Abstract
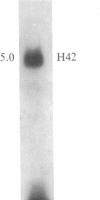
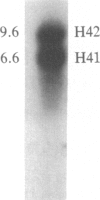
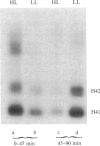
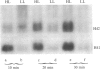
The time of replication of the two H4 histone genes (H41 and H42) was determined during the naturally synchronous mitotic cycle of Physarum polycephalum. 5-Bromo-2'-deoxyuridine labeling and density gradient centrifugation was used to isolate newly synthesized DNA from defined periods of S phase. The DNA was analyzed by Southern hybridization with a cloned probe containing one of the H4 histone genes of Physarum. The results indicate that the two H4 histone genes are replicated in the first 30 min of S phase but not exactly at the same time. H41 is replicated during the first 10 min of S phase, when only 15% of the genome is duplicated, whereas H42 replicates between 20 and 30 min after the onset of S phase. The possible relationship between the periodic expression of the genes and the timing of their replication is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alterman R. B., Ganguly S., Schulze D. H., Marzluff W. F., Schildkraut C. L., Skoultchi A. I. Cell cycle regulation of mouse H3 histone mRNA metabolism. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):123–132. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beach D., Piper M., Shall S. Isolation of newly-initiated DNA from the early S phase of the synchronous eukaryote, Physarum polycephalum. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Sep;129(1):211–221. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90344-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borun T. W., Gabrielli F., Ajiro K., Zweidler A., Baglioni C. Further evidence of transcriptional and translational control of histone messenger RNA during the HeLa S3 cycle. Cell. 1975 Jan;4(1):59–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90134-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun R., Mittermayer C., Rusch H. P. Sequential temporal replication of DNA in Physarum polycephalum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 May;53(5):924–931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.5.924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunstein J. D., Schulze D., DelGiudice T., Furst A., Schildkraut C. L. The temporal order of replication of murine immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region sequences corresponds to their linear order in the genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6887–6902. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broach J. R., Li Y. Y., Feldman J., Jayaram M., Abraham J., Nasmyth K. A., Hicks J. B. Localization and sequence analysis of yeast origins of DNA replication. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):1165–1173. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAIRNS J. The bacterial chromosome and its manner of replication as seen by autoradiography. J Mol Biol. 1963 Mar;6:208–213. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calza R. E., Eckhardt L. A., DelGiudice T., Schildkraut C. L. Changes in gene position are accompanied by a change in time of replication. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):689–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90349-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANIEL J. W., RUSCH H. P. The pure culture of Physarum polycephalum on a partially defined soluble medium. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 May;25:47–59. doi: 10.1099/00221287-25-1-47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epner E., Rifkind R. A., Marks P. A. Replication of alpha and beta globin DNA sequences occurs during early S phase in murine erythroleukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3058–3062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fouquet H., Sauer H. W. Differential cleavate of Physarum DNA from distinct points of S phase by restriction enzyme Eco RI. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jan 15;61(2):234–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)81045-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funderud S., Andreassen R., Haugli F. DNA replication in Physarum polycephalum: electron microscopic and autoradiographic analysis of replicating DNA from defined stages of the S-period. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Apr;6(4):1417–1431. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.4.1417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furst A., Brown E. H., Braunstein J. D., Schildkraut C. L. alpha-Globulin sequences are located in a region of early-replicating DNA in murine erythroleukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1023–1027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman M. A., Holmquist G. P., Gray M. C., Caston L. A., Nag A. Replication timing of genes and middle repetitive sequences. Science. 1984 May 18;224(4650):686–692. doi: 10.1126/science.6719109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Transcription of human histone genes in extracts from synchronized HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2713–2717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L., Bromley S., Osley M. A. Periodic transcription of yeast histone genes. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L., Fahrner K., Woolford J., Jr, Rosbash M., Kaback D. B. Isolation of yeast histone genes H2A and H2B. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1261–1271. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90237-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt B. F., Vogelstein B. Association of newly replicated DNA with the nuclear matrix of Physarum polycephalum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):349–363. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal M. A., Plumb M., Stein J., Stein G., Schildkraut C. L. Coordinate replication of members of the multigene family of core and H1 human histone genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7723–7727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H. Histone genes and histone messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:837–870. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller G. C., Kajiwara K. Early- and late-replicating deoxyribonucleic acid complexes in HeLa nuclei. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jan 18;114(1):108–115. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90258-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osley M. A., Hereford L. Identification of a sequence responsible for periodic synthesis of yeast histone 2A mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7689–7693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierron G., Durica D. S., Sauer H. W. Invariant temporal order of replication of the four actin gene loci during the naturally synchronous mitotic cycles of Physarum polycephalum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6393–6397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierron G., Sauer H. W., Toublan B., Jalouzot R. Physical relationship between replicons and transcription units in Physarum polycephalum. Eur J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;29(1):104–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumb M., Marashi F., Green L., Zimmerman A., Zimmerman S., Stein J., Stein G. Cell cycle regulation of human histone H1 mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):434–438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SACHSENMAIER W., RUSCH H. P. THE EFFECT OF 5-FLUORO-2'-DEOXYURIDINE ON SYNCHRONOUS MITOSIS IN PHYSARUM POLYCEPHALUM. Exp Cell Res. 1964 Oct;36:124–133. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(64)90166-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sittman D. B., Graves R. A., Marzluff W. F. Histone mRNA concentrations are regulated at the level of transcription and mRNA degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1849–1853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. M., Andrésson O. S. DNA sequences of yeast H3 and H4 histone genes from two non-allelic gene sets encode identical H3 and H4 proteins. J Mol Biol. 1983 Sep 25;169(3):663–690. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR J. H. Asynchronous duplication of chromosomes in cultured cells of Chinese hamster. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Jun;7:455–464. doi: 10.1083/jcb.7.3.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm M. L., Toublan B., Jalouzot R., Wilhelm F. X. Histone H4 gene is transcribed in S phase but also late in G(2) phase in Physarum polycephalum. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2659–2662. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02190.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm M. L., Wilhelm F. X. A transposon-like DNA fragment interrupts a Physarum polycephalum histone H4 gene. FEBS Lett. 1984 Mar 26;168(2):249–254. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80256-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]