Abstract
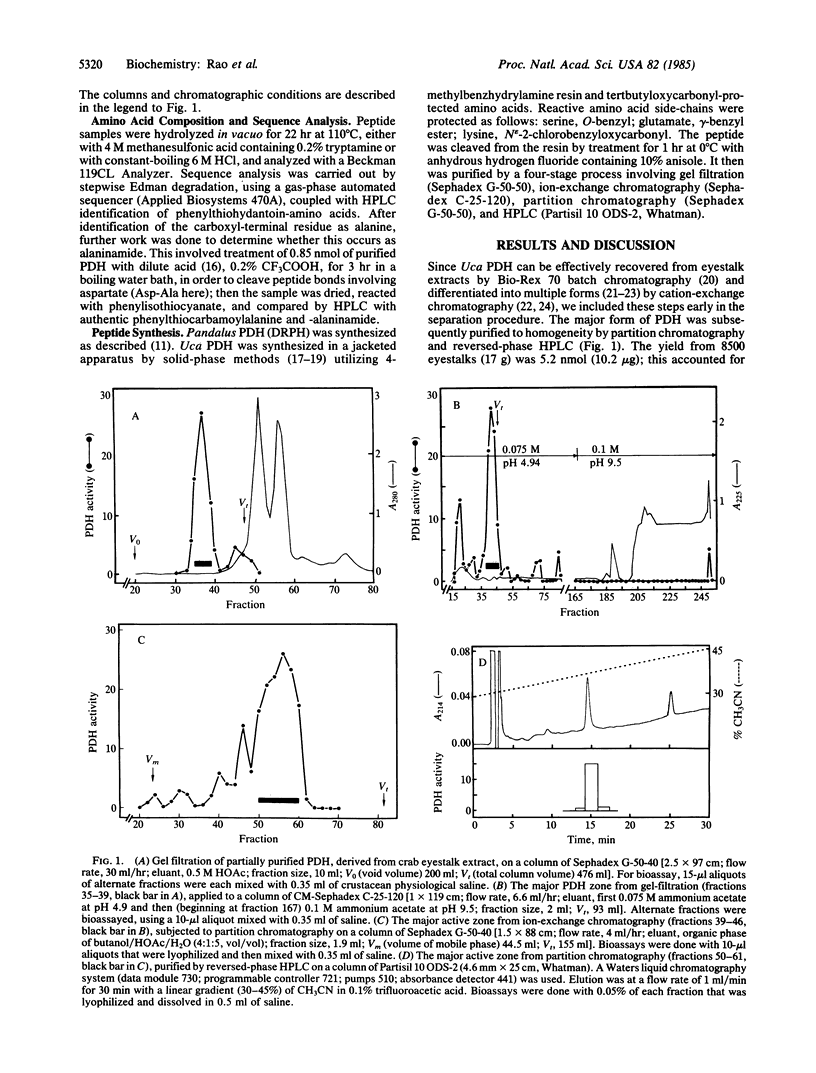
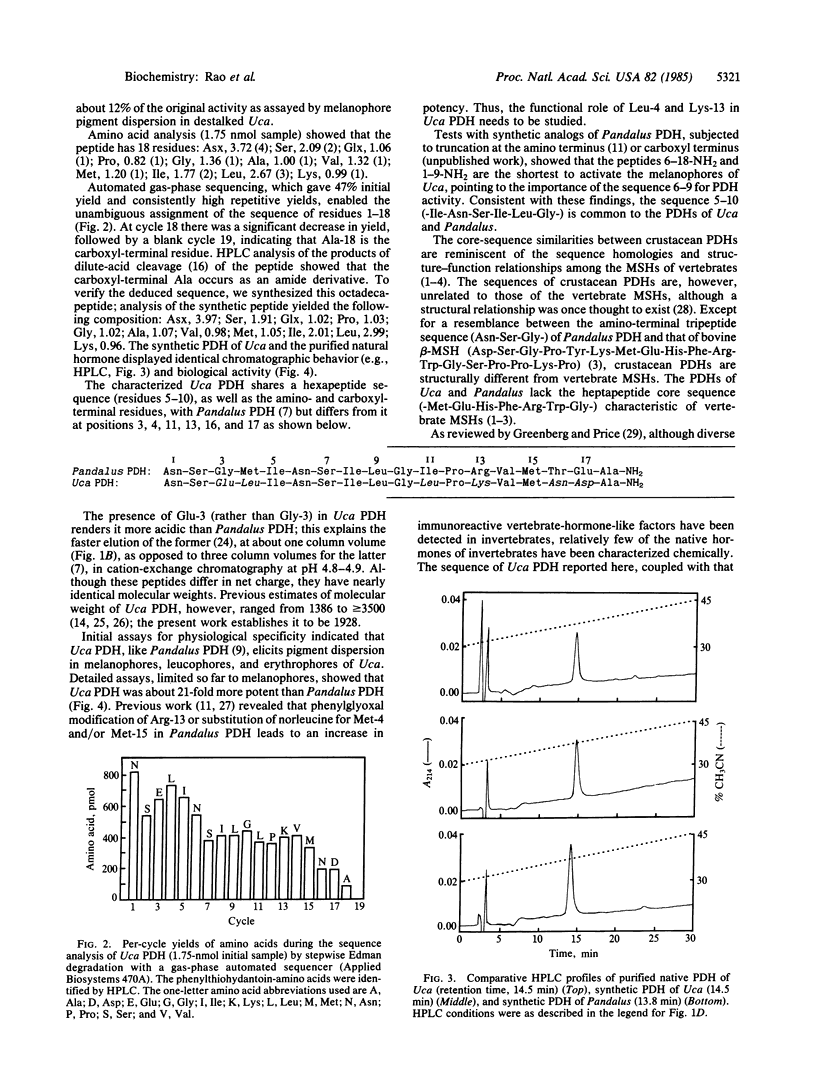
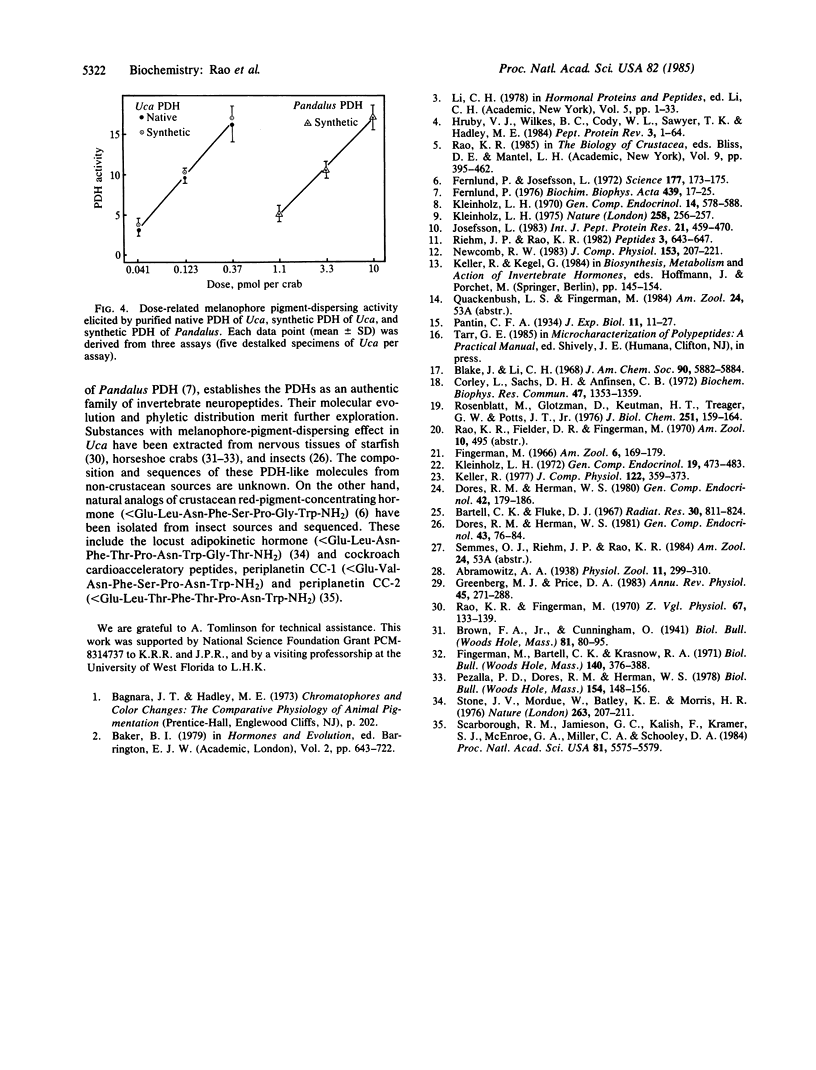
A pigment-dispersing hormone (PDH) from eyestalks of the fiddler crab Uca pugilator has been purified by gel filtration, ion-exchange chromatography, partition chromatography, and reversed-phase liquid chromatography. Based on automated gas-phase sequencing and subsequent identification of carboxyl-terminal amide, we have assigned the primary structure of this peptide as Asn-Ser-Glu-Leu-Ile-Asn-Ser-Ile-Leu-Gly-Leu-Pro-Lys-Val-Met-Asn-Asp-Ala-NH 2. We have confirmed the sequence by synthesizing this peptide and demonstrating that the synthetic PDH and the native PDH display identical chromatographic behavior and biological activity. This hormone is a member of a family of invertebrate neuropeptides that includes a light-adapting/pigment-dispersing octadecapeptide hormone from the prawn Pandalus borealis. In assays for melanophore pigment dispersion in destalked fiddler crabs, Uca PDH was 21-fold more potent than Pandalus PDH. These two hormones share a hexapeptide core sequence (residues 5-10: -Ile-Asn-Ser-Ile-Leu-Gly-) as well as the amino- and carboxyl-terminal residues but differ at positions 3, 4, 11, 13, 16, and 17. These results point to speciesrelated or group-specific structural differences among crustacean PDHs.
Keywords: invertebrate neuropeptide, chromatophorotropin, color change, amino acid sequence, peptide synthesis
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartell C. K., Fluke D. J. Temperature dependence of ionizing radiation effect on dry preparations of two melanophore-stimulating hormones. Radiat Res. 1967 Apr;30(4):811–824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake J., Li C. H. Adrenocorticotropins. XXXIX. The solid phase synthesis of methion-glutamyl-histidyl-phenylalanyl-arginyl-tryptophyl-glycine. J Am Chem Soc. 1968 Oct 9;90(21):5882–5884. doi: 10.1021/ja01023a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corley L., Sachs D. H., Anfinsen C. B. Rapid solid-phase synthesis of bradykinin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 28;47(6):1353–1359. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90221-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dores R. M., Herman W. S. Insect chromatophorotropic factors: the isolation of polypeptides from Periplaneta americana and Apis mellifera with melanophore-dispersing activity in the crustacean, Uca pugilator. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1981 Jan;43(1):76–84. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(81)90034-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dores R. M., Herman W. S. The purification and partial characterization of the melanophore-dispersing hormone of Uca pugilator. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1980 Oct;42(2):179–186. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(80)90186-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernlund P., Josefsson L. Crustacean color-change hormone: amino acid sequence and chemical synthesis. Science. 1972 Jul 14;177(4044):173–175. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4044.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernlund P. Structure of a light-adapting hormone from the shrimp, Pandalus borealis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jul 19;439(1):17–25. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90155-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fingerman M. Neurosecretory control of pigmentary effectors in crustaceans. Am Zool. 1966 May;6(2):169–179. doi: 10.1093/icb/6.2.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. J., Price D. A. Invertebrate neuropeptides: native and naturalized. Annu Rev Physiol. 1983;45:271–288. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.45.030183.001415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josefsson L. Invertebrate neuropeptide hormones. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1983 May;21(5):459–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1983.tb02672.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinholz L. H. A progress report on the separation and purification of crustacean neurosecretory pigmentary-effector hormones. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1970 Jun;14(3):578–588. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(70)90041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinholz L. H. Purified hormones from the crustacean eyestalk and their physiological specificity. Nature. 1975 Nov 20;258(5532):256–257. doi: 10.1038/258256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pezalla P. D., Dores R. M., Herman W. S. Separation and partial purification of central nervous system peptides from Limulus polyphemus with hyperglycemic and chromatophorotropic activity in crustaceans. Biol Bull. 1978 Feb;154(1):145–156. doi: 10.2307/1540780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riehm J. P., Rao K. R. Structure-activity relationships of a pigment-dispersing crustacean neurohormone. Peptides. 1982 Jul-Aug;3(4):643–647. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(82)90165-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt M., Goltzman D., Keutmann H. T., Tregear G. W., Potts J. T., Jr Chemical and biological properties of synthetic, sulfur-free analogues of parathyroid hormone. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 10;251(1):159–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarborough R. M., Jamieson G. C., Kalish F., Kramer S. J., McEnroe G. A., Miller C. A., Schooley D. A. Isolation and primary structure of two peptides with cardioacceleratory and hyperglycemic activity from the corpora cardiaca of Periplaneta americana. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5575–5579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J. V., Mordue W., Batley K. E., Morris H. R. Structure of locust adipokinetic hormone, a neurohormone that regulates lipid utilisation during flight. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):207–211. doi: 10.1038/263207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


