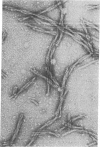
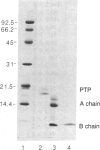
Abstract
An unusual hitherto unreported protein, extracted in acid from fresh bovine pancreas, has been purified and characterized biochemically. It precipitates in the neutral pH range in the form of uniform double-helical threads, each strand of which is smooth and of uniform diameter, about 7-8 nm. The threads dissolve to a nonviscous solution below pH 3.6 and above pH 9.4, and they reconstitute reversibly in the pH range in between. The monomer in acid has an apparent molecular weight of 17,800 and consists of two disulfide-linked nonidentical polypeptide chains of different lengths. It is rich in aromatic amino acids, particularly tryptophan. There is no significant content of carbohydrate, fatty acid, or bound phosphate. The amino acid sequences of the first NH2-terminal 48 residues of the A chain and 35 residues of the B chain appear to be unique, differing from all other reported animal proteins, including those of the pancreas. Thus far, a function has not been found.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey K. Tropomyosin: a new asymmetric protein component of the muscle fibril. Biochem J. 1948;43(2):271–279. doi: 10.1042/bj0430271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaven G. H., Gratzer W. B., Davies H. G. Formation and structure of gels and fibrils from glucagon. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Nov;11(1):37–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00735.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brauer A. W., Oman C. L., Margolies M. N. Use of o-phthalaldehyde to reduce background during automated Edman degradation. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):134–142. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90359-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Solal L., Lian J. B., Kossiva D., Glimcher M. J. Identification of organic phosphorus covalently bound to collagen and non-collagenous proteins of chicken-bone matrix. The presence of O-phosphoserine and O-phosphothreonine in non-collagenous proteins, and their absence from phosporylated collagen. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 1;177(1):81–98. doi: 10.1042/bj1770081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Caro A., Multigner L., Lafont H., Lombardo D., Sarles H. The molecular characteristics of a human pancreatic acidic phosphoprotein that inhibits calcium carbonate crystal growth. Biochem J. 1984 Sep 15;222(3):669–677. doi: 10.1042/bj2220669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANCHI C. M., de ROBERTIS E. Electron microscope observations on elastic fibers. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 Mar;76(3):515–518. doi: 10.3181/00379727-76-18540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figarella C., Amouric M., Guy-Crotte O. Proteolysis of human trypsinogen 1. Pathogenic implication in chronic pancreatitis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jan 13;118(1):154–161. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91080-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENE L. J., HIRS C. H., PALADE G. E. On the protein composition of bovine pancreatic zymogen granules. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jun;238:2054–2070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS J. Fiber formation in trypsinogen solutions; an electron optical study. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 Oct;78(1):241–244. doi: 10.3181/00379727-78-19034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Ein D., Eanes E. D., Bladen H. A., Terry W., Page D. L. Creation of "amyloid" fibrils from Bence Jones proteins in vitro. Science. 1971 Nov 12;174(4010):712–714. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4010.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Harada M., Isersky C. The purification of amyloid fibril proteins. Prep Biochem. 1972;2(1):39–51. doi: 10.1080/00327487208061451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy-Crotte O., Amouric M., Figarella C. Characterization and N-terminal sequence of a degradation product of 14,000 molecular weight isolated from human pancreatic juice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Dec 14;125(2):516–523. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90570-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. D., Jr, Krane S. M. An endopeptidase from rheumatoid synovial tissue culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 28;258(2):566–576. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heussen C., Dowdle E. B. Electrophoretic analysis of plasminogen activators in polyacrylamide gels containing sodium dodecyl sulfate and copolymerized substrates. Anal Biochem. 1980 Feb;102(1):196–202. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90338-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLER P. J., COHEN E., NEURATH H. The proteins of bovine pancreatic juice. J Biol Chem. 1958 Aug;233(2):344–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller P. J., Allan B. J. The protein composition of human pancreatic juice. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 25;242(2):281–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu T. Y., Chang Y. H. Hydrolysis of proteins with p-toluenesulfonic acid. Determination of tryptophan. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 10;246(9):2842–2848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz P. A., Rohwer R. G., Kascsak R., Wisniewski H. M., Somerville R. A., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Infection-specific particle from the unconventional slow virus diseases. Science. 1984 Jul 27;225(4660):437–440. doi: 10.1126/science.6377496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz P. A., Somerville R. A., Wisniewski H. M., Manuelidis L., Manuelidis E. E. Scrapie-associated fibrils in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):474–476. doi: 10.1038/306474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikes O., Holeysovský V., Tomásek V., Sorm F. Covalent structure of bovine trypsinogen. The position of the remaining amides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Aug 12;24(3):346–352. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90162-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow J. S., Marchesi V. T. Self-assembly of spectrin oligomers in vitro: a basis for a dynamic cytoskeleton. J Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;88(2):463–468. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.2.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen B. R., Svenneby G., Kvamme E., Tveit B., Eskeland T. Formation and ultrastructure of enzymically active polymers of pig renal glutaminase. J Mol Biol. 1970 Sep 14;52(2):239–245. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90028-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., McKinley M. P., Bowman K. A., Bolton D. C., Bendheim P. E., Groth D. F., Glenner G. G. Scrapie prions aggregate to form amyloid-like birefringent rods. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):349–358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheele G., Bartelt D., Bieger W. Characterization of human exocrine pancreatic proteins by two-dimensional isoelectric focusing/sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis. Gastroenterology. 1981 Mar;80(3):461–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J., Ihara Y., Salazar F. J. Alzheimer's disease: insolubility of partially purified paired helical filaments in sodium dodecyl sulfate and urea. Science. 1982 Mar 5;215(4537):1243–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.6120571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. A., Margolies M. N. Complete amino acid sequence of the heavy-chain variable region from an A/J mouse antigen-nonbinding monoclonal antibody bearing the predominant arsonate idiotype. Biochemistry. 1984 Sep 25;23(20):4726–4732. doi: 10.1021/bi00315a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartakoff A., Greene L. J., Palade G. E. Studies on the guinea pig pancreas. Fractionation and partial characterization of exocrine proteins. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 10;249(23):7420–7431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trelstad R. L., Lawley K. R. A simple economical buffer system for amino acid analysis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):287–289. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]