Abstract
Prazosin, an antagonist of alpha 1-adrenergic receptors, has been found to suppress the clinical and histological expression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) in the Lewis rat. Suppression was more significant in females than in males and was a dose-dependent phenomenon. Analysis of the effect of other adrenergic receptor antagonists supports the conclusion that the suppressive effect of prazosin is a consequence of blockade of the alpha 1-receptor since treatment with either the alpha 2-antagonist yohimbine or the beta-antagonist propranolol exacerbated the disease, whereas treatment with the long-acting mixed alpha 1/alpha 2-antagonist phenoxybenzamine had some suppressive activity. Treatment with prazosin was also able to suppress clinical and histological signs of EAE in animals sensitized by adoptive transfer with activated spleen or lymph node cells. Whether prazosin acts through altering vascular permeability or the immune response, or both, remains to be determined.
Full text
PDF



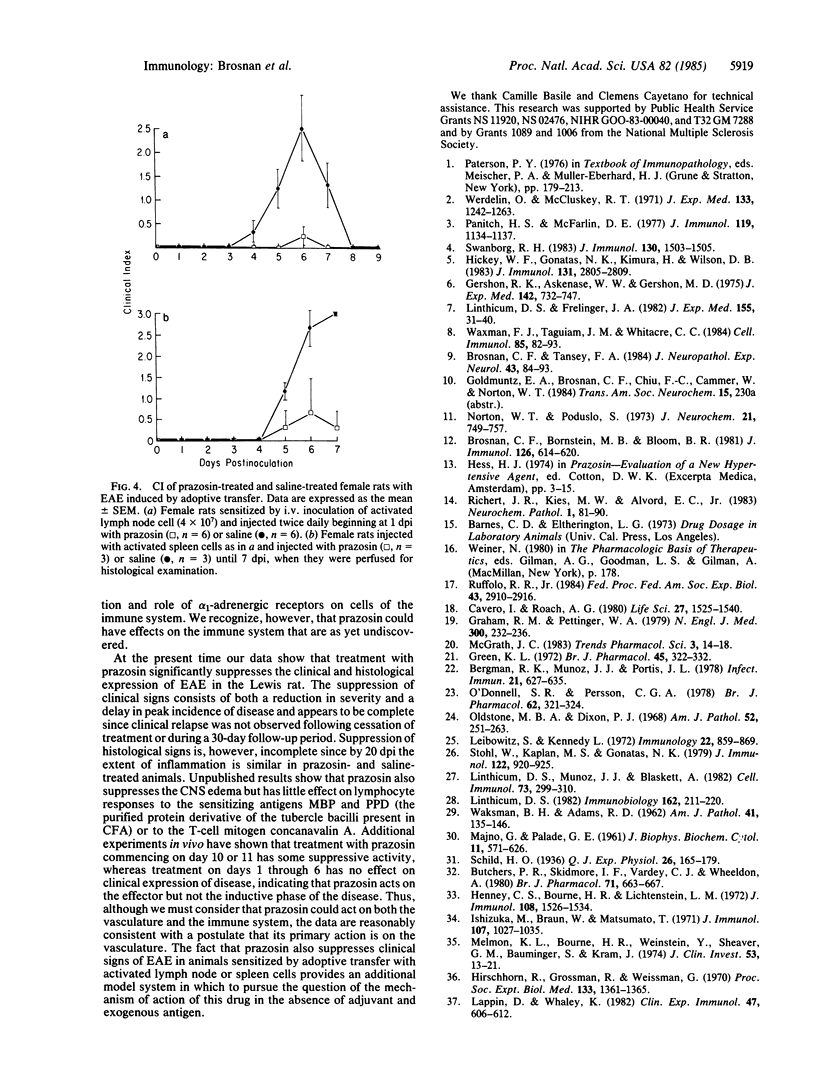
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergman R. K., Munoz J. J., Portis J. L. Vascular permeability changes in the central nervous system of rats with hyperacute experimental allergic encephalomyelitis induced with the aid of a substance from Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):627–637. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.627-637.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosnan C. F., Bornstein M. B., Bloom B. R. The effects of macrophage depletion on the clinical and pathologic expression of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):614–620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosnan C. F., Tansey F. A. Delayed onset of experimental allergic neuritis in rats treated with reserpine. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1984 Jan;43(1):84–93. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198401000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butchers P. R., Skidmore I. F., Vardey C. J., Wheeldon A. Characterization of the receptor mediating the antianaphylactic effects of beta-adrenoceptor agonists in human lung tissue in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1980;71(2):663–667. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10987.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavero I., Roach A. G. The pharmacology of prazosin, a novel antihypertensive agent. Life Sci. 1980 Oct 27;27(17):1525–1540. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90561-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon R. K., Askenase P. W., Gershon M. D. Requirement for vasoactive amines for production of delayed-type hypersensitvity skin reactions. J Exp Med. 1975 Sep 1;142(3):732–747. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.3.732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green K. L. The anti-inflammatory effect of catecholamines in the peritoneal cavity and hind paw of the mouse. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Jun;45(2):322–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb08086.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S., Bourne H. R., Lichtenstein L. M. The role of cyclic 3',5' adenosine monophosphate in the specific cytolytic activity of lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1972 Jun;108(6):1526–1534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickey W. F., Gonatas N. K., Kimura H., Wilson D. B. Identification and quantitation of T lymphocyte subsets found in the spinal cord of the Lewis rat during acute experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2805–2809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn R., Grossman J., Weissmann G. Effect of cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate and theophylline on lymphocyte transformation. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Apr;133(4):1361–1365. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizuka M., Braun W., Matsumoto T. Cyclic AMP and immune responses. I. Influence of poly A:U and cAMP on antibody formation in vitro. J Immunol. 1971 Oct;107(4):1027–1035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch-Weser J., Graham R. M., Pettinger W. A. Drug therapy. Prazosin. N Engl J Med. 1979 Feb 1;300(5):232–236. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197902013000505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lappin D., Whaley K. Adrenergic receptors on monocytes modulate complement component synthesis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Mar;47(3):606–612. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz S., Kennedy L. Cerebral vascular permeability and cellular infiltration in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Immunology. 1972 May;22(5):859–869. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linthicum D. S. Development of acute autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice: factors regulating the effector phase of the disease. Immunobiology. 1982 Aug;162(3):211–220. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80001-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linthicum D. S., Frelinger J. A. Acute autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice. II. Susceptibility is controlled by the combination of H-2 and histamine sensitization genes. J Exp Med. 1982 Jul 1;156(1):31–40. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linthicum D. S., Munoz J. J., Blaskett A. Acute experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice. I. Adjuvant action of Bordetella pertussis is due to vasoactive amine sensitization and increased vascular permeability of the central nervous system. Cell Immunol. 1982 Nov 1;73(2):299–310. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90457-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAJNO G., PALADE G. E., SCHOEFL G. I. Studies on inflammation. II. The site of action of histamine and serotonin along the vascular tree: a topographic study. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Dec;11:607–626. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.3.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melmon K. L., Bourne H. R., Weinstein Y., Shearer G. M., Kram J., Bauminger S. Hemolytic plaque formation by leukocytes in vitro. Control by vasoactive hormones. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):13–21. doi: 10.1172/JCI107530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton W. T., Poduslo S. E. Myelination in rat brain: method of myelin isolation. J Neurochem. 1973 Oct;21(4):749–757. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb07519.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell S. R., Persson C. G. Beta-adrenoceptor mediated inhibition by terbutaline of histamine effects on vascular permeability. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Mar;62(3):321–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb08463.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Dixon F. J. Immunohistochemical study of allergic encephalomyelitis. Am J Pathol. 1968 Feb;52(2):251–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panitch H. S., McFarlin D. E. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: enhancement of cell-mediated transfer by concanavalin A. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1134–1137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffolo R. R., Jr Interactions of agonists with peripheral alpha-adrenergic receptors. Fed Proc. 1984 Nov;43(14):2910–2916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohl W., Kaplan M. S., Gonatas N. K. A quantitative assay for experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the rat based on permeability of spinal cords to 125I-human gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1979 Mar;122(3):920–925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanborg R. H. Autoimmune effector cells. V.A monoclonal antibody specific for rat helper T lymphocytes inhibits adoptive transfer of autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1503–1505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAKSMAN B. H., ADAMS R. D. A histologic study of the early lesion in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the guinea pig and rabbit. Am J Pathol. 1962 Aug;41:135–162. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman F. J., Taguiam J. M., Whitacre C. C. Modification of the clinical and histopathologic expression of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by the vasoactive amine antagonist cyproheptadine. Cell Immunol. 1984 Apr 15;85(1):82–93. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90280-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werdelin O., McCluskey R. T. The nature and the specificity of mononuclear cells in experimental autoimmune inflammations and the mechanisms leading to their accumulation. J Exp Med. 1971 Jun 1;133(6):1242–1263. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.6.1242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



