Abstract
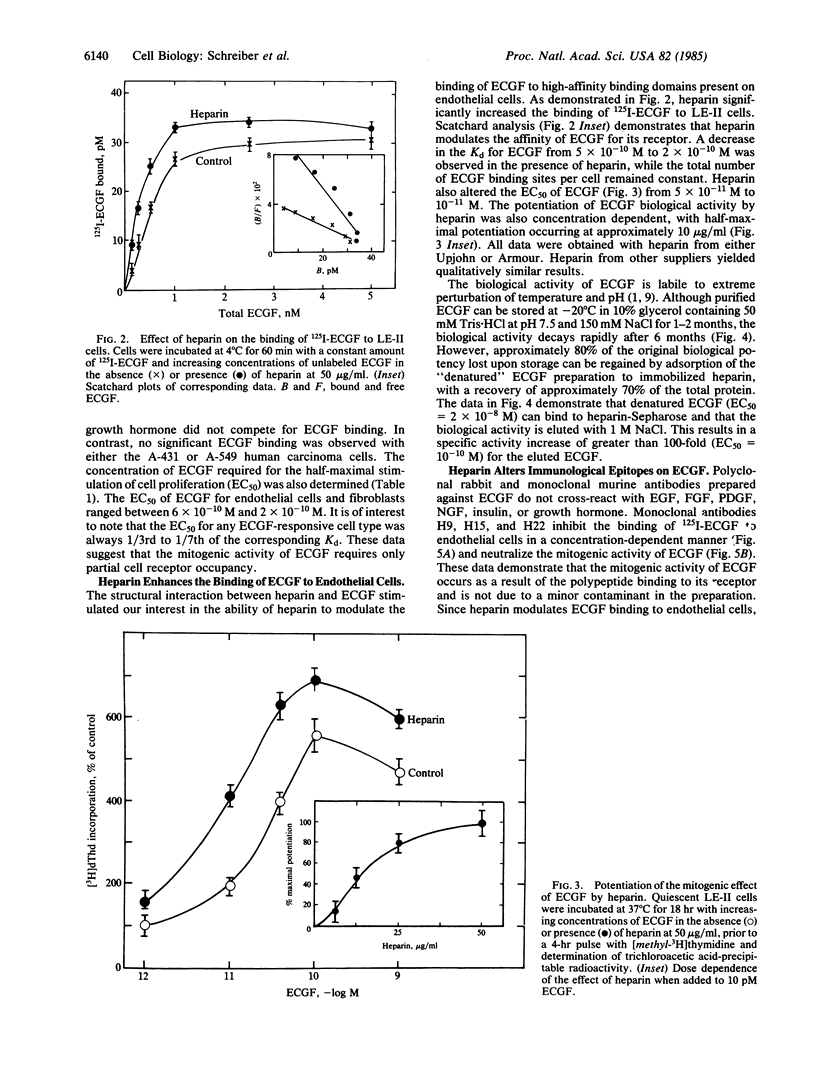
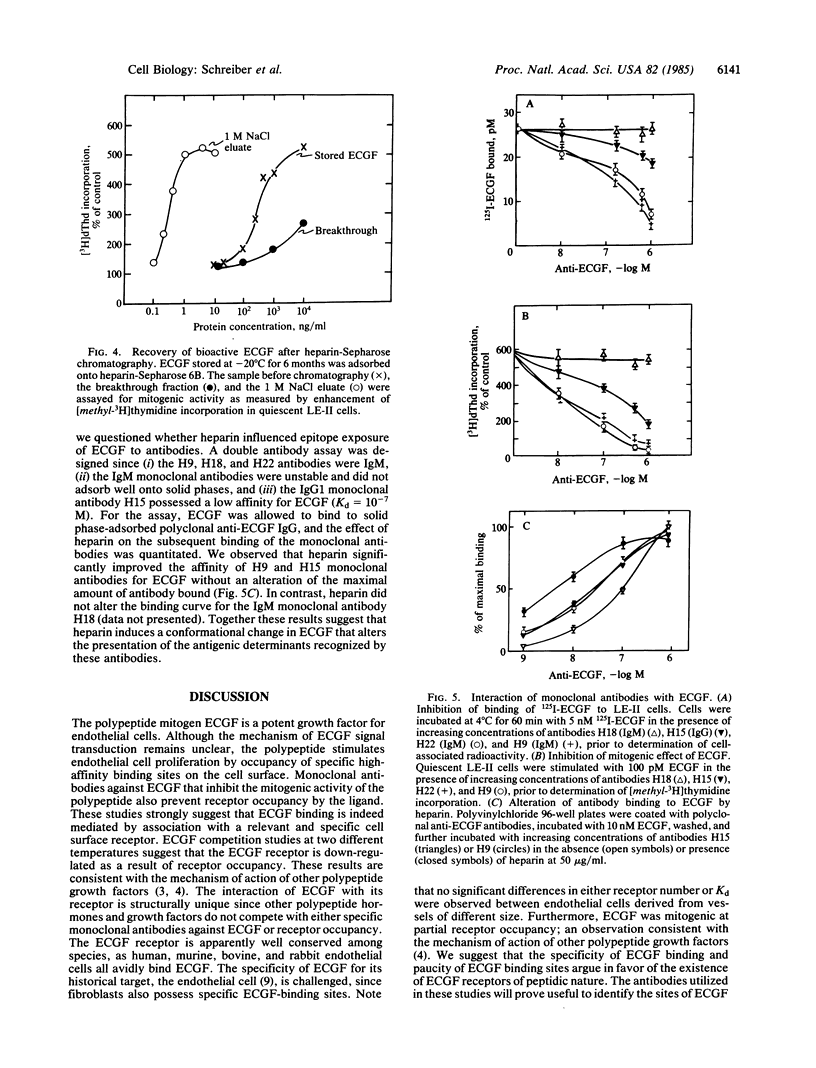
Endothelial cell growth factor (ECGF) binds specifically in vitro to membrane receptors present on the surface of several cell types, including murine and human endothelial cells and fibroblasts. Monoclonal antibodies prepared against ECGF that inhibit the mitogenic activity of the growth factor prevent receptor occupancy by the ligand. Heparin interacts structurally with ECGF [Maciag, T., Mehlman, T., Friesel, R. & Schreiber, A. B. (1984) Science 225, 932-935], potentiates the mitogenic activity of the polypeptide, restores the biological activity to inactivate ECGF, enhances the affinity of the ligand to cell surface receptors, and modifies antibody recognition of ECGF. These data suggest that the association between heparin and ECGF induces a conformational change in the polypeptide that increases or stabilizes the biological activity of the mitogen.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alessandri G., Raju K., Gullino P. M. Angiogenesis in vivo and selective mobilization of capillary endothelium in vitro by heparin-copper complex. Microcirc Endothelium Lymphatics. 1984 Jun;1(3):329–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azizkhan R. G., Azizkhan J. C., Zetter B. R., Folkman J. Mast cell heparin stimulates migration of capillary endothelial cells in vitro. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):931–944. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barritault D., Plouët J., Courty J., Courtois Y. Purification, characterization, and biological properties of the eye-derived growth factor from retina: analogies with brain-derived growth factor. J Neurosci Res. 1982;8(2-3):477–490. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490080235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhlen P., Baird A., Esch F., Ling N., Gospodarowicz D. Isolation and partial molecular characterization of pituitary fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5364–5368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellot J. J., Jr, Beeler D. L., Rosenberg R. D., Karnovsky M. J. Structural determinants of the capacity of heparin to inhibit the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Sep;120(3):315–320. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041200309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Underwood L. E., Chatelain P. G., Van Wyk J. J. Liberation of immunoreactive somatomedin-C from its binding proteins by proteolytic enzymes and heparin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Feb;56(2):384–389. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-2-384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F., Huang J. S., Proffitt R. T., Baenziger J. U., Chang D., Kennedy B. B. Human platelet-derived growth factor. Purification and resolution into two active protein fractions. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):8896–8899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Haudenschild C. Angiogenesis in vitro. Nature. 1980 Dec 11;288(5791):551–556. doi: 10.1038/288551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S., Folkman J. Human vascular endothelial cells in culture. Growth and DNA synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1974 Mar;60(3):673–684. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.3.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon P. B., Sussman I. I., Hatcher V. B. Long-term culture of human endothelial cells. In Vitro. 1983 Sep;19(9):661–671. doi: 10.1007/BF02628957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Cheng J., Lui G. M., Baird A., Böhlent P. Isolation of brain fibroblast growth factor by heparin-Sepharose affinity chromatography: identity with pituitary fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6963–6967. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Greenburg G., Bialecki H., Zetter B. R. Factors involved in the modulation of cell proliferation in vivo and in vitro: the role of fibroblast and epidermal growth factors in the proliferative response of mammalian cells. In Vitro. 1978 Jan;14(1):85–118. doi: 10.1007/BF02618177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Moran J. S. Growth factors in mammalian cell culture. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:531–558. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.002531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D. Purification of a fibroblast growth factor from bovine pituitary. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 10;250(7):2515–2520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James R., Bradshaw R. A. Polypeptide growth factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:259–292. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knauer D. J., Cunningham D. D. A reevaluation of the response of human umbilical vein endothelial cells to certain growth factors. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Dec;117(3):397–406. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041170315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughton C. Quantification of attached cells in microtiter plates based on Coomassie brilliant blue G-250 staining of total cellular protein. Anal Biochem. 1984 Aug 1;140(2):417–423. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90187-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemmon S. K., Riley M. C., Thomas K. A., Hoover G. A., Maciag T., Bradshaw R. A. Bovine fibroblast growth factor: comparison of brain and pituitary preparations. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):162–169. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner E. A. How to make a hybridoma. Yale J Biol Med. 1981 Sep-Oct;54(5):387–402. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maciag T. Angiogenesis. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1984;7:167–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maciag T., Cerundolo J., Ilsley S., Kelley P. R., Forand R. An endothelial cell growth factor from bovine hypothalamus: identification and partial characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5674–5678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maciag T., Hoover G. A., Weinstein R. High and low molecular weight forms of endothelial cell growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5333–5336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maciag T., Kadish J., Wilkins L., Stemerman M. B., Weinstein R. Organizational behavior of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;94(3):511–520. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.3.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maciag T., Mehlman T., Friesel R., Schreiber A. B. Heparin binds endothelial cell growth factor, the principal endothelial cell mitogen in bovine brain. Science. 1984 Aug 31;225(4665):932–935. doi: 10.1126/science.6382607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S., Folkman J. Protamine is an inhibitor of angiogenesis. Nature. 1982 May 27;297(5864):307–312. doi: 10.1038/297307a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. A., Rios-Candelore M., Fitzpatrick S. Purification and characterization of acidic fibroblast growth factor from bovine brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):357–361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton S. C., Mueller S. N., Levine E. M. Human endothelial cells: use of heparin in cloning and long-term serial cultivation. Science. 1983 Nov 11;222(4624):623–625. doi: 10.1126/science.6635659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


