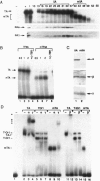
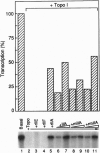
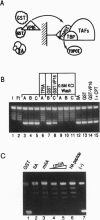
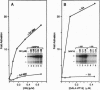
Abstract
Human transcription factor IIA (TFIIA) is composed of three subunits (alpha, beta, and gamma). TFIIA interacts with the TATA-box binding protein and can overcome repression of transcription. TFIIA was found to be necessary for VP16-mediated transcriptional activation through a coactivator function. We have separated the coactivator and antirepression activities of TFIIA. A TFIIA lacking the alpha subunit was isolated from HeLa cells. This "mini-TFIIA" interacts with the TATA-box binding protein and can overcome repression of transcription, but it is defective in transcriptional coactivator function.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auble D. T., Hansen K. E., Mueller C. G., Lane W. S., Thorner J., Hahn S. Mot1, a global repressor of RNA polymerase II transcription, inhibits TBP binding to DNA by an ATP-dependent mechanism. Genes Dev. 1994 Aug 15;8(16):1920–1934. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.16.1920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Guarente L., Sharp P. A. Five intermediate complexes in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):549–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90578-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Zhou H. Transcription factor IID mutants defective for interaction with transcription factor IIA. Science. 1992 Feb 28;255(5048):1130–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.1546314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Zhou H. Transcription factor IID mutants defective for interaction with transcription factor IIA. Science. 1992 Feb 28;255(5048):1130–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.1546314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. L., Attardi L. D., Verrijzer C. P., Yokomori K., Tjian R. Assembly of recombinant TFIID reveals differential coactivator requirements for distinct transcriptional activators. Cell. 1994 Oct 7;79(1):93–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90403-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choder M. A general topoisomerase I-dependent transcriptional repression in the stationary phase in yeast. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2315–2326. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortes P., Flores O., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: purification and analysis of transcription factor IIA and identification of transcription factor IIJ. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):413–421. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulombe B., Killeen M., Liljelund P., Honda B., Xiao H., Ingles C. J., Greenblatt J. Identification of three mammalian proteins that bind to the yeast TATA box protein TFIID. Gene Expr. 1992;2(2):99–110. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeJong J., Bernstein R., Roeder R. G. Human general transcription factor TFIIA: characterization of a cDNA encoding the small subunit and requirement for basal and activated transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 11;92(8):3313–3317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.8.3313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeJong J., Roeder R. G. A single cDNA, hTFIIA/alpha, encodes both the p35 and p19 subunits of human TFIIA. Genes Dev. 1993 Nov;7(11):2220–2234. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.11.2220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapkin R., Reardon J. T., Ansari A., Huang J. C., Zawel L., Ahn K., Sancar A., Reinberg D. Dual role of TFIIH in DNA excision repair and in transcription by RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1994 Apr 21;368(6473):769–772. doi: 10.1038/368769a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynlacht B. D., Hoey T., Tjian R. Isolation of coactivators associated with the TATA-binding protein that mediate transcriptional activation. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):563–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge H., Roeder R. G. Purification, cloning, and characterization of a human coactivator, PC4, that mediates transcriptional activation of class II genes. Cell. 1994 Aug 12;78(3):513–523. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90428-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge H., Zhao Y., Chait B. T., Roeder R. G. Phosphorylation negatively regulates the function of coactivator PC4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 20;91(26):12691–12695. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.26.12691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G., Tjian R. Eukaryotic coactivators associated with the TATA box binding protein. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Apr;2(2):236–242. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80279-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gstaiger M., Knoepfel L., Georgiev O., Schaffner W., Hovens C. M. A B-cell coactivator of octamer-binding transcription factors. Nature. 1995 Jan 26;373(6512):360–362. doi: 10.1038/373360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman A., Sinn E., Yamamoto T., Wang J., Roy A., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Highly conserved core domain and unique N terminus with presumptive regulatory motifs in a human TATA factor (TFIID). Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):387–390. doi: 10.1038/346387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inostroza J. A., Mermelstein F. H., Ha I., Lane W. S., Reinberg D. Dr1, a TATA-binding protein-associated phosphoprotein and inhibitor of class II gene transcription. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):477–489. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90172-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. D. The price of repression. Cell. 1995 Jun 2;81(5):655–658. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90524-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser K., Stelzer G., Meisterernst M. The coactivator p15 (PC4) initiates transcriptional activation during TFIIA-TFIID-promoter complex formation. EMBO J. 1995 Jul 17;14(14):3520–3527. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07358.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang J. J., Auble D. T., Ranish J. A., Hahn S. Analysis of the yeast transcription factor TFIIA: distinct functional regions and a polymerase II-specific role in basal and activated transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;15(3):1234–1243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.3.1234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao C. C., Lieberman P. M., Schmidt M. C., Zhou Q., Pei R., Berk A. J. Cloning of a transcriptionally active human TATA binding factor. Science. 1990 Jun 29;248(4963):1646–1650. doi: 10.1126/science.2194289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. J., Björklund S., Li Y., Sayre M. H., Kornberg R. D. A multiprotein mediator of transcriptional activation and its interaction with the C-terminal repeat domain of RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1994 May 20;77(4):599–608. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90221-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi N., Boyer T. G., Berk A. J. A class of activation domains interacts directly with TFIIA and stimulates TFIIA-TFIID-promoter complex assembly. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Nov;15(11):6465–6473. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.11.6465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretzschmar M., Meisterernst M., Roeder R. G. Identification of human DNA topoisomerase I as a cofactor for activator-dependent transcription by RNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11508–11512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Commitment and activation at pol II promoters: a tail of protein-protein interactions. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1161–1164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90675-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman P. M., Berk A. J. A mechanism for TAFs in transcriptional activation: activation domain enhancement of TFIID-TFIIA--promoter DNA complex formation. Genes Dev. 1994 May 1;8(9):995–1006. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.9.995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo Y., Fujii H., Gerster T., Roeder R. G. A novel B cell-derived coactivator potentiates the activation of immunoglobulin promoters by octamer-binding transcription factors. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):231–241. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90352-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo Y., Roeder R. G. Cloning, functional characterization, and mechanism of action of the B-cell-specific transcriptional coactivator OCA-B. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Aug;15(8):4115–4124. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.8.4115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma D., Watanabe H., Mermelstein F., Admon A., Oguri K., Sun X., Wada T., Imai T., Shiroya T., Reinberg D. Isolation of a cDNA encoding the largest subunit of TFIIA reveals functions important for activated transcription. Genes Dev. 1993 Nov;7(11):2246–2257. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.11.2246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maldonado E., Ha I., Cortes P., Weis L., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: role of transcription factors IIA, IID, and IIB during formation of a transcription-competent complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6335–6347. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maldonado E., Shiekhattar R., Sheldon M., Cho H., Drapkin R., Rickert P., Lees E., Anderson C. W., Linn S., Reinberg D. A human RNA polymerase II complex associated with SRB and DNA-repair proteins. Nature. 1996 May 2;381(6577):86–89. doi: 10.1038/381086a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S., Tjian R. Transcriptional selectivity of viral genes in mammalian cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):795–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisterernst M., Roeder R. G. Family of proteins that interact with TFIID and regulate promoter activity. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):557–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90530-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisterernst M., Roy A. L., Lieu H. M., Roeder R. G. Activation of class II gene transcription by regulatory factors is potentiated by a novel activity. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):981–993. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90443-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merino A., Madden K. R., Lane W. S., Champoux J. J., Reinberg D. DNA topoisomerase I is involved in both repression and activation of transcription. Nature. 1993 Sep 16;365(6443):227–232. doi: 10.1038/365227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima N., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: purification, genetic specificity, and TATA box-promoter interactions of TFIID. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4028–4040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozer J., Moore P. A., Bolden A. H., Lee A., Rosen C. A., Lieberman P. M. Molecular cloning of the small (gamma) subunit of human TFIIA reveals functions critical for activated transcription. Genes Dev. 1994 Oct 1;8(19):2324–2335. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.19.2324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor contains a promoter-region-specific DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. G., Tanese N., Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Functional domains and upstream activation properties of cloned human TATA binding protein. Science. 1990 Jun 29;248(4963):1625–1630. doi: 10.1126/science.2363050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Gann A. A. Activators and targets. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):329–331. doi: 10.1038/346329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Mechanism of transcriptional activation by Sp1: evidence for coactivators. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1187–1197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90683-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Transcription from a TATA-less promoter requires a multisubunit TFIID complex. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):1935–1945. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.1935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shykind B. M., Kim J., Sharp P. A. Activation of the TFIID-TFIIA complex with HMG-2. Genes Dev. 1995 Jun 1;9(11):1354–1365. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.11.1354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stargell L. A., Struhl K. The TBP-TFIIA interaction in the response to acidic activators in vivo. Science. 1995 Jul 7;269(5220):75–78. doi: 10.1126/science.7604282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strubin M., Newell J. W., Matthias P. OBF-1, a novel B cell-specific coactivator that stimulates immunoglobulin promoter activity through association with octamer-binding proteins. Cell. 1995 Feb 10;80(3):497–506. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90500-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X., Ma D., Sheldon M., Yeung K., Reinberg D. Reconstitution of human TFIIA activity from recombinant polypeptides: a role in TFIID-mediated transcription. Genes Dev. 1994 Oct 1;8(19):2336–2348. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.19.2336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanese N., Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Coactivators for a proline-rich activator purified from the multisubunit human TFIID complex. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2212–2224. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Maniatis T. Transcriptional activation: a complex puzzle with few easy pieces. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90227-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W., Gralla J. D., Carey M. The acidic activator GAL4-AH can stimulate polymerase II transcription by promoting assembly of a closed complex requiring TFIID and TFIIA. Genes Dev. 1992 Sep;6(9):1716–1727. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.9.1716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung K. C., Inostroza J. A., Mermelstein F. H., Kannabiran C., Reinberg D. Structure-function analysis of the TBP-binding protein Dr1 reveals a mechanism for repression of class II gene transcription. Genes Dev. 1994 Sep 1;8(17):2097–2109. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.17.2097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokomori K., Zeidler M. P., Chen J. L., Verrijzer C. P., Mlodzik M., Tjian R. Drosophila TFIIA directs cooperative DNA binding with TBP and mediates transcriptional activation. Genes Dev. 1994 Oct 1;8(19):2313–2323. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.19.2313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawel L., Reinberg D. Common themes in assembly and function of eukaryotic transcription complexes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1995;64:533–561. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.64.070195.002533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Q., Lieberman P. M., Boyer T. G., Berk A. J. Holo-TFIID supports transcriptional stimulation by diverse activators and from a TATA-less promoter. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1964–1974. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]