Abstract
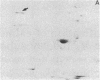
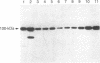
A major substrate, Mr 100,00 (100 kDa), for a Ca2+/calmodulin (CaM)-dependent protein kinase found in many mammalian tissues has been purified from rat pancreas. The purified substrate was used to identify and partially purify a CaM-dependent protein kinase (CaM kinase III) from rat pancreas. The physical properties and substrate specificity of CaM kinase III were distinct from those of all known CaM-dependent protein kinases. Only CaM kinase III was able to phosphorylate the 100-kDa protein; synapsin I, phosphorylase b, myosin light chain, and histone were poor substrates for this enzyme. Polyclonal antibodies, raised against the purified 100-kDa protein, recognized the protein in a variety of mammalian tissues and cell lines. Immunoassay revealed that the 100-kDa protein made up 0.3-1.7% of the total cytosolic protein in these samples. Analysis of CaM kinase III revealed that the enzyme had a similar widespread tissue distribution. These results demonstrate the existence of a fifth CaM-dependent protein phosphorylation system present in high levels in animal cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad Z., DePaoli-Roach A. A., Roach P. J. Purification and characterization of a rabbit liver calmodulin-dependent protein kinase able to phosphorylate glycogen synthase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8348–8355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amy C. M., Kirshner N. Phosphorylation of adrenal medulla cell proteins in conjunction with stimulation of catecholamine secretion. J Neurochem. 1981 Mar;36(3):847–854. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb01671.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., Erondu N. E., Kennedy M. B. Purification and characterization of a calmodulin-dependent protein kinase that is highly concentrated in brain. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12735–12744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brocklehurst K. W., Hutton J. C. Ca2+-dependent binding of cytosolic components to insulin-secretory granules results in Ca2+-dependent protein phosphorylation. Biochem J. 1983 Feb 15;210(2):533–539. doi: 10.1042/bj2100533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y. Calmodulin plays a pivotal role in cellular regulation. Science. 1980 Jan 4;207(4426):19–27. doi: 10.1126/science.6243188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Burchell A., Foulkes J. G., Cohen P. T., Vanaman T. C., Nairn C. Identification of the Ca2+-dependent modulator protein as the fourth subunit of rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase. FEBS Lett. 1978 Aug 15;92(2):287–293. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80772-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The subunit structure of rabbit-skeletal-muscle phosphorylase kinase, and the molecular basis of its activation reactions. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Apr 2;34(1):1–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabrowska R., Sherry J. M., Aromatorio D. K., Hartshorne D. J. Modulator protein as a component of the myosin light chain kinase from chicken gizzard. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 24;17(2):253–258. doi: 10.1021/bi00595a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dartt D. A., Guerina V. J., Donowitz M., Taylor L., Sharp G. W. Ca2+- and calmodulin-dependent protein phosphorylation in rat lacrimal gland. Biochem J. 1982 Mar 15;202(3):799–802. doi: 10.1042/bj2020799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drust D. S., Martin T. F. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone rapidly and transiently stimulates cytosolic calcium-dependent protein phosphorylation in GH3 pituitary cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7566–7573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- End D., Hanson M., Hashimoto S., Guroff G. Inhibition of the phosphorylation of a 1000,000-dalton soluble protein in whole cells and cell-free extracts of PC12 pheochromocytoma cells following treatment with nerve growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9223–9225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- End D., Tolson N., Hashimoto S., Guroff G. Nerve growth factor-induced decrease in the cell-free phosphorylation of a soluble protein in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6549–6555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga K., Yamamoto H., Matsui K., Higashi K., Miyamoto E. Purification and characterization of a Ca2+- and calmodulin-dependent protein kinase from rat brain. J Neurochem. 1982 Dec;39(6):1607–1617. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb07994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grand R. J., Perry S. V., Weeks R. A. Troponin C-like proteins (calmodulins) from mammalian smooth muscle and other tissues. Biochem J. 1979 Feb 1;177(2):521–529. doi: 10.1042/bj1770521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison D. E., Ashcroft S. J. Effects of Ca2+, calmodulin and cyclic AMP on the phosphorylation of endogenous proteins by homogenates of rt islets of langerhans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Feb 2;714(2):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(82)90339-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., Greengard P. Multiple phosphorylation sites in protein I and their differential regulation by cyclic AMP and calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5402–5406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarek L. K., Jennings K. R., Strumwasser F., Nairn A. C., Walter U., Wilson F. D., Greengard P. Microinjection of catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase enhances calcium action potentials of bag cell neurons in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7487–7491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. B., Greengard P. Two calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases, which are highly concentrated in brain, phosphorylate protein I at distinct sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1293–1297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Vanaman T. C. Calmodulin. Adv Protein Chem. 1982;35:213–321. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60470-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuinness T. L., Lai Y., Greengard P. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Isozymic forms from rat forebrain and cerebellum. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1696–1704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson J. M., Whitehouse S., Walsh D. A. Possibility of shape conformers of the protein inhibitor of the cyclic adenosine monophosphate dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 30;18(22):4835–4845. doi: 10.1021/bi00589a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nairn A. C., Perry S. V. Calmodulin and myosin light-chain kinase of rabbit fast skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1979 Apr 1;179(1):89–97. doi: 10.1042/bj1790089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler E. J., Greengard P. Protein phosphorylation in the brain. Nature. 1983 Oct 13;305(5935):583–588. doi: 10.1038/305583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palfrey H. C. Presence in many mammalian tissues of an identical major cytosolic substrate (Mr 100 000) for calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jun 27;157(1):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81142-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrie W. T., Smillie L. B., Perry S. B. A phosphorylated light-chain component of myosin from skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1973 Sep;135(1):151–164. doi: 10.1042/bj1350151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubart U. K., Erlichman J., Fleischer N. The role of calmodulin in the regulation of protein phosphorylation and insulin release in hamster insulinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):4120–4124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman H., Greengard P. Ca2+-dependent protein phosphorylation system in membranes from various tissues, and its activation by "calcium-dependent regulator". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5432–5436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenolikar S., Cohen P. T., Cohen P., Nairn A. C., Perry S. V. The role of calmodulin in the structure and regulation of phosphorylase kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct 15;100(2):329–337. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb04175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. A., Ingebritsen T. S., Manalan A., Klee C. B., Cohen P. Discovery of a Ca2+- and calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase: probable identity with calcineurin (CaM-BP80). FEBS Lett. 1982 Jan 11;137(1):80–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80319-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor L., Guerina V. J., Donowitz M., Cohen M., Sharp G. W. Calcium and calmodulin-dependent protein phosphorylation in rabbit ileum. FEBS Lett. 1981 Aug 31;131(2):322–324. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80395-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thams P., Capito K., Hedeskov C. J. Endogenous substrate proteins for Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent, Ca2+-phospholipid-dependent and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases in mouse pancreatic islets. Biochem J. 1984 Jul 1;221(1):247–253. doi: 10.1042/bj2210247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titani K., Koide A., Hermann J., Ericsson L. H., Kumar S., Wade R. D., Walsh K. A., Neurath H., Fischer E. H. Complete amino acid sequence of rabbit muscle glycogen phosphorylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4762–4766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Togari A., Guroff G. Partial purification and characterization of a nerve growth factor-sensitive kinase and its substrate from PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3804–3811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Greengard P. Adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein system of neuronal membranes. I. Solubilization, purification, and some properties of an endogenous phosphoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):5155–5163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi K., Yazawa M., Kakiuchi S., Ohshima M., Uenishi K. Identification of an activator protein for myosin light chain kinase as the Ca2+-dependent modulator protein. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1338–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi T., Fujisawa H. Purification and characterization of the brain calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (kinase II), which is involved in the activation of tryptophan 5-monooxygenase. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Apr 15;132(1):15–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07319.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]