Abstract
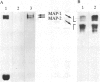
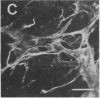
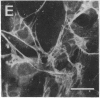
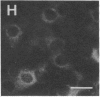
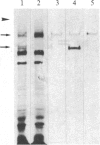
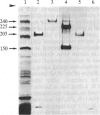
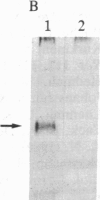
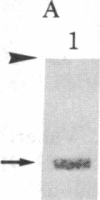
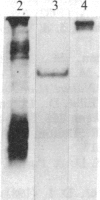
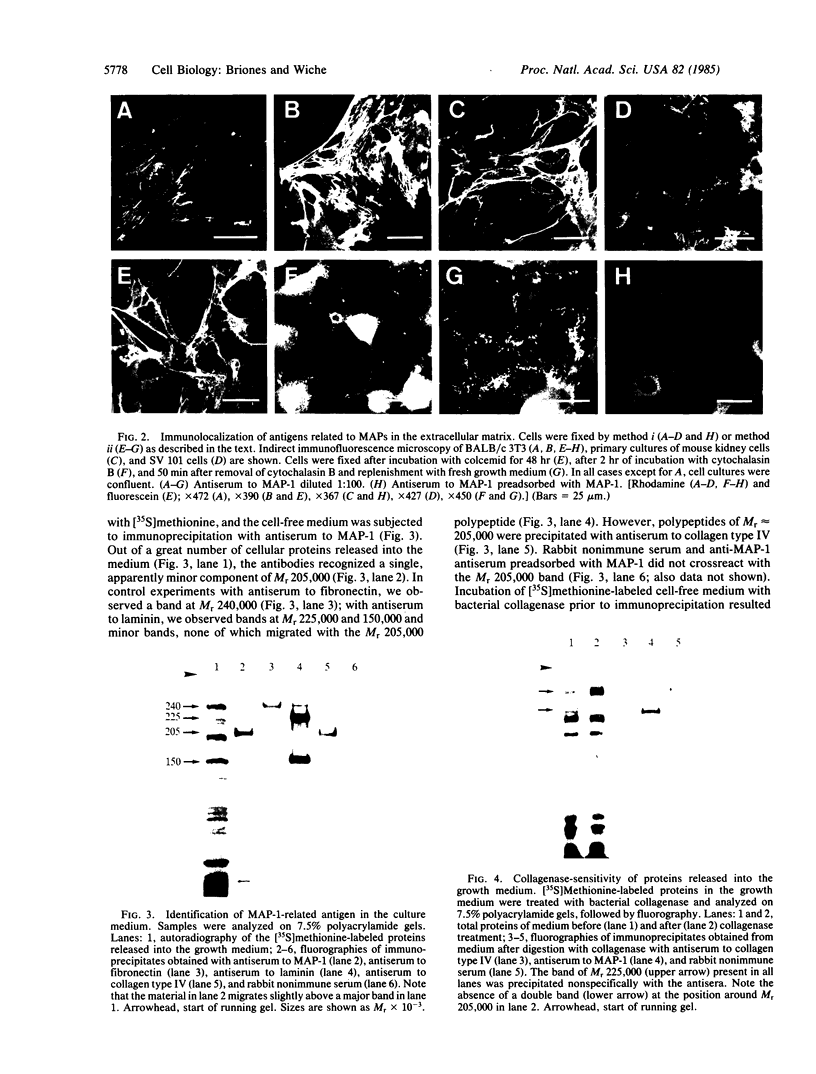
Rabbit antibodies raised against microtubule-associated protein 1 (MAP-1) from hog brain were found to crossreact with extracellular matrix components of mouse BALB/c 3T3 cell cultures. As shown by immunofluorescence microscopy of confluent cell cultures, the extracellular MAP-related antigen was located on dense fibrillar network arrays underlying and surrounding the cells. The immunoreactive material was sensitive to trypsin but resistant to collagenase. The microtubule-disrupting drug colcemid had no visible effect on the morphology of the anti-MAP-stained network, whereas treatment with cytochalasin B provoked its abolishment. Simian virus 40-transformed BALB/c 3T3 cells expressed considerably less extracellular antigen than did the nontransformed cells. After in vivo radiolabeling of BALB/c 3T3 cells, a secreted polypeptide of Mr 205,000 was isolated by immuno-precipitation from culture media as well as from cell-free extracellular matrices. This antigen was identified as a sulfoglycoprotein, noncollageneous in nature, that undergoes intermolecular disulfide bonding. Anti-MAP-1 antibodies affinity-purified on the extracellular Mr 205,000 protein were immunoreactive with MAP-1 and MAP-2 from brain and decorated cytoplasmic microtubules as demonstrated by immunoblotting and immunofluorescence microscopy. Thus, a structural relationship between cytoskeletal and extracellular polypeptides is demonstrated.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali I. U., Hynes R. O. Effects of cytochalasin B and colchicine on attachment of a major surface protein of fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 15;471(1):16–24. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90388-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amos L. A. Arrangement of high molecular weight associated proteins on purified mammalian brain microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1977 Mar;72(3):642–654. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.3.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhardt R., Matus A. Initial phase of dendrite growth: evidence for the involvement of high molecular weight microtubule-associated proteins (HMWP) before the appearance of tubulin. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):589–593. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom G. S., Luca F. C., Vallee R. B. Widespread cellular distribution of MAP-1A (microtubule-associated protein 1A) in the mitotic spindle and on interphase microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;98(1):331–340. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.1.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom G. S., Schoenfeld T. A., Vallee R. B. Widespread distribution of the major polypeptide component of MAP 1 (microtubule-associated protein 1) in the nervous system. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;98(1):320–330. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.1.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blose S. H., Meltzer D. I. Visualization of the 10-NM filament vimentin rings in vascular endothelial cells in situ: close resemblance to vimentin cytoskeletons found in monolayers in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Oct;135(2):299–309. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90166-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caceres A., Payne M. R., Binder L. I., Steward O. Immunocytochemical localization of actin and microtubule-associated protein MAP2 in dendritic spines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1738–1742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dentler W. L., Granett S., Rosenbaum J. L. Ultrastructural localization of the high molecular weight proteins associated with in vitro-assembled brain microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1975 Apr;65(1):237–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.65.1.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estridge M. Polypeptides similar to the alpha and beta subunits of tubulin are exposed on the neuronal surface. Nature. 1977 Jul 7;268(5615):60–63. doi: 10.1038/268060a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedman K., Kurkinen M., Alitalo K., Vaheri A., Johansson S., Hök M. Isolation of the pericellular matrix of human fibroblast cultures. J Cell Biol. 1979 Apr;81(1):83–91. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann H., Dalton J. M., Wiche G. Microheterogeneity of microtubule-associated proteins, MAP-1 and MAP-2, and differential phosphorylation of individual subcomponents. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5797–5803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann H., Pytela R., Dalton J. M., Wiche G. Structural homology of microtubule-associated proteins 1 and 2 demonstrated by peptide mapping and immunoreactivity. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):612–617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzog W., Weber K. Fractionation of brain microtubule-associated proteins. Isolation of two different proteins which stimulate tubulin polymerization in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Dec 1;92(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12716.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan B. L., Taylor A., Kurkinen M., Couchman J. R. Synthesis and localization of two sulphated glycoproteins associated with basement membranes and the extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):197–204. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg N. M. A comparison of membrane proteins of normal and transformed cells by lactoperoxidase labeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):489–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber G., Matus A. Immunocytochemical localization of microtubule-associated protein 1 in rat cerebellum using monoclonal antibodies. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):777–781. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karr T. L., White H. D., Purich D. L. Characterization of brain microtubule proteins prepared by selective removal of mitochondrial and synaptosomal components. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):6107–6111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurkinen M., Wartiovaara J., Vaheri A. Cytochalasin B releases a major surface-associated glycoprotein, fibronectin, from cultured fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Jan;111(1):127–137. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90243-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsov S. A., Rodionov V. I., Gelfand V. I., Rosenblat V. A. Microtubule-associated protein MAP1 promotes microtubule assembly in vitro. FEBS Lett. 1981 Dec 7;135(2):241–244. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80791-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matus A., Bernhardt R., Hugh-Jones T. High molecular weight microtubule-associated proteins are preferentially associated with dendritic microtubules in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3010–3014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. B., Borisy G. G. Association of high-molecular-weight proteins with microtubules and their role in microtubule assembly in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2696–2700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloboda R. D., Dentler W. L., Rosenbaum J. L. Microtubule-associated proteins and the stimulation of tubulin assembly in vitro. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 5;15(20):4497–4505. doi: 10.1021/bi00665a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack B. F., Dean J., Eilat D., Lorenz P. E., Schechter A. N. Tritium labeling of proteins to high specific radioactivity by reduction methylation. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8842–8847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee R. B., Davis S. E. Low molecular weight microtubule-associated proteins are light chains of microtubule-associated protein 1 (MAP 1). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiche G., Baker M. A. Cytoplasmic network arrays demonstrated by immunolocalization using antibodies to a high molecular weight protein present in cytoskeletal preparations from cultured cells. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Mar;138(1):15–29. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90086-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiche G., Briones E., Hirt H., Krepler R., Artlieb U., Denk H. Differential distribution of microtubule-associated proteins MAP-1 and MAP-2 in neurons of rat brain and association of MAP-1 with microtubules of neuroblastoma cells (clone N2A). EMBO J. 1983;2(11):1915–1920. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01679.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiche G., Briones E., Koszka C., Artlieb U., Krepler R. Widespread occurrence of polypeptides related to neurotubule-associated proteins (MAP-1 and MAP-2) in non-neuronal cells and tissues. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):991–998. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01918.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M. Immunological characterization of a major transformation-sensitive fibroblast cell surface glycoprotein. Localization, redistribution, and role in cell shape. J Cell Biol. 1978 Aug;78(2):520–541. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.2.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]