Abstract
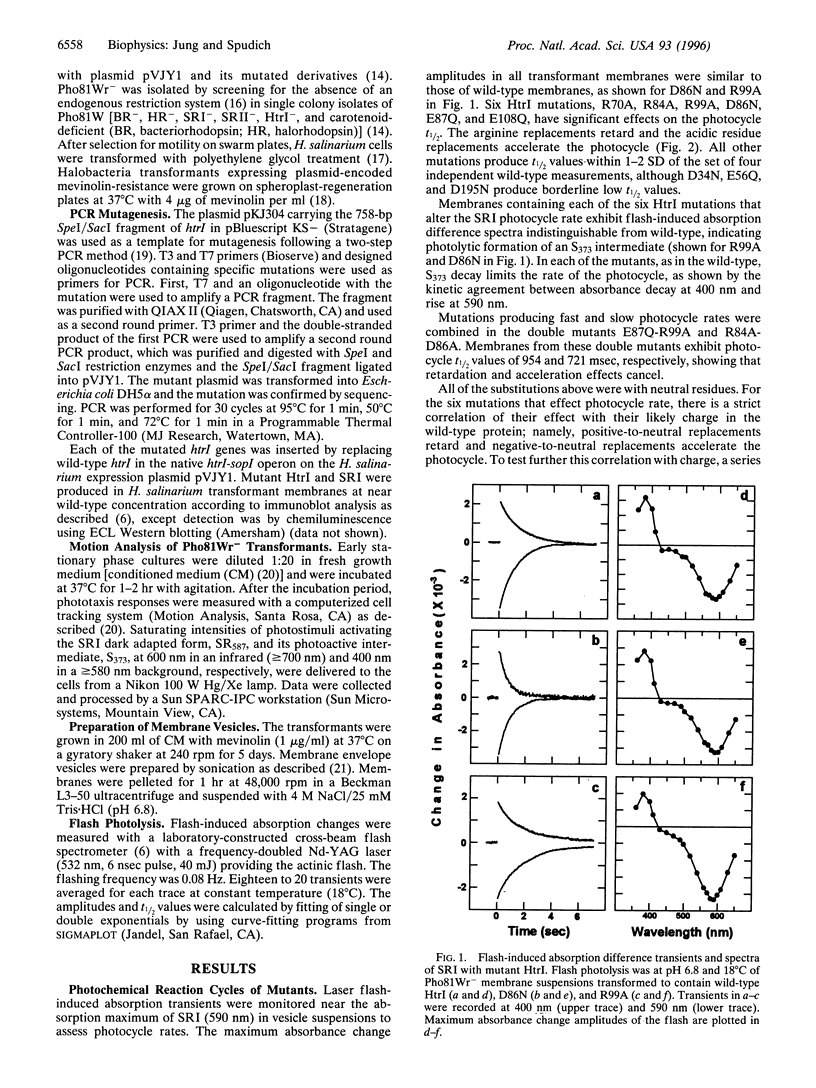
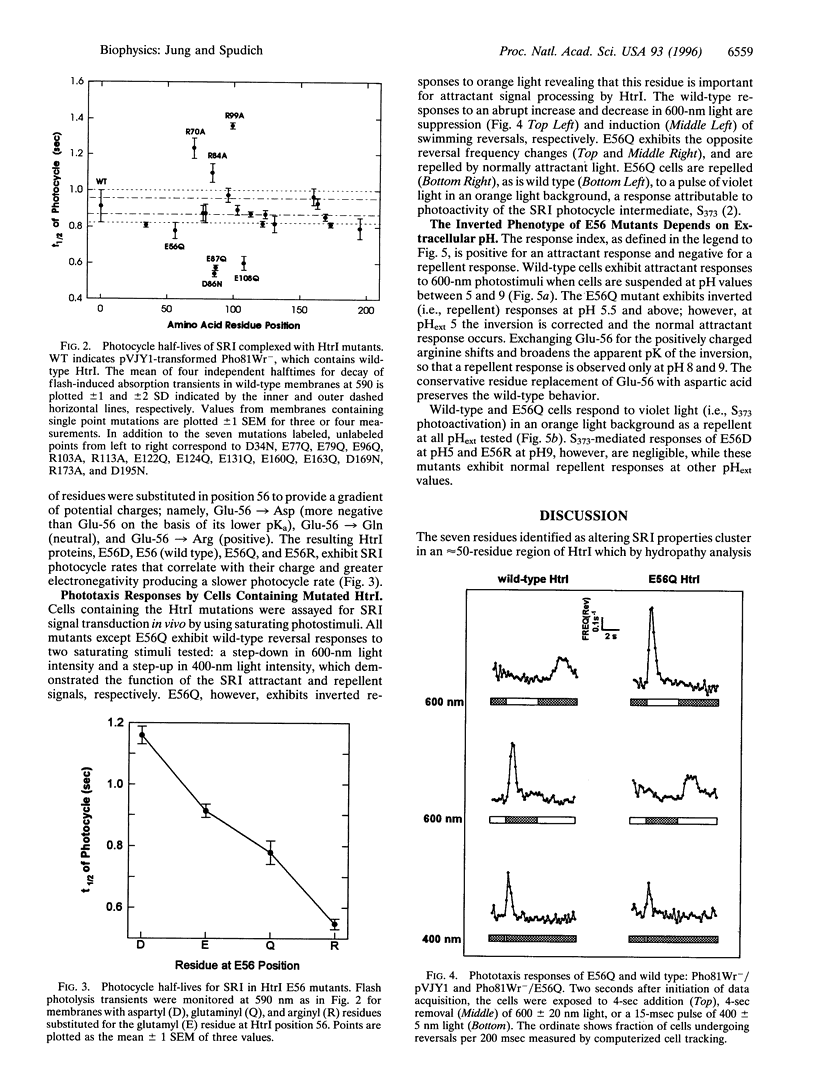
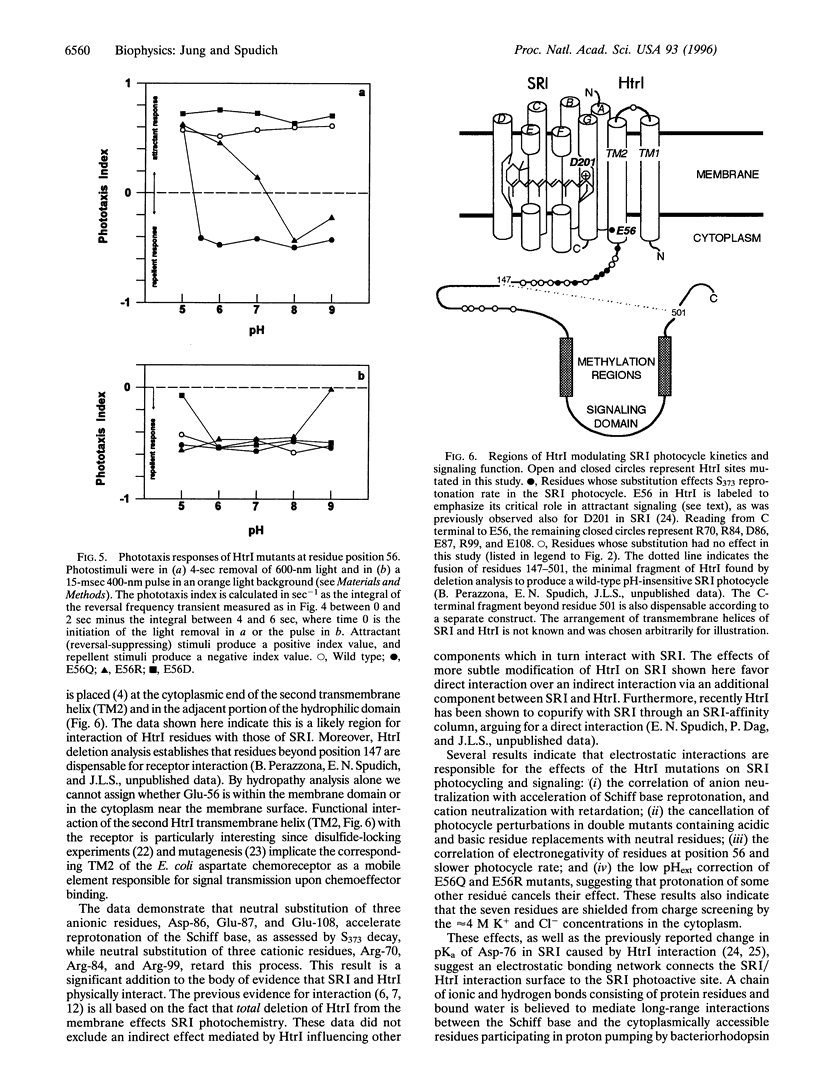
Neutral residue replacements were made of 21 acidic and basic residues within the N-terminal half of the Halobacterium salinarium signal transducer HtrI [the halobacterial transducer for sensory rhodopsin I (SRI)] by site-specific mutagenesis. The replacements are all within the region of HtrI that we previously concluded from deletion analysis to contain sites of interaction with the phototaxis receptor SRI. Immunoblotting shows plasmid expression of the htrI-sopI operon containing the mutations produces SRI and mutant HtrI in cells at near wild-type levels. Six of the HtrI mutations perturb photochemical kinetics of SRI and one reverses the phototaxis response. Substitution with neutral amino acids of Asp-86, Glu-87, and Glu-108 accelerate, and of Arg-70, Arg-84, and Arg-99 retard, the SRI photocycle. Opposite effects on photocycle rate cancel in double mutants containing one replaced acidic and one replaced basic residue. Laser flash spectroscopy shows the kinetic perturbations are due to alteration of the rate of reprotonation of the retinylidene Schiff base. All of these mutations permit normal attractant and repellent signaling. On the other hand, the substitution of Glu-56 with the isosteric glutamine converts the normally attractant effect of orange light to a repellent signal in vivo at neutral pH (inverted signaling). Low pH corrects the inversion due to Glu-56 -> Gln and the apparent pK of the inversion is increased when arginine is substituted at position 56. The results indicate that the cytoplasmic end of transmembrane helix-2 and the initial part of the cytoplasmic domain contain interaction sites with SRI. To explain these and previous results, we propose a model in which (i) the HtrI region identified here forms part of an electrostatic bonding network that extends through the SRI protein and includes its photoactive site; (ii) alteration of this network by photoisomerization-induced Schiff base deprotonation and reprotonation shifts HtrI between attractant and repellent conformations; and (iii) HtrI mutations and extracellular pH alter the equilibrium ratios of these conformations.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alam M., Lebert M., Oesterhelt D., Hazelbauer G. L. Methyl-accepting taxis proteins in Halobacterium halobium. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):631–639. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03418.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogomolni R. A., Spudich J. L. Identification of a third rhodopsin-like pigment in phototactic Halobacterium halobium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6250–6254. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogomolni R. A., Stoeckenius W., Szundi I., Perozo E., Olson K. D., Spudich J. L. Removal of transducer HtrI allows electrogenic proton translocation by sensory rhodopsin I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 11;91(21):10188–10192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.10188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourret R. B., Borkovich K. A., Simon M. I. Signal transduction pathways involving protein phosphorylation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:401–441. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X., Koshland D. E., Jr The N-terminal cytoplasmic tail of the aspartate receptor is not essential in signal transduction of bacterial chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 13;270(41):24038–24042. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.41.24038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chervitz S. A., Falke J. J. Lock on/off disulfides identify the transmembrane signaling helix of the aspartate receptor. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 13;270(41):24043–24053. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.41.24043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline S. W., Doolittle W. F. Efficient transfection of the archaebacterium Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1341–1344. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1341-1344.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haupts U., Eisfeld W., Stockburger M., Oesterhelt D. Sensory rhodopsin I photocycle intermediate SRI380 contains 13-cis retinal bound via an unprotonated Schiff base. FEBS Lett. 1994 Dec 12;356(1):25–29. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01226-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krah M., Marwan W., Verméglio A., Oesterhelt D. Phototaxis of Halobacterium salinarium requires a signalling complex of sensory rhodopsin I and its methyl-accepting transducer HtrI. EMBO J. 1994 May 1;13(9):2150–2155. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06491.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam W. L., Doolittle W. F. Shuttle vectors for the archaebacterium Halobacterium volcanii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5478–5482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marwan W., Bibikov S. I., Montrone M., Oesterhelt D. Mechanism of photosensory adaptation in Halobacterium salinarium. J Mol Biol. 1995 Mar 3;246(4):493–499. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.0101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Morowitz H. J. Molecular mechanisms for proton transport in membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):298–302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson K. D., Spudich J. L. Removal of the transducer protein from sensory rhodopsin I exposes sites of proton release and uptake during the receptor photocycle. Biophys J. 1993 Dec;65(6):2578–2585. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81295-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson K. D., Zhang X. N., Spudich J. L. Residue replacements of buried aspartyl and related residues in sensory rhodopsin I: D201N produces inverted phototaxis signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 11;92(8):3185–3189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.8.3185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson P. R., Cohen G. B., Zhukovsky E. A., Oprian D. D. Constitutively active mutants of rhodopsin. Neuron. 1992 Oct;9(4):719–725. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90034-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph J., Oesterhelt D. Chemotaxis and phototaxis require a CheA histidine kinase in the archaeon Halobacterium salinarium. EMBO J. 1995 Feb 15;14(4):667–673. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07045.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidel R., Scharf B., Gautel M., Kleine K., Oesterhelt D., Engelhard M. The primary structure of sensory rhodopsin II: a member of an additional retinal protein subgroup is coexpressed with its transducer, the halobacterial transducer of rhodopsin II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 28;92(7):3036–3040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.7.3036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich E. N., Spudich J. L. The photochemical reactions of sensory rhodopsin I are altered by its transducer. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16095–16097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich E. N., Takahashi T., Spudich J. L. Sensory rhodopsins I and II modulate a methylation/demethylation system in Halobacterium halobium phototaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7746–7750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. L., Bogomolni R. A. Mechanism of colour discrimination by a bacterial sensory rhodopsin. Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):509–513. doi: 10.1038/312509a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. L. Color sensing in the Archaea: a eukaryotic-like receptor coupled to a prokaryotic transducer. J Bacteriol. 1993 Dec;175(24):7755–7761. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.24.7755-7761.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and related pigments of halobacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:587–616. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Mochizuki Y., Kamo N., Kobatake Y. Evidence that the long-lifetime photointermediate of s-rhodopsin is a receptor for negative phototaxis in Halobacterium halobium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Feb 28;127(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80131-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki Y., Hatanaka M., Kandori H., Sasaki J., Karstens W. F., Raap J., Lugtenburg J., Bizounok M., Herzfeld J., Needleman R. Water structural changes at the proton uptake site (the Thr46-Asp96 domain) in the L intermediate of bacteriorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1995 May 30;34(21):7088–7093. doi: 10.1021/bi00021a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao V. J., Spudich E. N., Spudich J. L. Identification of distinct domains for signaling and receptor interaction of the sensory rhodopsin I transducer, HtrI. J Bacteriol. 1994 Nov;176(22):6931–6935. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.22.6931-6935.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao V. J., Spudich J. L. Primary structure of an archaebacterial transducer, a methyl-accepting protein associated with sensory rhodopsin I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11915–11919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


