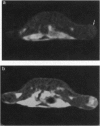
Abstract
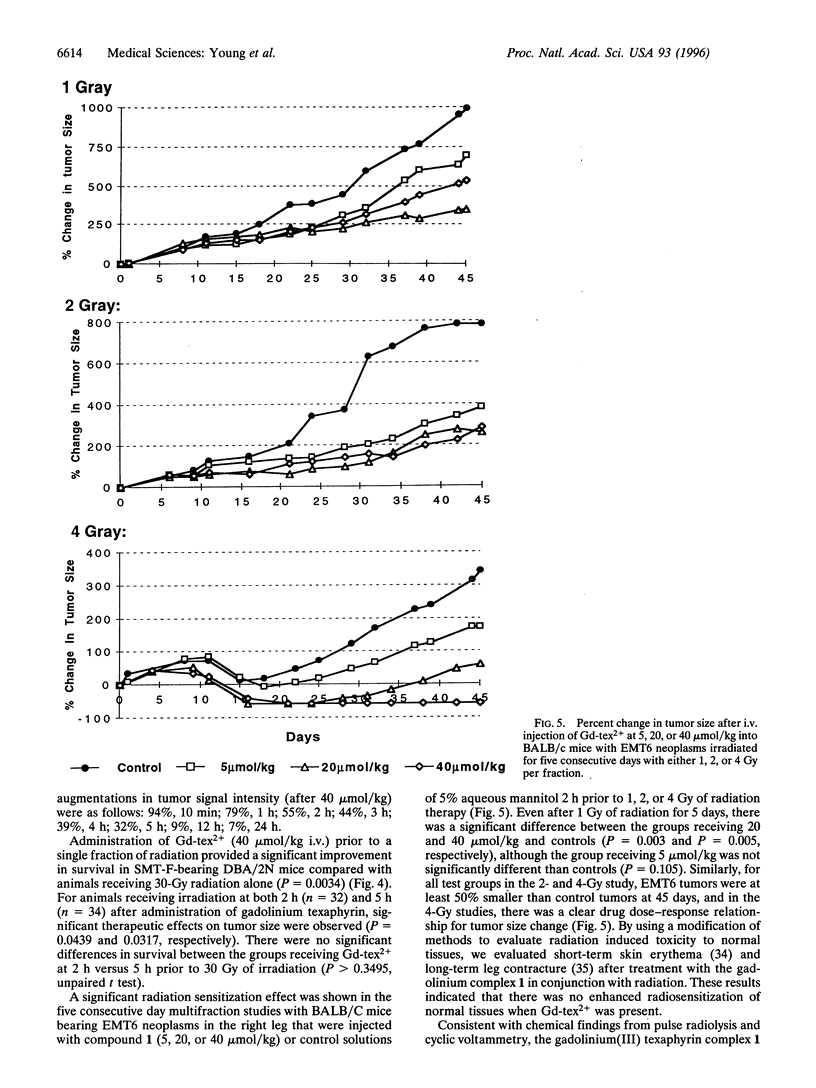
Gadolinium(III) texaphyrin (Gd-tex2+) is representative of a new class of radiation sensitizers detectable by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This porphyrin-like complex has a high electron affinity [E1/2 (red.) approximately = -0.08 V versus normal hydrogen electrode] and forms a long-lived pi-radical cation upon exposure to hydrated electrons, reducing ketyl radicals, or superoxide ions. Consistent with these chemical findings, Gd-tex2+ was found to be an efficient radiation sensitizer in studies carried out with HT29 cells in in vitro as well as in in vivo single and multifraction irradiation studies with a murine mammary carcinoma model. Selective localization of Gd-tex2+ in tumors was confirmed by MRI scanning.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams G. E. Failla Memorial Lecture. Redox, radiation, and reductive bioactivation. Radiat Res. 1992 Nov;132(2):129–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brada M., Ross G. Radiotherapy for primary and secondary brain tumors. Curr Opin Oncol. 1995 May;7(3):214–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. M., Lemmon M. J. SR 4233: a tumor specific radiosensitizer active in fractionated radiation regimes. Radiother Oncol. 1991;20 (Suppl 1):151–156. doi: 10.1016/0167-8140(91)90203-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. M., Lemmon M. J. Tumor hypoxia can be exploited to preferentially sensitize tumors to fractionated irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1991 Mar;20(3):457–461. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(91)90057-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman C. N., Halsey J., Cox R. S., Hirst V. K., Blaschke T., Howes A. E., Wasserman T. H., Urtasun R. C., Pajak T., Hancock S. Relationship between the neurotoxicity of the hypoxic cell radiosensitizer SR 2508 and the pharmacokinetic profile. Cancer Res. 1987 Jan 1;47(1):319–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dische S., Saunders M. I., Bennett M. H., Dunphy E. P., Des Rochers C., Stratford M. R., Minchinton A. I., Wardman P. A comparison of the tumour concentrations obtainable with misonidazole and Ro 03-8799. Br J Radiol. 1986 Sep;59(705):911–917. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-59-705-911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iliakis G., Kurtzman S., Pantelias G., Okayasu R. Mechanism of radiosensitization by halogenated pyrimidines: effect of BrdU on radiation induction of DNA and chromosome damage and its correlation with cell killing. Radiat Res. 1989 Aug;119(2):286–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallman R. F. The phenomenon of reoxygenation and its implications for fractionated radiotherapy. Radiology. 1972 Oct;105(1):135–142. doi: 10.1148/105.1.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella T. J., Dobson P. P., Mitchell J. B., Fornace A. J., Jr Enhancement of X ray induced DNA damage by pre-treatment with halogenated pyrimidine analogs. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1987 May;13(5):733–739. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(87)90292-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella T. J., Russo A., Mitchell J. B., Collins J. M., Rowland J., Wright D., Glatstein E. A phase I study of intravenous iododeoxyuridine as a clinical radiosensitizer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1985 Nov;11(11):1941–1946. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(85)90275-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella T. J., Russo A., Mitchell J. B., Rowland J., Jenkins J., Schwade J., Myers C. E., Collins J. M., Speyer J., Kornblith P. A Phase I study of intermittent intravenous bromodeoxyuridine (BUdR) with conventional fractionated irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1984 Jan;10(1):69–76. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(84)90414-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchgessner C. U., Patil C. K., Evans J. W., Cuomo C. A., Fried L. M., Carter T., Oettinger M. A., Brown J. M. DNA-dependent kinase (p350) as a candidate gene for the murine SCID defect. Science. 1995 Feb 24;267(5201):1178–1183. doi: 10.1126/science.7855601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. J., Skov K. A. Comparisons of cellular radiation response using absolute rather than relative parameters. Radiat Res. 1992 Oct;132(1):40–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees-Miller S. P., Godbout R., Chan D. W., Weinfeld M., Day R. S., 3rd, Barron G. M., Allalunis-Turner J. Absence of p350 subunit of DNA-activated protein kinase from a radiosensitive human cell line. Science. 1995 Feb 24;267(5201):1183–1185. doi: 10.1126/science.7855602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. M., Fowler J. F., Kinsella T. J. Linear-quadratic analysis of radiosensitization by halogenated pyrimidines. I. Radiosensitization of human colon cancer cells by iododeoxyuridine. Radiat Res. 1992 Jul;131(1):81–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman H. F., Ward R., Workman P., Bleehen N. M. The multi-dose clinical tolerance and pharmacokinetics of the combined radiosensitizers, Ro 03-8799 (pimonidazole) and SR 2508 (etanidazole). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1988 Nov;15(5):1073–1083. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(88)90187-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell M. J., Martenson J. A., Wieand H. S., Krook J. E., Macdonald J. S., Haller D. G., Mayer R. J., Gunderson L. L., Rich T. A. Improving adjuvant therapy for rectal cancer by combining protracted-infusion fluorouracil with radiation therapy after curative surgery. N Engl J Med. 1994 Aug 25;331(8):502–507. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199408253310803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavelic Z. P., Porter C. W., Allen L. M., Mihich E. Cell population kinetics of fast- and slow-growing transplantable tumors derived from spontaneous mammary tumors of the DBA/2 Ha-DD mouse. Cancer Res. 1978 Jun;38(6):1533–1538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. T., Bleehen N. M., Workman P., Walton M. I. A phase I study of the hypoxic cell radiosensitizer Ro-03-8799. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1984 Sep;10(9):1755–1758. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(84)90543-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rockwell S. C., Kallman R. F., Fajardo L. F. Characteristics of a serially transplanted mouse mammary tumor and its tissue-culture-adapted derivative. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Sep;49(3):735–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo A., Mitchell J., Kinsella T., Morstyn G., Glatstein E. Determinants of radiosensitivity. Semin Oncol. 1985 Sep;12(3):332–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders M. I., Anderson P. J., Bennett M. H., Dische S., Minchinton A., Stratford M. R., Tothill M. The clinical testing of Ro 03-8799--pharmacokinetics, toxicology, tissue and tumor concentrations. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1984 Sep;10(9):1759–1763. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(84)90544-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannock I. F. Oxygen diffusion and the distribution of cellular radiosensitivity in tumours. Br J Radiol. 1972 Jul;45(535):515–524. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-45-535-515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson E. R., Halnan K. E., Dische S., Saunders M. I., Cade I. S., McEwen J. B., Wiernik G., Perrins D. J., Sutherland I. Hyperbaric oxygen and radiotherapy: a Medical Research Council trial in carcinoma of the cervix. Br J Radiol. 1978 Nov;51(611):879–887. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-51-611-879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. W., Sidhu M. K., Qing F., Muller H. H., Neuder M., Zanassi G., Mody T. D., Hemmi G., Dow W., Mutch J. D. Preclinical evaluation of gadolinium (III) texaphyrin complex. A new paramagnetic contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging. Invest Radiol. 1994 Mar;29(3):330–338. doi: 10.1097/00004424-199403000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]