Abstract
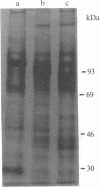
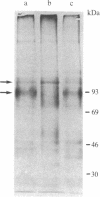
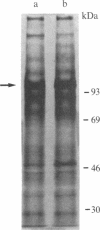
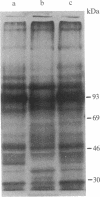
Expression of membrane glycoproteins in L6 myoblasts during the course of myogenesis was investigated. The effects of several inhibitors of myoblast fusion and differentiation were also studied. The predominant change in plasma membrane proteins concomitant with fusion was the reduction in the expression of a major 105-kDa glycoprotein and the appearance of a 90-kDa glycoprotein. This change was blocked by bromodeoxyuridine and two metalloendoprotease inhibitors, phenanthroline and benzyloxycarbonyl-Ser-Leu-NH2, all of which have been shown to inhibit myoblast fusion. The nature of this inhibition suggests a role for an endogenous metalloendoprotease in myoblast commitment to terminal differentiation. The possible function of the developmentally regulated glycoproteins in myogenesis is also discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Castle J. D., Palade G. E. Secretion granules of the rabbit parotid. Selective removal of secretory contaminants from granule membranes. J Cell Biol. 1978 Feb;76(2):323–340. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.2.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cates G. A., Brickenden A. M., Sanwal B. D. Possible involvement of a cell surface glycoprotein in the differentiation of skeletal myoblasts. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2646–2650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cates G. A., Holland P. C. Biosynthesis of plasma-membrane proteins during myogenesis of skeletal muscle in vitro. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 15;174(3):873–881. doi: 10.1042/bj1740873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couch C. B., Strittmatter W. J. Rat myoblast fusion requires metalloendoprotease activity. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):257–265. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90516-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couch C. B., Strittmatter W. J. Specific blockers of myoblast fusion inhibit a soluble and not the membrane-associated metalloendoprotease in myoblasts. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5396–5399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., White J. M., Waterfield M. D. Purification of the fusion protein of Sendai virus: analysis of the NH2-terminal sequence generated during precursor activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2737–2740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goz B. The effects of incorporation of 5-halogenated deoxyuridines into the DNA of eukaryotic cells. Pharmacol Rev. 1977 Dec;29(4):249–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linkhart T. A., Clegg C. H., Hauschka S. D. Control of mouse myoblast commitment to terminal differentiation by mitogens. J Supramol Struct. 1980;14(4):483–498. doi: 10.1002/jss.400140407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neff N. T., Lowrey C., Decker C., Tovar A., Damsky C., Buck C., Horwitz A. F. A monoclonal antibody detaches embryonic skeletal muscle from extracellular matrices. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):654–666. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olden K., Law J., Hunter V. A., Romain R., Parent J. B. Inhibition of fusion of embryonic muscle cells in culture by tunicamycin is prevented by leupeptin. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jan;88(1):199–204. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.1.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg J., Düzgüneş N., Kayalar C. Comparison of two liposome fusion assays monitoring the intermixing of aqueous contents and of membrane components. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Oct 26;735(1):173–180. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmel S. D., Kent C., Bischoff R., Vagelos P. R. Plasma membranes from cultured muscle cells: isolation procedure and separation of putative plasma-membrane marker enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3195–3199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senechal H., Delain D., Schapira G., Wahrmann J. P. Alterations in glycosylation of plasma membrane proteins during myogenesis. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Sep;147(2):341–350. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90216-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe D. Retention of differentiation potentialities during prolonged cultivation of myogenic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):477–483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]