action of the NusA protein. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):143–149. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90144-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I., Olson E. R., Georgopoulos C., Tilly K., Herskowitz I., Banuett F. Interactions of bacteriophage and host macromolecules in the growth of bacteriophage lambda. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Dec;48(4):299–325. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.4.299-325.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I., Schauer A. T., Baumann M. R., Baron L. S., Adhya S. L. Evidence that ribosomal protein S10 participates in control of transcription termination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1115–1118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos C. P., Swindle J., Keppel F., Ballivet M., Bisig R., Eisen H. Studies on the E. coli groNB (nusB) gene which affects bacteriophage lambda N gene function. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;179(1):55–61. doi: 10.1007/BF00268446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourse R. L., Stark M. J., Dahlberg A. E. Regions of DNA involved in the stringent control of plasmid-encoded rRNA in vivo. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1347–1354. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90315-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourse R. L., Takebe Y., Sharrock R. A., Nomura M. Feedback regulation of rRNA and tRNA synthesis and accumulation of free ribosomes after conditional expression of rRNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1069–1073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J., Li J., Adhya S., Friedman D. I., Baron L. S., Redfield B., Kung H. F., Weissbach H. L factor that is required for beta-galactosidase synthesis is the nusA gene product involved in transcription termination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1991–1994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J., McLimont M., Hanly S. Termination of transcription by nusA gene protein of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):215–220. doi: 10.1038/292215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holben W. E., Morgan E. A. Antitermination of transcription from an Escherichia coli ribosomal RNA promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6789–6793. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T., Nomura M. Expression of spacer tRNA genes in ribosomal RNA transcription units carried by hybrid Col E1 plasmids in E. coli. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):779–793. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90291-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jinks-Robertson S., Gourse R. L., Nomura M. Expression of rRNA and tRNA genes in Escherichia coli: evidence for feedback regulation by products of rRNA operons. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):865–876. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Chamberlin M. J. Pausing and attenuation of in vitro transcription in the rrnB operon of E. coli. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):523–531. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90394-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. C., Squires C. L., Squires C. Antitermination of E. coli rRNA transcription is caused by a control region segment containing lambda nut-like sequences. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):851–860. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90280-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan E. A. Insertions of Tn 10 into an E. coli ribosomal RNA operon are incompletely polar. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):257–265. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Uchida H. Isolation of conditionally lethal amber mutations affecting synthesis of the nusA protein of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;190(2):196–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00330640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierlich D. P. Regulation of bacterial growth, RNA, and protein synthesis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:393–432. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.002141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Gourse R., Baughman G. Regulation of the synthesis of ribosomes and ribosomal components. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:75–117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.000451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salstrom J. S., Szybalski W. Coliphage lambdanutL-: a unique class of mutants defective in the site of gene N product utilization for antitermination of leftward transcription. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 5;124(1):195–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90156-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siehnel R. J., Morgan E. A. Efficient read-through of Tn9 and IS1 by RNA polymerase molecules that initiate at rRNA promoters. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):672–684. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.672-684.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg N. A class of rifR RNA polymerase mutations that interferes with the expression of coliphage lambda late gene. Virology. 1976 Aug;73(1):139–154. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90068-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward D. F., Gottesman M. E. The nus mutations affect transcription termination in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):212–215. doi: 10.1038/292212a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


